Coronavirus 'Came Here on an Airplane' and GermFalcon Promises to Stop it in the Sky
Rachel Uranga is dot.LA's Managing Editor, News. She is a former Mexico-based market correspondent at Reuters and has worked for several Southern California news outlets, including the Los Angeles Business Journal and the Los Angeles Daily News. She has covered everything from IPOs to immigration. Uranga is a graduate of the Columbia School of Journalism and California State University Northridge. A Los Angeles native, she lives with her husband, son and their felines.
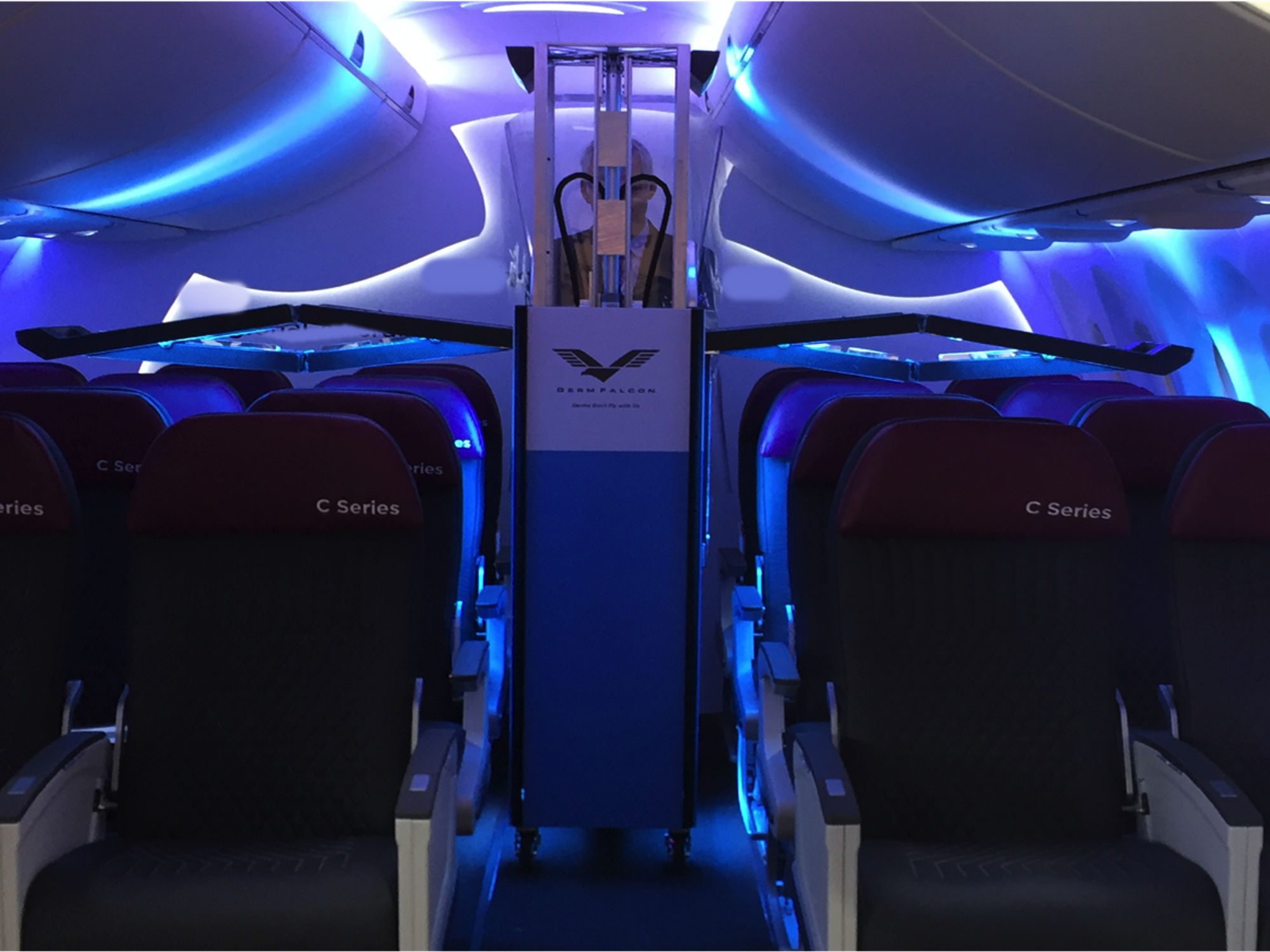

Seven years ago, Elliot Kreitenberg and his father, orthopedic surgeon Arthur Kreitnberg, built a UV-C light machine called GermFalcon to kill viruses on planes, but the airline industry largely rejected their pitch.
Years later with coronavirus all but wiping out air travel, their machine is looking a lot more attractive.
The founders of Long Beach-based Dimer UVC Innovations are in talks with airlines, transit authorities and others desperate to disinfect airplanes, subways and other transportation vehicles where COVID-19 quickly travels.
"We are in serious discussions with U.S. airlines as well as ground service providers, as well as international airlines in Canada, Europe and Southeast Asia," Elliot Kreitenberg said. The company is also talking to several transit authorities about manufacturing their product for them, although he could not reveal the names of anyone due to non-disclosure agreements.
GermFalcon Airplane Disinfection Demowww.youtube.com
Artificially produced UV-C is a common method of sterilization used in hospitals or to clean drinking water, but it hasn't been widely adopted to fight the virus in transportation. That's in part because studies haven't caught up to prove it works, although the light has been shown to be effective against other coronaviruses.
But, in China, busses have been blasted with the blue UV-C rays in an effort to fight the pandemic.
The Environmental Protection Agency and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are looking at UV light as a solution for large-scale disinfecting in places like schools and offices. And it's attracted the interest of other government agencies, including the Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transit Authority, which is considering using UVC light to clean its fleet of busses and trains.
"We're already increasing the frequency of our cleanings and we are doing more deep cleaning," said Jesus Montes, an executive at L.A. Metro's vehicle acquisition and engineering department. "To supplement that, we're looking to things such as foggers and vaporizers and UV."
Montes has been inviting UV vendors to demonstrate their products. The advantage he's found over vapors or foggers, which can cause damage to the electrical engines, is that UV rays are far less labor intensive and can be used off site.
Other companies that supply the light to hospitals have seen an uptick in sales. Kreitenberg said they have also been getting orders and expect to have up to 100 of their UV machine made for hospitals finished by mid-May. From there, they will go into production of 10 a day. He said he's already provided Paine Field Airport with a machine that's now in use. And his machine was cleaning airplanes at Los Angeles Airport that had been in-bound from China when travel had not been restricted.
Dimer keeps its rays to surfaces, where it says it can kill up to 99.9% of bacteria.
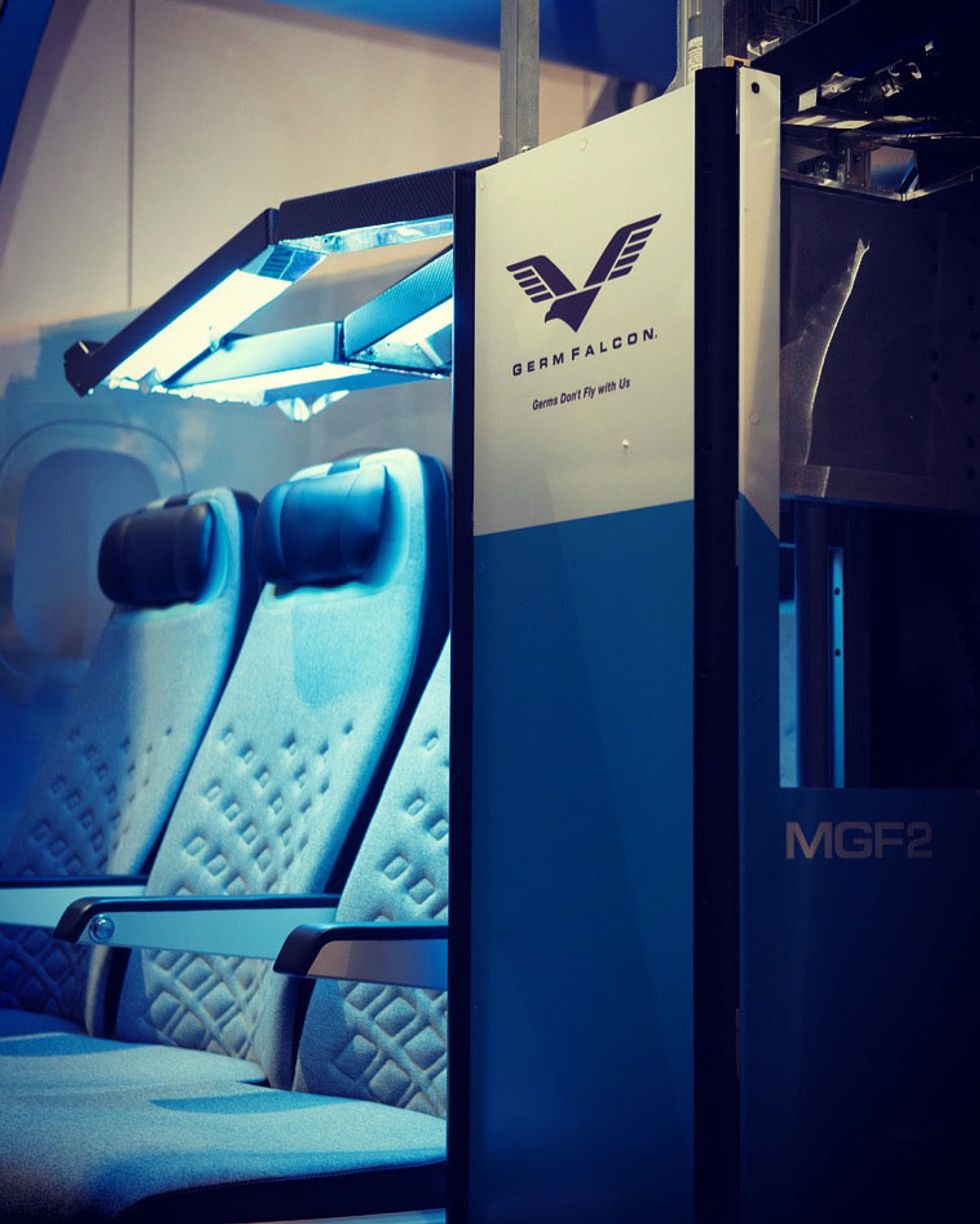

Courtesy of GermFalcon
"What's nice about this technology is that it's not going to promote resistance to anti-microbial agents," said Leonard Mermel, a professor at Brown University and the medical director of Rhode Island Hospital's Department of Epidemiology and Infection Control who is familiar with the technology.
Airplanes are particularly tricky because microbes can potentially survive longer.
"We know some viruses can survive certainly overnight...cooler temperatures and the dryness of airplanes actually improves survival of some viruses like flu."
Other companies offer UV lighting. But what makes Dimer's $100,000 disinfectant machine different than others that attacks microorganisms, bacterias and superbug is that it's made for airplanes. Amortized over a conservative 5-year lifespan, the machine costs 10¢ per passenger.

Courtesy of GermFalcon
About the width of a drink cart, the machine slides easily down an airplane aisle and has a winglike feature that spreads the light over seating. He's also making another product that's geared toward hospitals and space that aren't as tight.
A few years ago, he said he brokered a deal with Virgin America to use the GermFalcon, but it went belly up when Alaska Air Group bought the company for $2.6 billion.
Arthur Kreinberg, who is also the co-founder of the company, became familiar with the lights through his experience with them in hospitals. He then worked with his son to build their first designs in their garage.
"(My paternal grandfather) was a Holocaust survivor and plumber and when my father graduated from medical school he said 'plumbers save more lives than doctors because sanitation plays a big role in public health.' When the toilet was invented it doubled human life expectancy. I think GermFalcon is the most important invention since the toilet."
The World Health Organization considers those that are in contact with an individual infected on a flight and those sitting within two rows at most risk. But, airplanes have a reputation as vectors of germs.
Elliot Kreitenberg, once a frequent flier, said he's been keeping a log every time he travels of the dirtiest places on the airplane. It's not the toilet handle but, according to his own informal survey, the back of head rests where people touch as they walk down the aisle.
"Airlines play a direct role in the way that disease spreads around the world," Elliot Kreitenberg said. "We see that here with coronavirus. It flew here on airplane."
- Catch Up With This Week's Startup News in Our Weekly Video Recap ›
- GermFalcon Designs Ultra Violet Light 'Drink Cart' for Planes - dot.LA ›
- CVS and UPS team up for drone deliveries to retirees amid outbreak ... ›
- Germfalcon Strikes a Deal with Honeywell to Sell, Produce Its Antiviral 'Drink Cart' For Cleaning Airplanes - dot.LA ›
- Germfalcon Strikes a Deal with Honeywell to Sell, Produce Its Antiviral Airplane Cleaner - dot.LA ›
Rachel Uranga is dot.LA's Managing Editor, News. She is a former Mexico-based market correspondent at Reuters and has worked for several Southern California news outlets, including the Los Angeles Business Journal and the Los Angeles Daily News. She has covered everything from IPOs to immigration. Uranga is a graduate of the Columbia School of Journalism and California State University Northridge. A Los Angeles native, she lives with her husband, son and their felines.



 Image Source: Skyryse
Image Source: Skyryse
 Image Source: Northwood Space
Image Source: Northwood Space