

Get in the KNOW
on LA Startups & Tech
X
Photo by Israel Andrade on Unsplash
LinearB Raises $50M To Help Software Engineers Manage Workflow
Keerthi Vedantam
Keerthi Vedantam is a bioscience reporter at dot.LA. She cut her teeth covering everything from cloud computing to 5G in San Francisco and Seattle. Before she covered tech, Keerthi reported on tribal lands and congressional policy in Washington, D.C. Connect with her on Twitter, Clubhouse (@keerthivedantam) or Signal at 408-470-0776.
Santa Monica-based software engineering startup LinearB has raised $50 million in Series B funding led by San Francisco’s Tribe Capital, the company announced Monday.
New investor Salesforce Ventures and existing investors Battery Ventures and 83North also participated in the round, which takes LinearB’s total capital raised to $71 million.
LinearB, which also has offices in Tel Aviv, Israel, was founded in 2018 by Ori Keren and Dan Lines, former executives at cybersecurity firm Cloudlock (which was acquired by Cisco for $293 million in 2016). Informed by difficulties in scaling software development at Cloudlock, the pair launched LinearB, which is essentially a productivity tracker for engineers that provides data analytics and workflow metrics. The platform documents how many hours have been spent coding, how long it took to deploy code and what percentage of code was failing or creating problems.
The startup said it has grown its customer base from 1,500 to 5,000 software development teams “in the past year,” including clients at Bumble, BigID, Cloudinary, Unbabel and Drata. The new funding will be used to expand LinearB’s engineering, sales and marketing teams and further develop its product.
As working from home becomes the norm, LinearB is one of several software-focused companies aiming to meet the demands of a remote engineering workforce. Sourcegraph, a code-collaboration startup based in San Francisco, has been used by the likes of Tinder and Amazon to help scattered engineers annotate and collaborate on code. Jellyfish, a Boston-based productivity startup, helps managers see what work engineers spend their time on each day.
From Your Site Articles
Related Articles Around the Web
Keerthi Vedantam
Keerthi Vedantam is a bioscience reporter at dot.LA. She cut her teeth covering everything from cloud computing to 5G in San Francisco and Seattle. Before she covered tech, Keerthi reported on tribal lands and congressional policy in Washington, D.C. Connect with her on Twitter, Clubhouse (@keerthivedantam) or Signal at 408-470-0776.
https://twitter.com/KeerthiVedantam
keerthi@dot.la
Resy Cofounder’s New App Lands in LA: A Loyalty Tool Restaurants Actually Want
10:08 AM | October 24, 2025
🔦 Spotlight
Hello LA,
Blackbird, the loyalty and payments startup from Resy and Eater co-founder Ben Leventhal, officially landed in LA this week. The product is simple in the wild: you check in, pay through the app, and earn rewards that restaurants can actually act on, helping them spot and serve regulars without guessing. The LA launch goes live with more than 50 partners centered on the Westside, including names like Gjelina and Felix, plus spots across groups such as Rustic Canyon and Citrin, with expansion planned beyond Venice and Santa Monica.

Under the hood, Blackbird has been building a national network and says it is live at more than 1,000 restaurants. The company raised fresh capital earlier this year to expand markets and roll out cross-restaurant rewards, positioning LA as a key beachhead for growth. If you dine out a lot, the appeal is that the app collapses discovery, payment, and loyalty into one flow. If you run a dining room, the promise is cleaner data on guests you actually see, instead of a generic points program that lives somewhere else.
For LA specifically, the draw is that this model fits how the city eats. We spread across neighborhoods, follow chefs, and rotate between a small set of favorites and a long list of next-ups. A networked loyalty layer that recognizes that pattern could move real dollars, particularly for independents that want to keep the relationship direct. We’ll be watching how quickly the footprint moves east from the coast and which operators lean into memberships and targeted rewards first.
Scroll for this week’s LA venture deals, funds, and acquisitions.
🤝 Venture Deals
LA Companies
- GammaTime, a Los Angeles based premium micro drama platform founded by former Miramax CEO Bill Block, raised $14M seed led by vgames and Pitango, with participation from Alexis Ohanian, Kris Jenner, Kim Kardashian, and Traverse Ventures. The app is live on iOS and Android, features more than 20 vertical phone native originals, and plans new series from “CSI” creator Anthony E. Zuiker as it scales a freemium model for U.S. audiences. - learn more
- Wolf Games, a generative-AI gaming startup backed by Dick Wolf, raised a $9M Series A led by Main Street Advisors. The company also inked a partnership with NBCUniversal to develop interactive games using NBCU IP, built on Wolf Games’ platform for creating “living, cinematic” game worlds. Notable participants include Maverick Carter, Tom Werner, and Rashid Johnson, alongside returning investors Jimmy Iovine, Paul Wachter, and Dick Wolf. - learn more
- Quantum Elements, a Los Angeles based startup, launched Constellation, an AI native platform that helps teams build quantum software and co design hardware using agentic AI, natural language prompts, and a large noisy qubit simulator. The company emerged from stealth with funding from QDNL Participations and support from USC Viterbi, and says Constellation can speed code generation, debugging, and testing for applications in pharma, energy, and finance. - learn more
- Arbor Energy raised a $55M Series A co-led by Lowercarbon Capital and Voyager Ventures, with Gigascale Capital and Marathon Petroleum Corporation participating, to accelerate deployment of its zero-emission, fuel-flexible turbines. The funding completes a 1 MW pilot called ATLAS and advances HALCYON, a 25 MW modular turbine that uses oxy-combustion with supercritical CO₂ for efficient, carbon-neutral baseload power aimed at data centers, utilities, and industrial customers. - learn more
- Dialogue AI raised a $6M seed led by Lightspeed Venture Partners to scale its AI-native research platform, which uses a live conversational AI interviewer to run real-time customer interviews and deliver insights faster. Participants include Seven Stars, Uncommon Projects, the Tornante Company, and notable angels, and the funds will accelerate product and go-to-market efforts with early customers such as Wayfair, Square, Nextdoor, and Suno. - learn more
LA Venture Funds
- March Capital participated in Uniphore’s $260M Series F, joining strategic investors NVIDIA, AMD, Snowflake, and Databricks. The funding will accelerate development and adoption of Uniphore’s Business AI Cloud and expand its partner ecosystem, alongside investors like NEA, BNF Capital, National Grid Partners, and Prosperity7 Ventures. - learn more
- Beast Ventures participated in Nutropy’s latest funding round to scale precision-fermented casein for next-gen dairy ingredients. The France-based startup will use the capital to ramp production and deliver larger samples of its “cheeseable milk” powder to food manufacturers as it targets a 2027 launch. - learn more
- Patron participated in Notch’s $8M seed financing round, alongside investors such as Wing, Samsung, and Balaji, to scale the company’s AI platform for generating performance ads. Notch has since launched a “URL-to-animated-ads” feature that turns a product link into ready-to-run animated creatives within minutes, supporting a faster workflow for marketers rolling out motion ads. - learn more
- B Capital participated in CurbWaste’s $28M Series B, which was led by Socium Ventures with Flourish Ventures, TTV Capital, and Squarepoint Capital also joining. The funding brings total capital to $50M and will accelerate product and go-to-market work on CurbWaste’s operating system for independent waste haulers, including AI-driven dispatch, reporting, and payments. - learn more
- Thin Line Capital participated in SenseNet’s $14M Series A to scale its AI wildfire-detection network in the United States. The round was led by Stormbreaker with Fusion Fund, Plaza Ventures, FOLD36 Capital, and B Current also joining; funds go toward new offices and installations as SenseNet fuses gas sensors, AI cameras, satellites, and weather data to spot fires before they are visible. The company says it already monitors about 130 million acres and can flag ignitions within minutes. - learn more
- MANTIS Venture Capital participated in Keycard’s $38M financing for its identity and access platform for AI agents. The combined seed and Series A were led by Andreessen Horowitz, Acrew Capital, and Boldstart Ventures, and coincide with Keycard’s early-access launch. Keycard says its system issues short-lived, auditable identity tokens to help developers govern agent actions and data across apps. - learn more
- WndrCo participated in Defakto’s $30.75M Series B, a round led by XYZ Venture Capital with The General Partnership and Bloomberg Beta also joining. Defakto, formerly SPIRL, builds a Non-Human Identity and Access Management platform that replaces static credentials with dynamic, auditable identities for services, pipelines, workloads, and AI agents across multi-cloud environments. The company will use the capital to accelerate product development and expand go-to-market efforts. - learn more
- CIV co led 1001’s $9M round alongside General Catalyst and Lux Capital to build an AI native operating system for decision making in critical industries. 1001 combines live data ingestion, operational mapping, AI driven decisioning, and governance to help operators act in real time, with early pilots in aviation, logistics, and large infrastructure projects. The raise also includes backers like Chris Ré and Amjad Masad and will fund early deployments and hiring in Dubai, London, and beyond. - learn more
- Brentwood Associates led Throne Labs’ $15M Series B initial close to expand the company’s smart restroom infrastructure across new and existing U.S. markets. Existing investors including Uncorrelated Ventures, DiPalo Ventures, Rabil Ventures, and Arpiné Capital participated as Throne scales its network of sensor-equipped, ADA-compliant restrooms and city partnerships. - learn more
- M13 led Estuary’s $17M Series A, with participation from FirstMark and Operator Partners, to scale the company’s “right-time data” platform. Estuary unifies change data capture, streaming, and batch into one managed system with BYOC deployment so enterprises can control latency and feed AI applications more reliably; funds will support product and go-to-market expansion. - learn more
- Strong Ventures provided follow-on funding in Unjeonseonsaeng’s ₩2.8B (~$2.0M) Series A, backing the driving-school comparison and booking platform as it scales nationwide. New investors Fast Ventures and Korea Credit Guarantee Fund joined the round, with proceeds going to expand the company’s SaaS tools for driving schools and enhance data-driven features like AI recommendations and advertising. The startup reports monthly GMV above ₩1B and its first profitable quarter in 2025. - learn more
- Interlagos led Adaptyx Biosciences’ $14M seed, with Hyperlink Ventures participating alongside Overwater Ventures, Starbloom Capital, Stanford University, the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub, and others. Adaptyx is developing a biowearable for continuous, multi-analyte molecular monitoring; the raise brings total funding to about $23M and supports R&D, clinical progress toward FDA clearance, and platform scaling. - learn more
- B Capital participated in Faeth Therapeutics’ new $25M financing, which brings the company’s total funding to $92M and supports a randomized Phase 2 trial of its PIKTOR regimen in endometrial cancer with the GOG Foundation. The raise, led by S2G Ventures with additional new and existing backers, follows Phase 1b data showing an 80% overall response rate and 11-month median PFS when PIKTOR was combined with paclitaxel. - learn more
- Btech Consortium participated in PortX’s strategic growth round, joining renewed backers alongside new investors Allied Solutions and the American Bankers Association. The funding extends PortX’s Series B and underscores industry support for its AI-powered data integration platform for banks and credit unions. - learn more
LA Exits
- Breez was acquired by JumpCloud to bolster JumpCloud’s identity threat detection and response capabilities and accelerate its security roadmap. The deal brings Breez’s ITDR technology and team into JumpCloud’s platform; terms were not disclosed. The Breez group is led by former Adobe executive Abhinav Srivastava. - learn more
Read moreShow less
LA Tech Week: Final Days • Coco’s bots, Anduril’s helmet AI, Impulse’s moon freight
08:05 AM | October 17, 2025
🔦 Spotlight
Happy Friday Los Angeles,
Founders are closing out Tech Week, robots are getting a new research brain, space logistics are taking shape, and defense tech just moved mission command into a helmet.
Anduril’s EagleEye: mission command, heads up
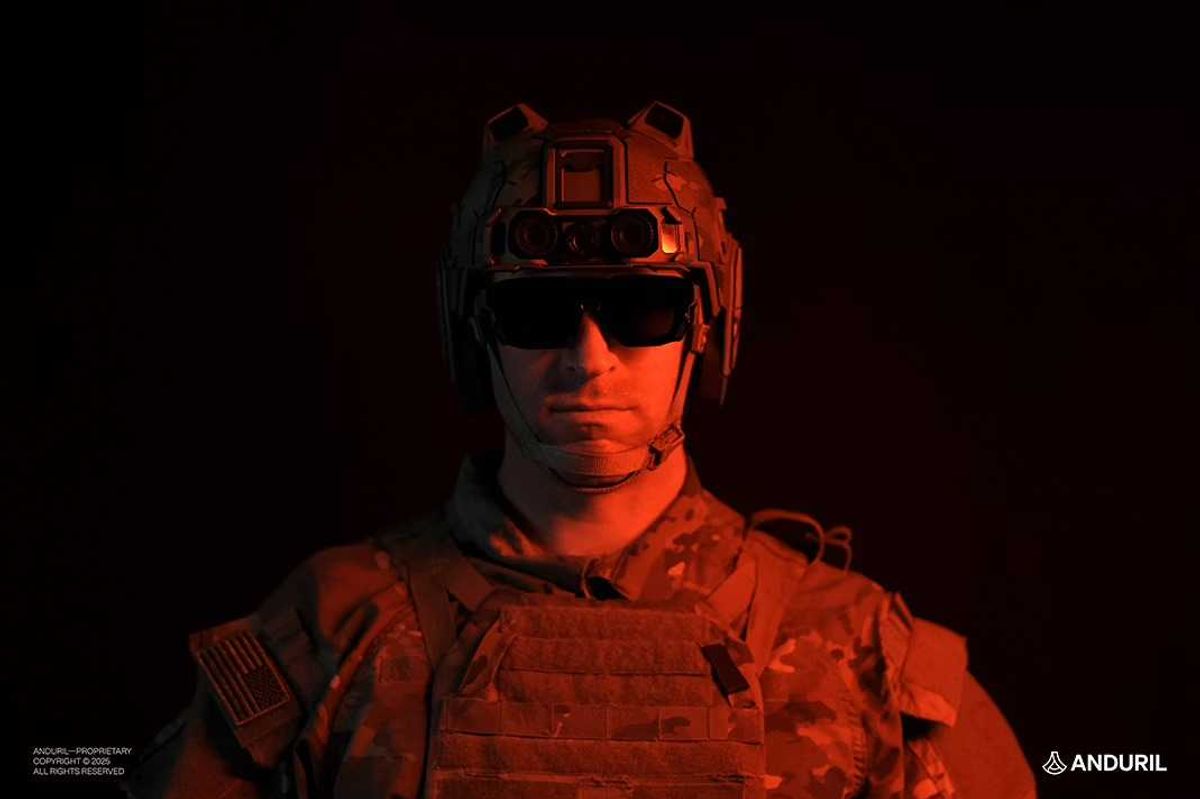

Anduril introduced EagleEye, a helmet mounted system that puts maps, comms, sensor fusion, and on device AI directly in a warfighter’s line of sight, integrated with the Lattice stack. The goal is simple: less time looking down at a tablet and more decisions made at the edge.
Impulse Space: a practical path to lunar deliveries
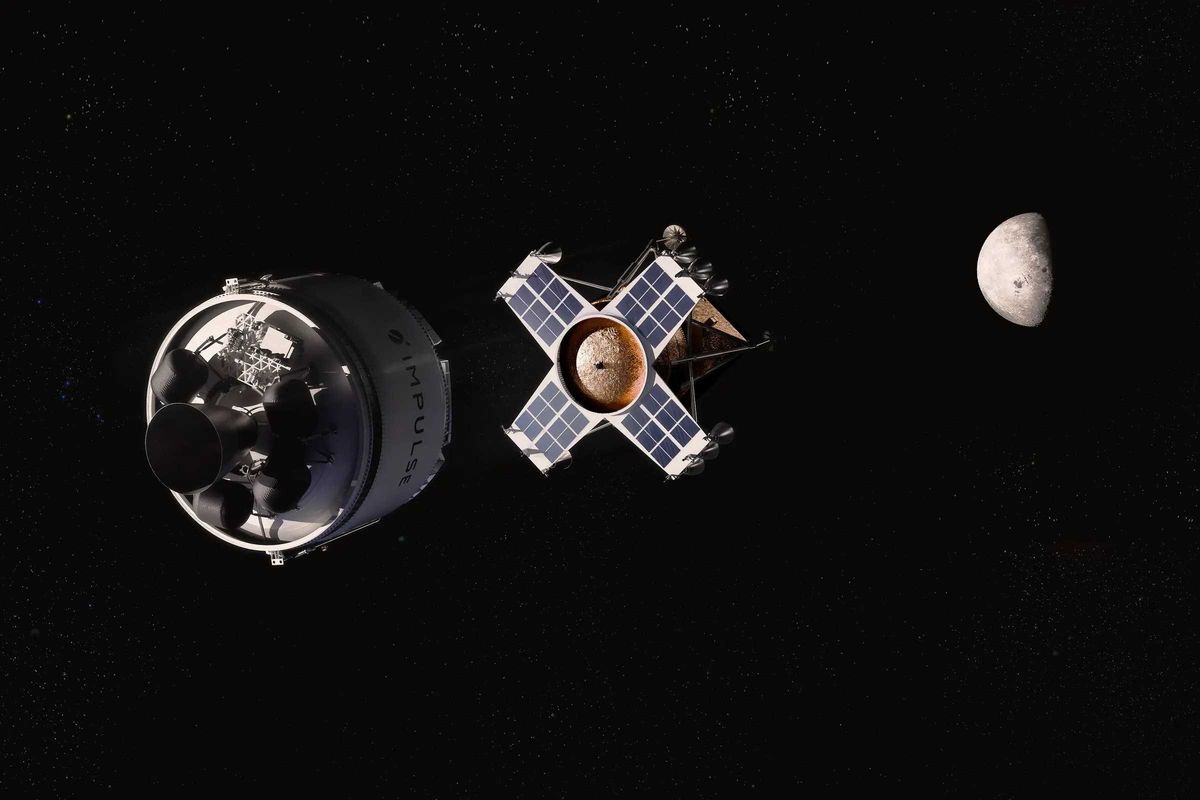
Impulse outlined a two piece ride to the Moon. Its Helios stage ferries an Impulse built lander to lunar orbit in about a week, the lander detaches, then descends to the surface without in-space refueling. The company says each mission could carry about three tons and that starting in 2028 it could run two missions per year for roughly six tons total, filling the gap between today’s small CLPS deliveries and future heavy landers.
Coco Robotics: new lab, new chief AI scientist
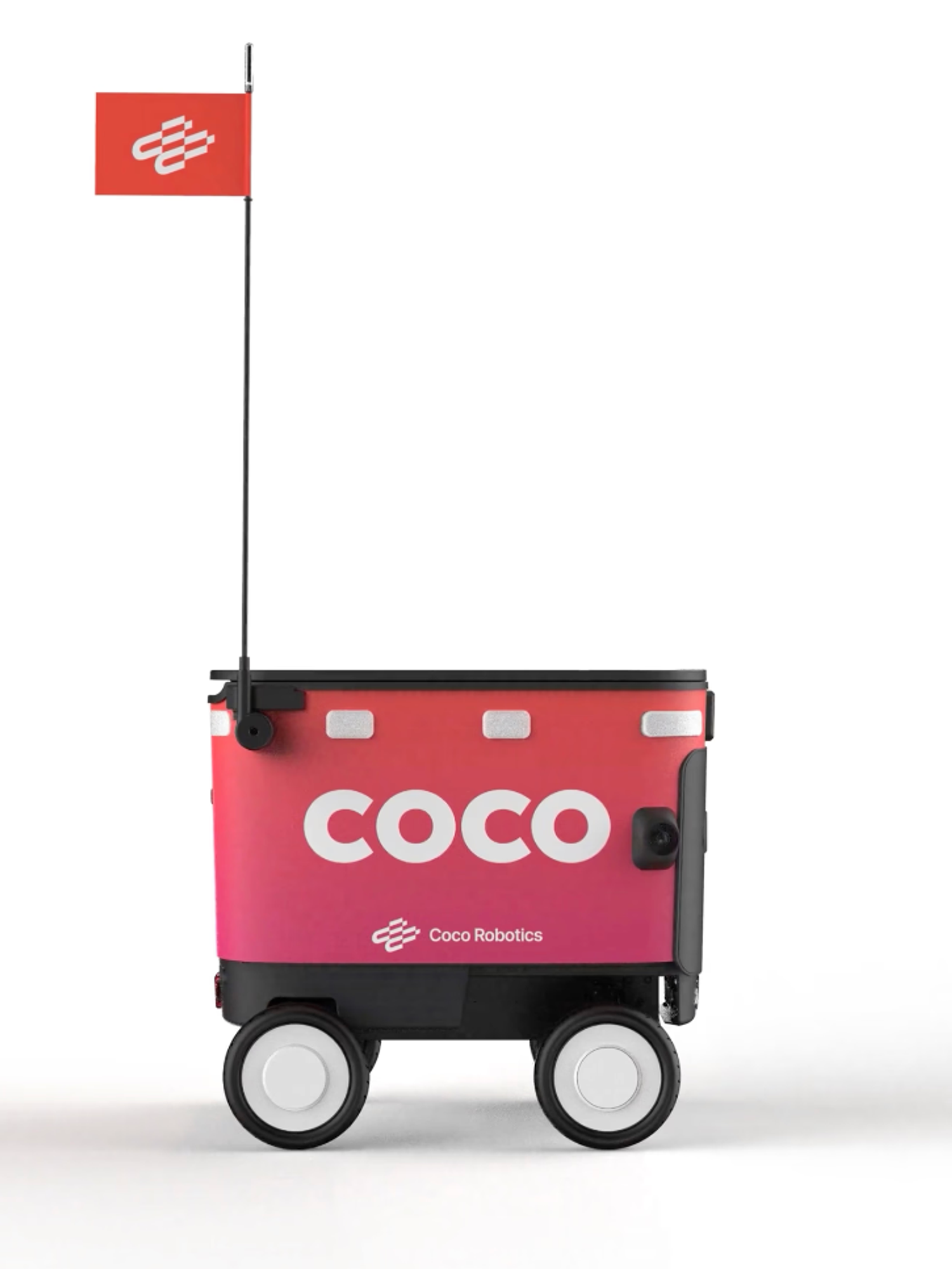

Coco named UCLA’s Bolei Zhou chief AI scientist and is launching a physical AI research lab to turn years of curbside driving data into faster, more autonomous sidewalk deliveries. Expect quicker iteration from data collection to local models on the bots.
LA Tech Week: last three days
We are down to the final few days of LA Tech Week 2025. If you are still slotting meetings or panels, use the rundowns to plan your route:
Scroll for the most recent LA venture deals, funds, and acquisitions.
🤝 Venture Deals
LA Companies
- Second Nature, an AI role-play training platform for sales and service teams, raised $22M Series B led by Sienna VC with participation from Bright Pixel, StageOne Ventures, Cardumen, Signals VC, and Zoom (also a customer). The company will use the funding to expand operations and advance its platform, which generates AI-driven practice scenarios and feedback for enterprise clients like Oracle, Zoom, Adobe, Teleperformance, and Check Point. - learn more
- Pelage Pharmaceuticals, a Los Angeles–based biotech developing regenerative treatments for hair loss, raised a $120M Series B co-led by ARCH Venture Partners and GV. Participants include Main Street Advisors, alongside Visionary Ventures and YK Bioventures; proceeds advance PP405, a topical small molecule that reactivates dormant hair-follicle stem cells, toward Phase 3 in 2026 following positive Phase 2a data. - learn more
- Launchpad, an AI-first robotics company for factory automation, raised an $11M Series A to speed product development and meet demand across the U.S., U.K., and Europe. The round was co-led by Lavrock Ventures and Squadra Ventures, with participation from Ericsson Ventures, Lockheed Martin Ventures, Cox Exponential, and the Scottish National Investment Bank; it follows $2.5M in grant funding from Scottish Enterprise. - learn more
- Mythical Games raised a Series D round, with a strategic investment from Eightco Holdings alongside ARK Invest and the World Foundation. The partnership focuses on human verification and digital identity in gaming, tapping Worldchain/Worldcoin’s Proof-of-Human infrastructure. The transaction is expected to close the week of October 20. - learn more
- Electric Entertainment, the L.A. studio behind “Leverage,” “The Librarians,” and “The Ark,” secured a $20M investment from Content Partners Capital. The funding follows CPC’s launch of an investment arm in April 2024 and is aimed at supporting Electric’s growth across production and distribution. - learn more
- Everyset raised $9M to launch Background Payroll, a SAG-AFTRA approved platform that automates timecards and payroll for background performers, including overtime, penalties, and premiums. The round was led by Crosslink Capital and Haven Ventures, and the company says studios such as Netflix, CBS, Apple TV, Sony, and Amazon already use its tools as it expands into fully integrated background payroll. - learn more
- TORL Biotherapeutics raised $96M in Series C funding to advance TORL-1-23, its Claudin-6 targeted antibody-drug conjugate, through a pivotal Phase 2 study in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer and into a confirmatory Phase 3 program. The company also reported that updated Phase 1 data for TORL-1-23 will be presented at ESMO 2025, bringing total funding since its 2019 founding to more than $450 million. - learn more
- The Plug, a plant-based liver health brand, raised $5M in a venture round of equity and debt to fuel marketing and retail expansion after rolling out its Pill Jar in June and entering all Total Wine & More locations nationwide in September. The company is keeping the round open for additional strategic investors and says it recently hit its first profitable month, is pursuing a partnership with a $500 million nutrition telehealth company, and is targeting a 40% boost to gross margins through a new operational milestone. - learn more
LA Venture Funds
- Clocktower Technology Ventures participated in MGT’s $21.6M Series B, an oversubscribed round led by Mubadala Capital with Tacora Capital and existing backers also joining. The AI-native commercial P&C neo-insurer for small businesses will use the capital to accelerate R&D, deepen vertical AI capabilities, and expand its E&S initiatives nationwide. - learn more
- M13 participated in Daylight’s $75M financing, which combines $15M in equity led by Framework Ventures with a $60M project facility led by Turtle Hill Capital. Daylight is building a decentralized energy network that turns homes into mini power plants via a subscription model and crypto-enabled incentives, aiming to lower costs and dispatch battery power back to the grid. - learn more
- Presight Capital co-led Peptilogics’ $78M Series B2, with Beyond Ventures participating, to fund a Phase 2/3 pivotal trial of zaloganan (PLG0206) for prosthetic joint infections. The raise brings Peptilogics’ total equity financing to about $120M and positions the company to begin the pivotal program in late 2025, pending approvals. - learn more
- Patron participated in Ego AI’s $6.7M seed round to help the YC-backed startup launch human-like AI characters for games via its new character.world engine. The round also included Y Combinator, Accel, and Boost VC, and the capital will support research on Ego’s proprietary model, which combines small language models with reinforcement learning, plus partnerships in Singapore to scale compute and development. - learn more
- Untapped Ventures participated in Woz’s $6M seed round, joining Cervin Ventures (lead), Y Combinator, Burst Capital, MGV, and the Lacob family. The funding will help Woz scale its platform that blends agentic AI with expert human oversight to deliver production-ready mobile apps for enterprises. - learn more
- Perseverance Capital participated in Kailera Therapeutics’ $600M Series B, which was led by Bain Capital Private Equity. The funding advances KAI-9531, an injectable dual GLP-1/GIP agonist, into global Phase 3 trials by year end and supports a broader pipeline of oral and injectable obesity therapies. - learn more
- March Capital participated in Lila Sciences’ $350M Series A, which lifts the company’s total funding to $550M. The capital will scale Lila’s AI Science Factories and commercialize its “scientific superintelligence” platform for partners across materials, energy, and biopharma. - learn more
- Mucker Capital participated in Pear Suite’s $7.6M Series A, which was co-led by Rock Health Capital and Nexxus Holdings. The L.A. based company equips community health workers with an AI-powered platform and provider network, and it will use the funding to expand product development, grow its network, and support new Medicaid and Medicare health plan contracts. Other investors include Enable Ventures, The SCAN Foundation, Acumen America, Impact Engine, and the California Health Care Foundation. - learn more
- Upfront Ventures participated in Renew’s $12M Series A, which was led by Haymaker Ventures with Goldcrest Capital and several Renew customers also investing. Renew’s AI-powered resident retention platform helps apartment operators automate renewals and prevent fraud, and the company says the new funding will scale the product and launch what it calls the industry’s first Resident Referral Network. - learn more
- Acre Venture Partners co-led Ascribe Bio’s oversubscribed $12M Series A with Corteva to scale its natural crop protection platform and launch Phytalix, a broad spectrum “biofungicide without compromise.” The funding advances Ascribe’s small molecule technology derived from the soil microbiome toward commercial rollout, with participation from Syngenta Group Ventures, Trailhead Capital, Silver Blue, Cultivation Capital, and others. - learn more
- Alexandria Venture Investments participated in Tr1X’s $50M financing, announced alongside FDA clearance of the IND for TRX319, an allogeneic CAR-Tr1 Treg cell therapy for progressive multiple sclerosis. The funding extends Tr1X’s runway into 2027 and supports a Phase 1/2a dose-escalation trial slated to start in early 2026, while the company continues its TRX103 studies in Crohn’s disease and other indications. - learn more
- LFX Venture Partners participated in FleetWorks’ $17M funding, which supports the launch and expansion of its “always-on” AI dispatcher for the U.S. trucking industry. The round was led by First Round Capital with participation from Y Combinator and Saga Ventures, and the company says the capital will go toward hiring, commercial rollout, and product development. FleetWorks’ platform automates freight matching between carriers and brokers to speed up bookings and reduce manual calls, emails, and texts. - learn more
- Clocktower Technology Ventures participated in Yendo’s $50M Series B. The fintech behind a vehicle-secured credit card will use the funding to expand its AI credit platform toward an inclusive digital bank that taps “trapped” consumer equity, aiming to unlock up to $4 trillion from assets like cars and homes for underserved borrowers. - learn more
- Alpha Edison participated in TransCrypts’ $15M seed round. The company builds a blockchain-based verified-credentials platform to fight AI-driven fraud and plans to expand beyond employment verification into health and education records. - learn more
- Alexandria Venture Investments participated in Nilo Therapeutics’ $101M Series A, which launched the company to develop medicines that modulate neural circuits to restore immune balance in disease. The round was led by The Column Group, DCVC Bio, and Lux Capital; Nilo also appointed Kim Seth, Ph.D., as CEO and plans to build out New York labs and advance preclinical programs. - learn more
- Chapter One participated in Glue’s $20M Series A. Glue builds an “agentic team chat” platform that embeds MCP-powered AI directly in workplace messaging, with 35 in-app integrations and support for thousands more via custom MCP servers. The funding will help expand product development and infrastructure as Glue pushes this model to more teams. - learn more
- StillMark participated in Meanwhile’s $82M raise, backing the Bermuda-regulated bitcoin life insurer as it expands bitcoin-denominated savings, retirement, and life insurance products for individuals and institutions. The round was co-led by Bain Capital Crypto and Haun Ventures with participation from Apollo, Northwestern Mutual Future Ventures, and Pantera Capital, and brings Meanwhile’s 2025 funding to $122 million after an earlier $40 million Series A. - learn more
- Blue Bear Capital co-led Energy Robotics’ $13.5M Series A with Climate Investment. The Darmstadt-based company provides AI software that lets robots and drones autonomously inspect critical infrastructure, and it will use the funding to scale deployments across energy, chemical, industrial, and utility sites. Customers already include majors like Shell, BP, BASF, Merck, and E.ON, and the company reports more than one million inspections completed to date. - learn more
- B Capital participated in EvenUp’s $150M Series E, which values the AI legal-tech company at over $2 billion. EvenUp builds AI tools for personal-injury law firms and plans to use the new capital to scale its platform and product suite; the round was led by Bessemer Venture Partners, with investors including REV (LexisNexis) and others. - learn more
- WndrCo participated in Zingage’s $12.5M seed round to build an AI care-delivery platform for home-based healthcare. Zingage is rolling out “Operator,” which automates scheduling, staffing, billing, and compliance for home care agencies, and “Perform,” which boosts caregiver retention, with the new capital supporting product expansion and go-to-market. The round was led by Bessemer Venture Partners with additional investors including TQ Ventures and South Park Commons. - learn more
- Alexandria Venture Investments participated in AeroRx Therapeutics’ $21M Series A, which was led by Avalon BioVentures with Correlation Ventures also investing. The funding advances AERO-007, a first-in-class nebulized LABA/LAMA for COPD, into late-stage clinical development aimed at patients who struggle with handheld inhalers. - learn more
- Alexandria Venture Investments participated in Affinia Therapeutics’ $40M Series C, alongside lead investor NEA and new investor Eli Lilly, to advance its AAV gene therapy pipeline. Proceeds will fund an IND submission in Q4 2025 and initial clinical work for AFTX-201 in BAG3 dilated cardiomyopathy, with a Phase 1/2 trial targeted for Q1 2026. - learn more
- Clocktower Ventures participated in Vycarb’s $5M seed round, which was led by Twynam with participation from MOL Switch, Hatch Blue, Idemitsu, and SGInnovate. The Brooklyn startup develops sensor-driven, water-based carbon capture and storage systems that convert CO₂ into stable bicarbonate, with the new funding aimed at scaling deployments at industrial sites. - learn more
LA Exits
- Empaxis Data Management was acquired by Communify, which is integrating Empaxis’ custodial and accounting data connections and operations expertise into its financial AI platform. The aim is to remove fragmented data so wealth and asset managers can deploy MIND AI apps like Client Stories and Portfolio Stories more quickly with cleaner, unified data. Communify also cites pre-integrations with over 175 market-data vendors to speed rollouts. - learn more
- TrueCar is being acquired by founder-led Fair Holdings (Scott Painter) in an all-cash deal at $2.55/share (~$227M), with Painter set to return as CEO. A 30-day go-shop runs through Nov. 13, 2025; largest holder Caledonia supports the acquisition, which is expected to close Q4 2025 or early 2026 pending approvals. - learn more
- Kate Somerville Skincare was acquired by Rare Beauty Brands, as Unilever moves to divest the prestige label it has owned for a decade. The deal includes the skincare and body-care lines as well as the brand’s Melrose Place clinic in Los Angeles; terms weren’t disclosed and closing is expected in Q4 2025 pending approvals. - learn more
- 3GC Group was acquired by Pandoblox, combining 3GC’s enterprise IT operations and cybersecurity services with Pandoblox’s Themis AI data platform to form a unified, AI-ready data and IT operations offering for mid-market companies. The deal aims to solve fragmented data and IT workflows so growing businesses can get enterprise-grade intelligence, security, and support through a single partner. - learn more
- The Free Press was acquired by Paramount, and co-founder Bari Weiss will become editor in chief of CBS News as part of the deal. Paramount says the move pairs CBS News’ scale with The Free Press’ voice, with Weiss reporting to CEO David Ellison and working to “modernize” the brand. - learn more
Read moreShow less
RELATEDTRENDING
LA TECH JOBS


