
Get in the KNOW
on LA Startups & Tech
X
Shutterstock
Venture Deals in LA Are Slowing Down, And Other Takeaways From Our Quarterly VC Survey
Keerthi Vedantam
Keerthi Vedantam is a bioscience reporter at dot.LA. She cut her teeth covering everything from cloud computing to 5G in San Francisco and Seattle. Before she covered tech, Keerthi reported on tribal lands and congressional policy in Washington, D.C. Connect with her on Twitter, Clubhouse (@keerthivedantam) or Signal at 408-470-0776.
It looks like venture deals are stagnating in Los Angeles.
That’s according to dot.LA’s most recent quarterly VC sentiment survey, in which we asked L.A.-based venture capitalists for their take on the current state of the market. This time, roughly 83% of respondents reported that the number of deals they made in L.A. either stayed the same or declined in the first quarter of 2022 (58% said they stayed the same compared to the fourth quarter of 2021, while 25% said they decreased).
That’s not hugely surprising given the sluggish dynamics gripping the venture capital world at large these days, due to macroeconomic factors including the ongoing stock market correction, inflation and Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. While startups and VC investors haven’t been hit as hard as public companies, it looks like the ripple effects are beginning to bleed into the private capital markets.
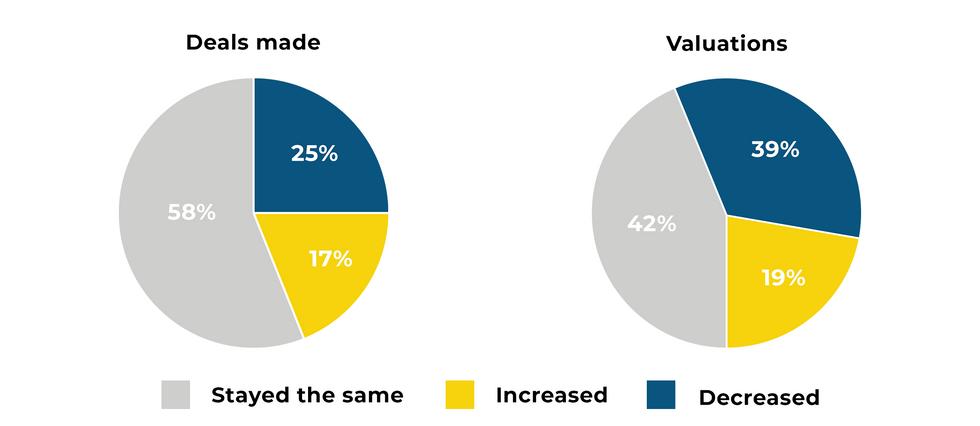
In addition to slowing deal volumes, most investors said they’re seeing startup valuations lose momentum, as well: Roughly 81% said valuations either stayed the same or decreased from the previous quarter, with nearly 39% noting a decline.
Should that sentiment continue moving forward, it could spell bad news for startups as far as raising the money they need for growth, investors said.
“If I was a startup right now, I would be making sure I have plenty of runway,” said Krisztina ‘Z’ Holly, a venture partner at Good Growth Capital. “When it looks like there's some potential challenges ahead in the market, it’s good to fill your war chest.”
Among VC respondents, about 86% said they believed that valuations in the first quarter were too high—one potential reason why deals slowed down in the first quarter, according to TenOneTen Ventures partner Minnie Ingersoll. She noted that L.A.’s growing startup scene features more early-stage ventures, whose valuations haven’t come down the way later-stage startup valuations have.
“I would say we are just more cautious about taking meetings where the valuations are at pre-correction levels,” Ingersoll said. “We didn’t take meetings because their valuations weren’t in line with where we thought the market was.”
While most respondents said the Russia-Ukraine war didn’t have much impact on their investment strategies, some 22% said it did have an effect—with one VC noting they had to pass on a deal in Russia that they liked.
Is There a Flight Out of Los Angeles?
Los Angeles was heralded as the third-largest startup ecosystem in the U.S. at the beginning of the year, behind only San Francisco and New York. Yet nearly one-third (31%) of VC respondents said that at least one of their portfolio companies had left L.A. within the past year. It won’t come as a huge surprise that the city of Austin, Texas has been one of the prime beneficiaries of this shift—with roughly half of those who reported that a portfolio company had left L.A. identifying Austin as the destination.
The tech industry’s much-hyped “exodus” from California has been widely reported on, especially as more companies have embraced the work-from-home lifestyle and also opted to move their operations to lower-cost cities and states. Most notably, Elon Musk has recently moved two of his companies, electric automaker Tesla and tunnel infrastructure startup The Boring Company, from California to Texas (with both of those firms moving in and around Austin).
“In today's competitive market with lots of capital to invest, we think the next generation of successful VCs are going to be diverse in markets (not just Silicon Valley)... [and] have access to undiscovered founders from everywhere,” said one survey respondent.
NFTs Aren’t Popular With VCs—But Web 3 Is
“It’s the future,” according to one respondent. “Buckle up and get on board.”
Are NFTs...

More than 71% of VC survey respondents said they were bullish on Web3—the new blockchain-enabled iteration of the internet, which promises decentralization and a whole range of applications involving cryptocurrencies, NFTs, DeFi and more. It’s the same sentiment informing Santa Monica-based VC firm M13’s new $400 million fund, which considers Web3 a core piece of its investment thesis.
In Q2 2022, do you expect your portfolio companies to:

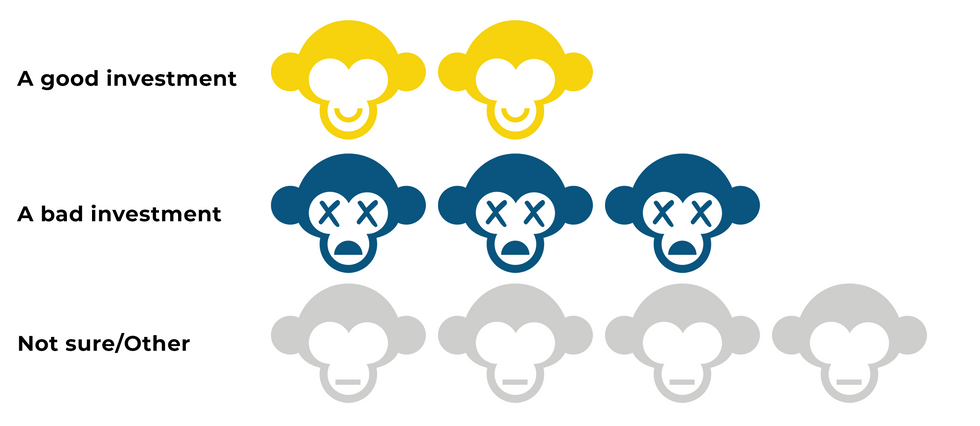
L.A. is home to an ever-growing cadre of Web3-focused startups operating across the realms of finance, entertainment and other industries. But while local investors are willing to pour money into blockchain-related ventures, one segment of the space continues to evoke skepticism: Only 18% of respondents would describe NFTs as “a good investment,” while 33% thought they were “bad” investments and 39% said they were unsure.
As in our last survey several months ago, it appears that NFTs continue to divide opinion, with respondents expressing differing perspectives on their value and utility. One referred to them as “get rich quick schemes,” but added that the art pieces and social communities that emerge from them may be valuable. Another said that “NFTs as a digital medium are a legitimate thing”—but noted the vast majority are “awful investments with no intrinsic value.”
Graphics courtesy of Hagan Blount.
From Your Site Articles
- Los Angeles Venture Funds Grow, but Spend Less in LA - dot.LA ›
- LA's Top Venture Capitalists of 2022 - dot.LA ›
- Los Angeles Venture Capital News - dot.LA ›
- Here Are Los Angeles' Top Venture Capitalists - dot.LA ›
- Venture Deals Fall in LA Amid Economic Worries - dot.LA ›
Related Articles Around the Web
Keerthi Vedantam
Keerthi Vedantam is a bioscience reporter at dot.LA. She cut her teeth covering everything from cloud computing to 5G in San Francisco and Seattle. Before she covered tech, Keerthi reported on tribal lands and congressional policy in Washington, D.C. Connect with her on Twitter, Clubhouse (@keerthivedantam) or Signal at 408-470-0776.
https://twitter.com/KeerthiVedantam
keerthi@dot.la
From Pitch Meetings to Power Lunches: LA’s Exclusive Membership Clubs 🗝️
10:37 AM | June 26, 2024
Summer's here, so it's time to zhuzh up your work environment. Discovering the best membership and social clubs in Los Angeles for meetings can boost networking and collaboration, offering exclusive venues and premium amenities tailored for professionals and creatives to thrive amidst the city's vibrant backdrop. These clubs provide a sophisticated setting for productive gatherings and meaningful connections in LA. Here are some top private member clubs perfect for meetings and productive work sessions.
The Jonathan Club
Club Details: The Jonathan Club, one of Los Angeles' original membership clubs, has been a cornerstone of the city's elite social scene since its founding in the mid-1890s. Its legacy is intertwined with the growth and development of LA itself, most notably through a pivotal meeting held at the club that sparked the idea for a southern campus of the University of California—what would eventually become UCLA. Today, the Jonathan Club continues to offer its members an unparalleled experience of exclusivity and refinement. With locations in both DLTA and Santa Monica, members enjoy access to premium amenities and spaces and a calendar with hundreds of social events and workshops throughout the year, providing ample opportunities for networking, personal growth, and leisure activities.
Membership Details: Initiation fee is around $50,000, and admission typically requires that you be invited or know someone who is already a member.
Spring Place

Image Source: Spring Place
Neighborhood: Beverly Hills
Club Details: A mix between co-working space and social club, this Beverly Hills hotspot is a more exclusive version of similar clubs. Spring Place Beverly Hills spans three floors and offers a stunning art collection. The interior is filled with tons of natural light and has an intentional design that fuels members to harness some of their best work. Members also have access to luxurious dining and nightlife pop-ups that happen at Spring Place.
Membership Details: There is a non-refundable initiation fee of $500 and then local membership for people under 30 starts at $300 per month, while monthly membership for locals over 30 is $600.
Griffin Club
Image Source: Griffin Club
Neighborhood: Cheviot Hills
Club Details: Located in Cheviot Hills, Griffin Club LA is a sporty club with ample shared workspace. Following a $20M renovation in 2020, the club now boasts seven LED-lit tennis courts, four LED-lit pickleball courts, two recreational lap pools, a 25-meter family pool for kids, an adults-only resort pool, and childcare services. It's the ideal destination for a clientele looking to mix work with competitive sport.
Membership Details: Membership is by invitation only and is subject to approval. Membership prices at the club vary. A family membership entails a $12,000 initial fee plus a $450 monthly fee, while a junior membership only entails a $2,000 initiation fee and a $205 monthly fee.
Soho House West Hollywood
Image Source: Soho House West Hollywood
Neighborhood: West Hollywood
Club Details: Soho House West Hollywood provides a stylish and exclusive work and meeting destination, featuring chic meeting rooms and workspaces with panoramic views of Los Angeles. Combining luxury amenities with a creative atmosphere, it offers an ideal setting for networking, collaboration, productive sessions, and an amazing Sunday brunch!
Membership Details: Two current member referrals are needed, plus an online application, and a recent photo to confirm your identity. Quarterly memberships start at $675.25, but if you’re under 27, you can pay $337.75 quarterly. However, if you want access to every house, membership costs $5,250.00 annually, or $2,650.00 if you’re under 27.
Little Beach House Malibu
Image Source: Little Beach House Malibu
Neighborhood: Malibu
Club Details: The Little Beach House Malibu is a small, local club for the creative community of Malibu and the surrounding coastal areas. The club is known for its magnificent dining room, bar, sitting room and terrace. It is the perfect place for a truly memorable work meal.
Membership Details: Malibu Beach House is not included in the Soho House membership. If you are an existing member, you can apply for “Malibu Plus” for an additional $2,190 a year, or $1,095 if you’re under 27.
San Vicente Bungalows
Image Source: San Vicente Bungalows
Neighborhood: West Hollywood
Club Details: San Vicente Bungalows is an exclusive, members-only social club located in West Hollywood, California, offering a luxurious and private environment for its high-profile clientele. The club is renowned for its strict privacy policies, elegant decor, and high-end amenities, catering to celebrities (and royals) and industry elites seeking a discreet space to unwind and socialize.
Membership Details: You must be nominated by a current club member to apply. Applications are evaluated monthly and annual dues start at $4,200 plus a $1,800 initiation fee.
The Aster
Image Source: The Aster
Neighborhood: Hollywood
Club Details: The Aster, located at the iconic intersection of Hollywood Boulevard and Vine Street, redefines the modern members' club with its emphasis on warmth and hospitality, blending public hotel amenities with private club exclusivity. Featuring bright, airy spaces and top-notch facilities such as an outdoor pool, recording studio, and rooftop bar, it offers a fluid environment for work, relaxation, and socializing.
Membership Details: Memberships start at $3,600 per year and be acquired by filling out an application. In addition to uploading a photo, hopeful members also have to write a small bio while highlighting their interests, skills, profession, and hobbies.
NeueHouse
Image Source: NeueHouse
Neighborhood: Venice/Hollywood/DTLA
Club Details: NeueHouse in LA is a chic private workspace and cultural hub designed for creative professionals, offering sophisticated workspaces, a dynamic calendar of cultural programming, and luxurious amenities. Situated in three bustling neighborhoods across LA, it provides a collaborative environment where members can work, network, and unwind in style.
Membership Details: You have to apply for the Salon membership, which includes questions like “dream dinner guests (dead or alive?)." Annual dues for Salon memberships are $3,000 plus a $200 joining fee. You can also inquire about the Gallery membership for flexible workspaces and offices for individuals or teams, starting at $595 per month, with various options depending on your needs.
Read moreShow less
Brex’s $5.15B Deal With Capital One Marks A New Era For Fintech
11:18 AM | January 23, 2026
🔦 Spotlight
Happy Friday, Los Angeles. 💳
The first big fintech plot twist of 2026 is here. Capital One is buying Brex in a cash and stock deal valued at about $5.15 billion, in what the companies are calling the largest bank - fintech deal in history.
From college dropouts to a multibillion exit
Brex launched in 2017, when Brazilian founders Henrique Dubugras and Pedro Franceschi, then in their early 20s after dropping out of Stanford, set out to fix the “startup card” problem. That project turned into an AI-native finance platform that now serves tens of thousands of companies, from early-stage startups to hundreds of public enterprises.
A few years into that journey, both founders moved to Los Angeles and continued running Brex from here as the company embraced a fully remote model. Now that same LA-based duo is steering a multibillion-dollar acquisition that will plug their software directly into one of the biggest banks in the country. Pedro will stay on as CEO of Brex inside Capital One, with the brand and product continuing rather than disappearing into a rebrand.
Why this looks like a win
“Big bank buys fintech” can sound like the end of the startup story, but here it reads more like an expansion pack. Capital One gets Brex’s cloud-based spend stack, AI-powered controls and roughly $13 billion in commercial deposits. Brex gets a massive balance sheet, a regulated rails partner and access to the mainstream business market it has been edging toward for years.
For founders and operators here, it is also quiet validation that building hard fintech infrastructure still pays off. Brex spent years doing the unglamorous work of licenses, compliance, underwriting and integrations. The outcome isn’t a hype cycle spike; it is a classic, real-money exit for a very modern stack.
What it signals for LA’s ecosystem
LA is not getting a new headquarters out of this. Brex has embraced a “no HQ” model. What the city does have is a pair of founders who chose to build their lives here and just proved that you can run a global finance platform from Los Angeles and end up selling it to a top-six U.S. bank.
It also fits a broader pattern our ecosystem is leaning into. Whether it is fintech, defense tech or climate, the most interesting LA stories right now are not about front-end apps. They are about deep, regulated infrastructure that incumbents eventually need more than startups need them.
For Brex, this is the start of a new chapter inside Capital One. For LA, it is one more data point that the city’s founders can build products the rest of the financial system has to buy.
Scroll on for the latest LA venture rounds, fund news and acquisitions.
🤝 Venture Deals
LA Companies
- L-Nutra secured a new $36.5M investment from Mubadala, bringing its total Series D proceeds to $83.5M. The company, which develops longevity-focused and medical nutrition therapies, plans to use the funding to accelerate global expansion, advance clinical research, and scale adoption of its nutrition programs across healthcare providers and consumers. - learn more
- RiskFront AI raised $3.3M in pre-seed funding to make financial crime and compliance work far less manual. The US-based startup uses “agentic AI” to automate time-consuming tasks like research, data analysis and documentation, with its Airos platform handling much of the day-to-day workload so human analysts can focus on higher-value judgment calls. The new capital will help expand engineering and product teams and deepen integrations with banks and fintechs already piloting the system. - learn more
- Balance Homes relaunched with a $30M investment led by Falco Group to scale its equity-sharing model for homeowners who are “house rich but cash and credit constrained.” The company buys a co-ownership stake in a home to free up trapped equity so owners can pay down mortgages and high-interest debt while staying in their homes, instead of being forced to sell. After stabilizing its existing portfolio following EasyKnock’s shutdown, Balance Homes is now resuming originations in six states, with plans to expand as affordability and household debt pressures intensify. - learn more
LA Venture Funds
- Distributed Global co-led Superstate’s $82.5M Series B, backing the Robert Leshner - founded tokenization platform as it builds regulated, on-chain capital markets infrastructure. The round, alongside Bain Capital Crypto and other institutional investors, will help Superstate expand beyond its existing tokenized U.S. Treasury funds to a full issuance layer for SEC-registered equities on Ethereum and Solana. The company, which already manages over $1.1B in tokenized assets, plans to scale its Opening Bell platform and transfer agent stack so public companies can issue and manage compliant on-chain shares directly. - learn more
- Krew Capital participated in GIGR (Playad.ai)’s $5.4M pre-seed round, backing the San Francisco based startup as it builds multi-agent AI workflows for marketing teams. GIGR’s Playad platform starts with interactive ads, using AI agents to help marketers create, test and iterate on playable and other ad formats much faster while turning performance data into continuous creative improvement. The new funding will support product development, expansion of its AI-native creative workflow and scaling to more customers looking to cut production costs and tighten the loop between ad performance and creative decisions. - learn more
- Trousdale Ventures participated in AheadComputing’s additional $30M Seed2 round, backing the Portland-based chip startup as it reimagines CPU architecture for the AI era. AheadComputing is developing high-performance RISC-V based CPUs and breakthrough microarchitecture aimed at handling the growing wave of AI data center, workstation and embedded workloads where CPU performance has become a bottleneck. The new funding, which brings total capital raised to $53M, will support R&D, software innovation and test chip development as the company races to deliver next-generation general purpose processors. - learn more
- Untapped Ventures participated in Nexxa.ai’s $9M seed round, backing the Sunnyvale-based startup as it scales specialized AI agents for heavy-industry workflows. Nexxa’s Nitro platform layers multi-agent automation on top of existing tools used in sectors like rail, construction, manufacturing and critical infrastructure, helping engineers plan and execute complex projects without ripping out legacy systems. The new funding brings Nexxa.ai’s total capital raised to $14M and will go toward expanding deployments, forward-deployed engineering teams and support for more industrial customers. - learn more
- UP.Partners participated in Zanskar’s $115M Series C, backing the Salt Lake City based geothermal startup as it uses AI to uncover overlooked conventional geothermal resources across the Western U.S. The company has already validated several high-potential sites and plans to use the funding to expand its discovery platform and begin developing multiple greenfield power plants, with a goal of bringing significant new clean baseload capacity to the grid before 2030. - learn more
- Smash Capital participated in Stream’s $90M Series D, backing the UK based workplace finance startup as it ramps expansion into the U.S. market. Formerly known as Wagestream, Stream partners with employers to offer workers tools like earned wage access, savings, budgeting and pensions in a single app, targeting financial stress for lower and middle income employees. The new funding, led by Sofina, brings total capital raised to about $228M and will help Stream scale its multi-product platform across more brands and workers globally. - learn more
- Fika Ventures participated in Ivo’s $55M funding round, backing the San Francisco based legal AI startup alongside lead investor Blackbird and others. Ivo builds contract intelligence tools for in-house legal teams and enterprises, using a highly structured approach that breaks reviews into hundreds of smaller AI tasks to boost accuracy and reduce hallucinations. The new capital, which reportedly values the company at around $355M, will go toward accelerating product development and hiring more sales and go-to-market talent to meet growing demand. - learn more
- Amplify.LA participated in Overworld’s latest funding round, backing the AI startup as it unveils a real-time diffusion world model for playable, AI-native worlds. Overworld’s system runs locally and generates persistent, interactive environments on the fly, aiming to become core infrastructure for next-generation games, simulations and creative tools built around world models rather than static assets. The new capital will support further development of its Waypoint 1 research preview and help the team expand its platform for researchers, engineers and builders working on interactive AI experiences. - learn more
- Dangerous Ventures participated in Carbogenics’ $3M investment and grant funding round, backing the Edinburgh-based bio-carbon startup as it scales its carbon removal technology. Carbogenics turns difficult-to-recycle organic waste into CreChar, a biochar product that boosts biogas production, supports wastewater treatment and locks away carbon. The new funding will help the company expand manufacturing in the US, grow its centralized UK operations and deploy its biocarbon products across the UK, Europe and North America. - learn more
LA Exits
- Farcaster is being acquired by Neynar, the infrastructure company that already powers much of the Farcaster ecosystem, in a full-stack handoff from Merkle Manufactory. Neynar will assume control of the decentralized social protocol’s smart contracts, code repositories, official app and Clanker client, while Farcaster co-founders Dan Romero and Varun Srinivasan step back from day-to-day operations after five years. The deal keeps the network running without disruption and sets Neynar up to roll out a new, builder-focused roadmap for on-chain social. - learn more
- ScribbleVet has been acquired by Instinct Science, which is folding the veterinary AI-scribing startup into its Instinct EMR platform to create what it calls an “intelligent-native” practice management system. The combined offering aims to move traditional PIMS beyond record-keeping by embedding AI scribing, workflow automation and clinical decision support in one system, reducing documentation burden and helping veterinary teams focus more on patient care. ScribbleVet’s team is joining Instinct, with founder and CEO Rohan Relan taking on a key role leading product strategy for intelligence features across the platform. - learn more
Read moreShow less
RELATEDTRENDING
LA TECH JOBS



