Column: How Music Tech is Making it Easier — and Harder Than Ever — for Artists
Larry Miller is a professor at NYU where he directs the undergraduate and graduate Music Business programs. He produces and hosts the Musonomics podcast.
For many musicians, the democratization of music production and distribution carried the promise of reaching multitudes of eager fans at the touch of an upload button.
Yet with over 40,000 new tracks being uploaded each day, creating a virtually infinite selection of music available on most streaming platforms, breaking through as an artist has in some ways become more difficult than ever, especially on the global stage.
It is certainly possible today for artists to create and self-distribute their music, gain a following and begin building a career. But there's a big difference between having access to the tools of music creation, distribution, and building a sustainable career and the potential to become a global superstar. And that's where modern record labels are best positioned to help.
So What Does a Music Label Do These Days?
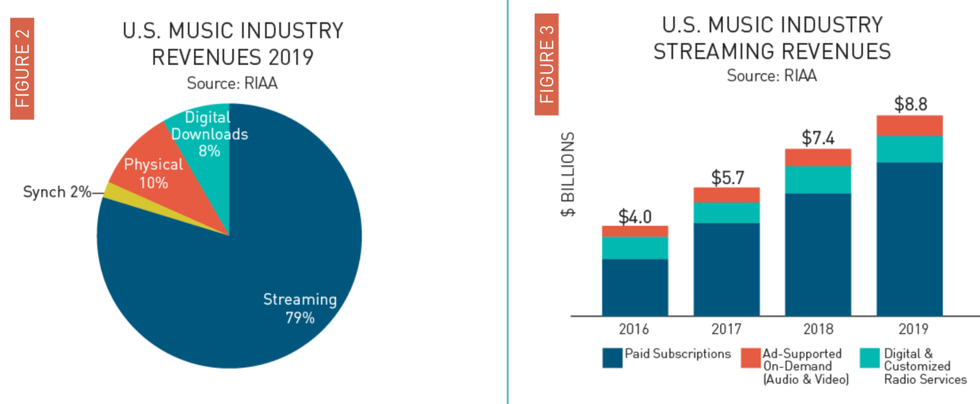
Revenues from recorded music in the United States grew 13% in 2019 to $11.1 billion at estimated retail value.
Image from The Recording Industry Association of America's report on year end revenues for 2019.
Fact is, what record labels do has not changed much since the industry's digital transformation. Now, as ever, labels discover and develop artists, connect them with creative collaborators to make great records, promote and position them in the media and wherever fans go to get music and reward successful outcomes. Over the last decade or so, the digital transition has fundamentally changed how and when virtually every functional area of a record label is done.
One difference that touches every facet of a label's operation is the massive amounts of real-time discovery and consumption data. Label teams analyze thousands of global inputs: Facebook fans, Twitter followers, YouTube views, Instagram activity, Shazam queries and Wikipedia look-ups. That's on top of analyzing the daily tsunami of music service plays around the world. The end goal: to develop an agile, highly customized response plan for every track of an artist's release.
Corollary to all this data is how today's music fans discover and consume music. Many fans now listen to music via premium subscription services that give them access to tens of millions of tracks for less than the price of one CD per month, or in a "feels free" option of ad-supported delivery. Fans also access music by watching label-created visual content on a myriad of screens, large and small, over video channels and via social media. At the same time they may still buy CDs or vinyl records and listen to the radio. To properly synthesize and optimize all these inputs and extract actionable insights requires hands-on experience that is both broad and deep, relationships, investment and instant access to a global marketing and distribution network; that is, it requires boots on the ground. Lots of them.
Revenues from recorded music in the United States grew 13% in 2019 to $11.1 billion at estimated retail value, the fourth year in a row of double digit growth reflecting continued increases — primarily from paid subscription streaming services, which reached more than 60 million subscriptions in the United States and accounted for 80% of recorded music revenue.
To put these numbers in a global perspective, as recently as 2018 and with streaming growth surging in developed markets, the worldwide recorded music business generated not quite half the peak revenues achieved in 1999 on an inflation-adjusted basis. CD sales crashed after 1999 with the launch of Napster and other illegal peer-to-peer file trading services, all of which were eventually litigated out of existence. The growth of iTunes downloads beginning in 2003 mitigated the decline of CD sales; Spotify didn't enter the U.S. market until 2011, the same year global revenues returned to growth after over a decade of painful decline. Midia Research pegged the 2019 global music industry at $76.2 billion including recorded music, publishing, live music, merchandising and sponsorships.
And just as the mode of consumer listening has shifted from mostly physical products and permanent downloads to on-demand streams, every aspect of label operations has reoriented toward a streaming-first consumption model and an always-on consumer mindset. The business of minting hits is no longer narrowly based on the 20th century model of maximizing short-term campaign outcomes for scarce broadcast radio slots or displays in retail stores. Every label function is now organized around fighting for a share of the attention economy, where consumers have unlimited access and choice, but not unlimited time.
Welcome to the Age of the Artist

The Age of the Artist
Photo by @plqml // felipe pelaquim on UnsplashToday, an artist's decision to partner with a label is a choice, not a requirement. The expanding galaxy of startups designed to help the DIY artist record, distribute, and market digital music has given artists more options to stay independent longer, and enables some artists to make a sustainable living while building a fan base. Every musician starts out as an independent, DIY project. When they attract the attention of a record label, whether indie or major, they may be in a very different negotiating position than a decade or so ago. In this way, the point at which labels interact with artists has largely shifted to a point that's further along an artist's development.
Although labels continued to invest in developing and breaking new artists during the industry's downturn following an explosion of file sharing led to the collapse of the CD earlier this century, the improvement in industry revenue, driven by the growth of subscriptions to streaming services, is being re-invested in A&R.
Two years ago, 12% more artists signed to major label rosters for the first time as compared with the end of 2014. I'll be doing research to update this data later this year, but all signs point to further growth in artist signings. At the same time, independent artists are the fastest-growing segment in the music economy, so much so that industry analyst Mark Mulligan has dubbed the 2020s The Age of the Artist, a fundamental departure from previous decades/eras defined by a mode of distribution or packaged media format.
Major labels understand it is in their interest to maintain a front-row seat to the edge of innovation through various approaches. For example, Warner Music's WMG Boost invests directly in early stage companies; Universal's Accelerator Engagement Network invests through top accelerators located in innovation hubs around the world. But as the world's largest music-based entertainment companies and guardians of a century of the world's most popular music, their attention is focused elsewhere.
Where Is the Investment in New Music Technology Going?

Where Is the Investment in New Music Technology Going?
Photo by James Owen on UnsplashSo where exactly is the innovation occurring? The current cohort of international startup competitions like MidemLab and those receiving support from top accelerators like L.A.'s Techstars Music or Abbey Road Red fit into an emerging post-pandemic investment pattern.
- Creator tools. There is a mind-numbing array of unbundled offerings for artists to support collaboration, production and mastering, funding and financial management, distribution, marketing and promotion. A generation of data insight and analytics startups were acquired by the majors along with Spotify, Apple Music and Pandora. HiFi, a new entrant in financial management and transparency, was launched with $53 million in backing 'to financially empower the creative class.'
- Live streaming and virtual events. The live concert business came to a screeching halt to mid-March. Touring represents 70 – 80% of revenue for many artists. Virtually no one expects a meaningful restart of this segment until 2021. And although live streaming and virtual events are not a substitute for the live concert experience, this trend is likely to stay with us even after the pandemic recedes.
- The New Merch – In China, Tencent Music has done a spectacular job proving music fans will pay for virtual goods, gifts and currencies – at scale. This is especially noteworthy in a market not known for generating revenue directly from the sale of recorded music. Now, the West is paying attention. Opportunities abound in limited edition merchandise, premium chat services, virtual merchandise and much more.
Over the last two decades, the music industry has faced extreme disruption as digital services were born and entered the mainstream. Independent and unsigned artists have a myriad of options to self-release their music. While some musicians have found sustainable success without a label's backing, there are certain things that only a label can do, particularly for artists with global ambition. Opportunities for innovation and value creation are distributed across the music industry value chain, especially in the areas of creator tools, live streaming and monetizing fandom. It's no secret that many of the most exciting startups envisioning the way music will be created and experienced are in L.A. today.
Larry Miller is a professor at NYU where he directs the undergraduate and graduate Music Business programs. He produces and hosts the Musonomics podcast.
- LA's Music-Tech Startups Are Poised to Reshape the Industry. - dot.LA ›
- Meet 3 Early Stage Science Startups at First Look's Showcase - dot.LA ›
- Music Tectonics Conference Announces its 2020 Lineup - dot.LA ›
- Are Livestream Concerts Music's Future or a Pandemic Fad? - dot.LA ›
- Output Raises $46M to Make Creating Easier for Musicians - dot.LA ›
- Tencent Doubles Stake in Universal Music Group - dot.LA ›
- Music Tech Trends to Watch in 2021 - dot.LA ›
- Music Marketplaces Are Supplanting Record Labels (Column) - dot.LA ›
- Snafu Records Wants to Replace Record Executives with AI - dot.LA ›
- Music Tectonics Returns to LA - dot.LA ›
Larry Miller is a professor at NYU where he directs the undergraduate and graduate Music Business programs. He produces and hosts the Musonomics podcast.




 Image Source: Revel
Image Source: Revel