'Keep the American Dream Alive': Equity Crowdfunding Is Surging From an Appeal to Patriotism and Altruism
Ben Bergman is the newsroom's senior finance reporter. Previously he was a senior business reporter and host at KPCC, a senior producer at Gimlet Media, a producer at NPR's Morning Edition, and produced two investigative documentaries for KCET. He has been a frequent on-air contributor to business coverage on NPR and Marketplace and has written for The New York Times and Columbia Journalism Review. Ben was a 2017-2018 Knight-Bagehot Fellow in Economic and Business Journalism at Columbia Business School. In his free time, he enjoys skiing, playing poker, and cheering on The Seattle Seahawks.
When Christine Outram, founder and CEO of Everydae, a digital tutoring app, met with investors last year to try to raise a seed round she kept being told to come back in six months.
"I guess you can say we were turned down," she said.
Outram decided to try a different route, turning to equity crowdfunding, which allows mom and pop investors to dabble in something that until recently was solely the domain of professional investors. Her campaign proved successful – she raised $1.2 million from 1,586 people who wrote checks between $250 and $50,000.
"I've been really pleasantly surprised by the whole process," said Outram.
For reasons no one can quite explain, equity crowdfunding is having its moment during the coronavirus pandemic. Wefunder, the largest funding portal, recently had its best three months in the company's four-year history, with investor volume up 35% February through April. In early May, the site recorded $2 million of investment in a single day, a new record.
"I have been so confused," said Nick Tommarello, co-founder and CEO of Wefunder. "I don't know the answer. The big question for us was always how we would respond to a recession. You would assume that people would not want to invest."
Tommarello theorizes that more startups are turning to platforms like his as other sources of capital dry up, attracting casual investors who don't mind parting with what usually amounts to no more than the cost of an expensive meal to take a lark on a company. The median investment is $200 and 80% are less than $500.
"Our users aren't rich but they're middle class," said Tommarello. "People are not allocating it as an investment, but as discretionary income. They say they can go out for dinner or back someone and support them."
Brian Citizen, who lives outside Washington D.C., has invested in about a dozen startups through Wefunder usually at $250 a piece, including Everydae.
"It's become a passion of mine and something I really believe in and it's also fun because I get to help out entrepreneurs and be a part of the building process," said Citizen, who adds that COVID-19 has made him more excited to invest. "I think there's an opportunity to get better deals. The terms are going to be better for investors."
There is an oft repeated statistic that 90% of startups fail. Even professional VCs who have been at it for decades expect most of their portfolio to be a bust, so experts are wary about casual investors trying their luck in such a risky asset class.
"Some analysts even project that equity crowdfunding could surpass VC investments in the not-too-distant future," Waverly Deutsch, clinical professor of entrepreneurship at The University of Chicago Booth School of Business, wrote in a post warning investors. "This may be exciting news for entrepreneurs, and perhaps for people eager to help start-up founders that they know—but will likely lead to a start-up bubble and massive losses for the majority of individual investors."
Citizen says he is well aware of the risks and limits his total crowdfunding investments to about $2,000 a year. "I'm only willing to invest what I'm willing to lose," he said. "But the returns have the opportunity to be great."
Wefunder is upfront with users about the risks and avoids any impression that users will strike it rich, according to Tommarello.
"Our marketing is very blunt that you might lose all your money and most startups will fail," he said. "We say that over and over again. We don't even talk about our investment returns."
Instead of returns, the site tries to appeal to a blend of users' patriotism and altruism with a hopeful message on the homepage: "Keep the American Dream alive. Back founders solving the problems you care about and help their startups grow."
Equity crowdfunding was made possible by the SEC allowing anyone to invest in private companies in 2016, a privilege previously only accorded to "accredited investors" who made more than $200,000 per year or had investable assets of $1 million or more. A further loosening of the rules went into effect this year, which Tommarello says is likely contributing to the platform's popularity.
"A lot of the downsides have been taken away," he said. "The biggest crowdfunders previously needed to have thousands of direct shareholders on their cap table."
The SEC announced in May it would temporarily make it easier for companies affected by COVID to qualify. "In the current environment, many established small businesses are facing challenges accessing urgently needed capital in a timely and cost-effective manner," SEC Chairman Jay Clayton said in a statement.
Wefunder has backed 382 startups with $135 million, an amount smaller than many individual venture capital funds. Crowdfunding is still a niche, but it is gaining more widespread acceptance.
"I do think VCs are opening up to it more," said Kevin Morris, Chief Financial Officer at Wavemaker Labs, an early stage firm with offices in Santa Monica and Singapore. "Crowdfunding has been a bit of a bright spot in this economy so I think it would only help them."
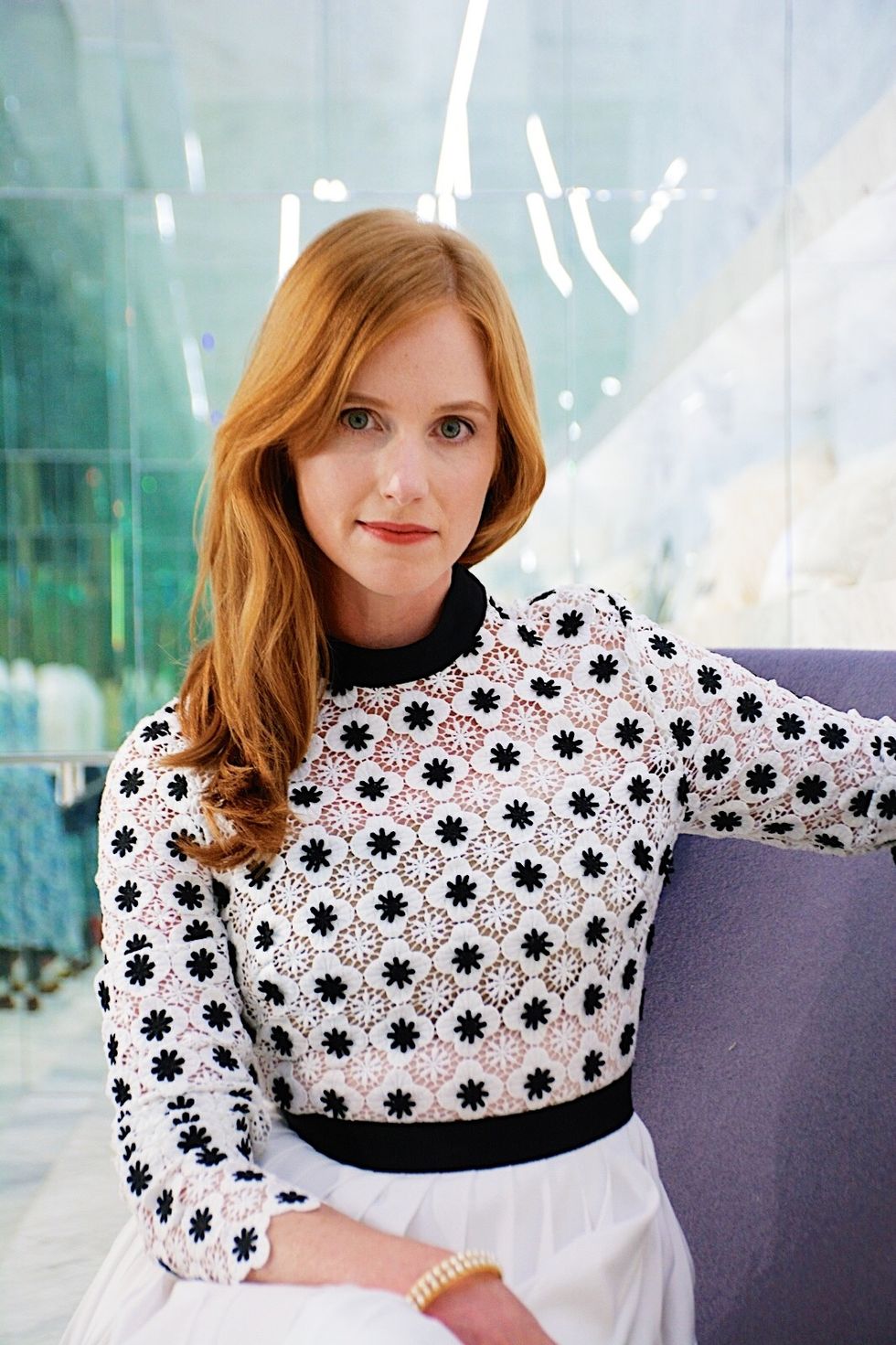

Christine Outram, founder and CEO of Everydae, a digital tutoring platform.
Wavemaker invests in the pre-seed and seed rounds of companies and then raises follow-up capital via equity crowdfunding, a strategy that has worked well with Miso Robotics, a robotic kitchen assistant and Graze, which makes a roomba-type device that mows lawns.
"Both of these businesses were always well suited for crowdfunding but what we've seen in COVID is businesses in the automation space are doing even better," said Morris. "With crowdfunding in general you can get slightly higher valuations than you would from a VC and in a business that is consumer facing you're not only getting capital but you're building brand ambassadors."
Marketing her virtual tutoring app has been one of the most appealing parts of equity crowdfunding for Everydae's Outram, but she says attracting investors took considerable effort. Most campaigns, including hers, see a spike at the beginning but trail off after the initial excitement.
"My job was to always have new news to draw eyeballs to the page," she said.
Outram posted a steady stream of content to her Wefunder page and appealed directly to podcasts and groups centered around education and investing. She also bought ads on Instagram and Facebook, which proved to be worthwhile when a Facebook ad led to a $150,000 commitment.
"What a lot of founders don't realize Is that equity crowdfunding is as much work as other kinds of fundraising," she said.
- Kickstarter Co-Founder Yancey Strickler on 'Bentoism' - dot.LA ›
- When to Accept Startup Equity — and Why - dot.LA ›
- Event: 2021 Equity Crowdfunding Week - dot.LA ›
- Crowdfund Platform StartEngine To Grow Collectibles Exchange - dot.LA ›
- Skybound Entertainment Crowdfunding Raises $12 Million - dot.LA ›
Ben Bergman is the newsroom's senior finance reporter. Previously he was a senior business reporter and host at KPCC, a senior producer at Gimlet Media, a producer at NPR's Morning Edition, and produced two investigative documentaries for KCET. He has been a frequent on-air contributor to business coverage on NPR and Marketplace and has written for The New York Times and Columbia Journalism Review. Ben was a 2017-2018 Knight-Bagehot Fellow in Economic and Business Journalism at Columbia Business School. In his free time, he enjoys skiing, playing poker, and cheering on The Seattle Seahawks.




 Image Source: JetZero
Image Source: JetZero
