Column: As the Streaming Wars Heat Up, Why Are Consumers Losing Out?

Want to watch the next season of "Stranger Things" when it comes out? I know I do, so I pay for Netflix each month. "Jack Ryan"? That's over on Amazon Prime. "The Handmaid's Tale"? Hulu. If you think Picard was the best Star Trek captain, you'll need CBS All Access – but at this point in your budget you may be choosing between that or "The Mandalorian," for which you'll need Disney+. And let's not forget the new content exclusive to HBO Max, Apple TV+, BET+, and NBC Peacock.
Most of us are aware of the recent fragmentation of content across subscription streaming services, and we've either had to make some hard choices about which content we will watch or else we're now paying bills for streaming services that resemble the bundled cable bills we paid before we cut the cord. And it's not just the cost that bothers us. When nearly everything was on one of just a few services, we knew where to find it. Now, keeping track of which services have which content – and whether we currently have that service – seems like a job in itself.
I don't think I need to convince most readers that this scenario isn't ideal for the consumer. So why are we here?
It's not that producers and distributors of entertainment content don't want to satisfy customers… they certainly do! But over the last decade or so, movie studios and television networks have seen the incredible power of using data analytics to inform decisions about what content to make, how to market it, to whom to market it and more. Subscription streaming services (like Netflix) observe everything that their viewers watch, and in turn use that information to determine what content to suggest to each viewer next. They even use it to inform decisions regarding what content to license or produce themselves and then to market that content most efficiently. They effectively create a series of personalized channels for each of their viewers, helping to connect you with content that you would love but might not be aware of. And in doing so, they can make investments in content in ways that differ from the traditional models and they reduce the inherent risk involved in bringing new shows and films to market. If you don't believe me, just ask the two professors from Carnegie Mellon who wrote a book about this.
In an era where there is more quality content – both old and new – available to us than ever before, it feels increasingly hard to know what to watch and where to watch it.
The problem that a traditional television network (or movie studio) has is that they do not get this kind of personalized data on each of their over-the-air or box office viewers – nor do they usually get these data from the subscription services that license their shows and films. Even if they had such data, they don't have a platform that serves as a direct connection to the consumer, and so they cannot personalize which shows they market to each viewer and how they market them. That's what subscription streaming services have been able to do. And for a while, networks and studios have felt pretty left out of the new data-driven entertainment revolution. This largely explains why so many major players in the industry want to have a successful streaming service now — to gather individual data about each viewer and have a personalized connection / marketing channel to every one of their customers.
If you are a major network or studio trying to get into the streaming game and you need to compete with an established service like Netflix – who consumers already know and like – what do you do? You fall back on what you are already great at and make content that everyone wants to watch, and you make it exclusive to your streaming service as a draw to new customers. Or you stop licensing your best catalog content to the established streaming players and make it exclusive to your new service (sorry, "Friends" fans, you'll need to pay for HBO Max!). Hence, nearly every one of the subscription services out there has at least a few shows that you probably want to watch, and great content feels fragmented across a plethora of services for which you struggle to remember all of the names.
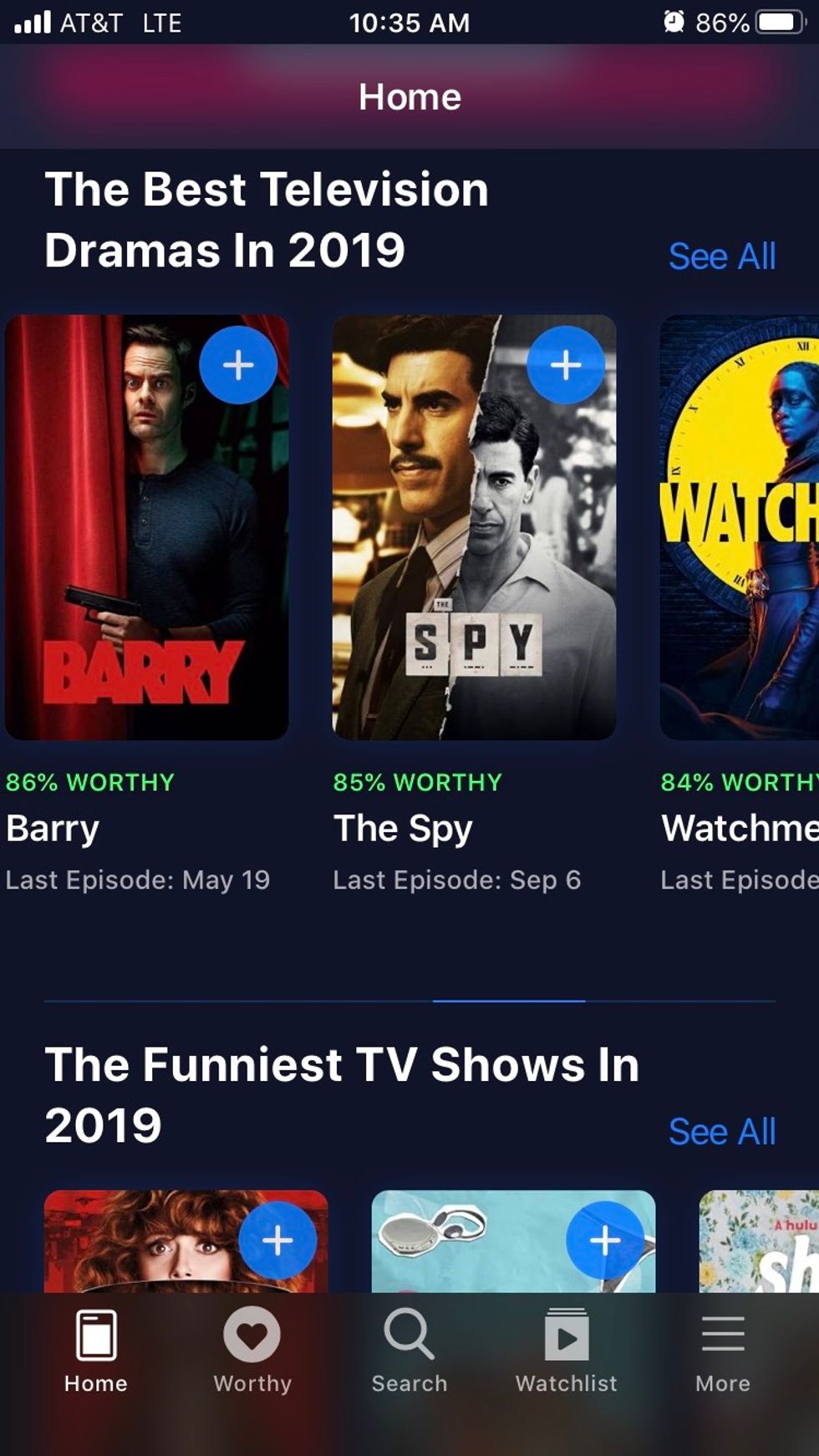
Watchworthy's app is one of several trying to make it easier for viewers to find the content they're looking for, across services.
But even if the current fragmentation of content across so many services can be explained as a form of business competition, that does not make it ideal for the end consumer. I've already mentioned the obvious result that consumers are back to facing the choice of paying an ever-increasing multitude of subscription fees, missing out on content, or else turning to piracy. But there is another, less obvious consequence for the customer. When most content that was online was centralized on just one or two services, those services observed most of what a customer viewed online, and thus had a strong understanding of each consumer's preferences. Those services also had an incentive to recommend or market to you the content that you would like most.
Now, however, if you only do 15% of your online viewing on, for example, Hulu, they observe a lot less about your viewing preferences than when you did 50-60% of your television and movie viewing there. They just don't know you as well. Moreover, a service like Netflix or Disney+ only has the incentive to recommend to you the content that is on their service, even if there are shows or films that you would meaningfully prefer on other subscription services. And this leads us to the irony that in an era where there is more quality content – both old and new – available to us than ever before, it feels increasingly hard to know what to watch and where to watch it. By fragmenting content across so many services in an effort to draw in customers and have a more personalized relationship with them, players in the industry have unintentionally left customers struggling to search for and find the content that is best suited for them.
One of the most commonly offered solutions to streaming fragmentation is that we should just bundle the services again – some have suggested that you should be able to pick up a bundle of Hulu, Netflix, HBO Max, etc. for perhaps half of what it would cost to buy them each separately. This may partly solve the customer's budget problems, but note that it does not solve the problem outlined above – if our viewing is spread out across a multitude of services, then the underlying viewer data are still fragmented. No one service knows us particularly well, and no service has the incentive to connect us with the content that best matches our preferences.
Where this eventually leads is a subject for another article – perhaps we will see the failure or consolidation of some of these services, or perhaps a third party can solve the problems I have described even while a number of subscription services retain exclusive content.
There are examples of companies trying to address this issue such as Likewise, Justwatch, or WatchWorthy, but it is not clear whether or not they will succeed (disclosure: I myself am involved in a stealth startup working on a solution to this). Either way, I see this problem as one that requires a consumer-friendly solution, and I fully expect that the market will provide this one way or another.
- Can Niche Streaming Services Survive in a Netflix World? ›
- Peacock, NBCUniversal's Streaming Service, Takes Flight - dot.LA ›
- HBO Max Is Hoping to Get You to What You Want, Faster - dot.LA ›
- Watchworthy App Aims to Make it Easier to Choose What to Watch ... ›
- Making At-Home Healthcare As Easy as Ordering Pizza - dot.LA ›
- The LA Dodgers Get Into Food Delivery - dot.LA ›
- Streaming Piracy Is Now a Billion-Dollar Industry - dot.LA ›
- Streaming Piracy Is Now a Billion-Dollar Industry - dot.LA ›
- Warner Bros.’ Films Will Be Released in Theaters, HBO Max - dot.LA ›
- Streaming Trends to Watch in 2021 - dot.LA ›
- Amazon Buys MGM for $8.45B, Acquires Bond Franchise - dot.LA ›
- Documentary Plus Will Share Streaming Data With Filmmakers - dot.LA ›
- Video Streaming Trends to Watch - dot.LA ›
- Analysts Say Gaming and Shopping Won't Save Netflix - dot.LA ›
- Analysts Say Gaming and Shopping Won't Save Netflix - dot.LA ›
- Peacock Sees Mobile Users Surge During Olympics - dot.LA ›
- Peacock Sees Mobile Users Surge During Olympics - dot.LA ›
- VideoAmp Raises $275 Million to Dethrone Nielsen - dot.LA ›
- Former Disney CEO Backs Struum, a Streaming Sample App - dot.LA ›
- Nacelle’s CEO Says Hollywood Sees Creators as Entrepreneurs - dot.LA ›
- Paramount, Discovery Execs Discuss Future of Streaming - dot.LA ›
- Streaming Services and New Tech Storm Upfront - dot.LA ›
- Are the 'Stranger Things' Edit Rumors True? - dot.LA ›
- WB Discovery's Pivot And the End of Streaming's Dominance - dot.LA ›
- Warner Bros. Discovery Ditches Nielsen for VideoAmp - dot.LA ›
- Is the Globalization of Content a Good Thing? - dot.LA ›
- Why Streaming Services Are Looking More Like Cable TV - dot.LA ›



 Image Source: Revel
Image Source: Revel