Relativity Hires Microsoft’s Scott Van Vliet to Boost Its Factory Operating System for 3D-Printed Rockets
GeekWire contributing editor Alan Boyle is an award-winning science writer and veteran space reporter. Formerly of NBCNews.com, he is the author of "The Case for Pluto: How a Little Planet Made a Big Difference." Follow him via CosmicLog.com, on Twitter @b0yle, and on Facebook and MeWe.
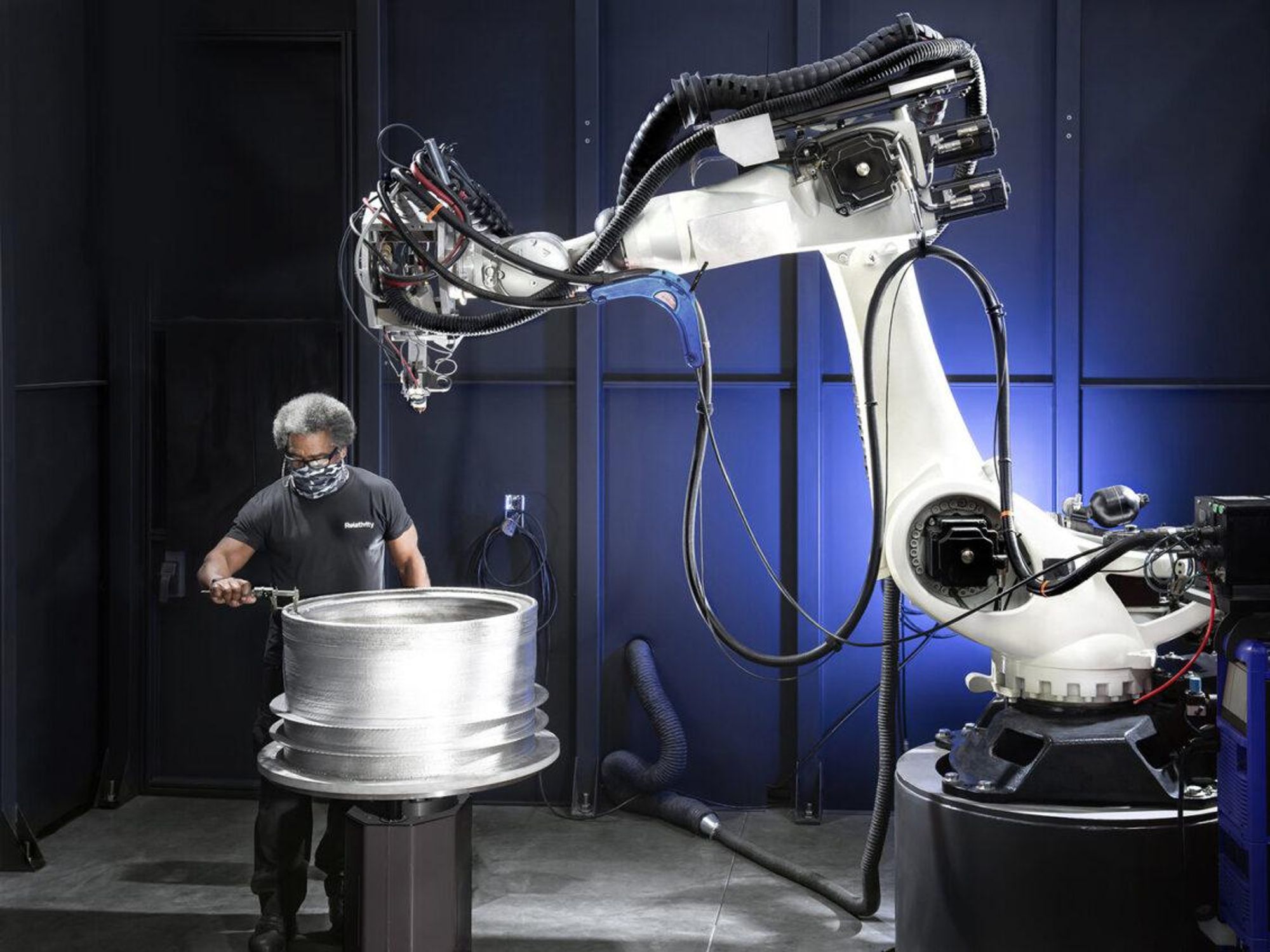

Relativity Space, the startup that was founded in Seattle and is now building 3D-printed rockets in Southern California, has brought in a Microsoft executive to lead its growing software engineering team and expand upon its AI-powered “Factory Operating System.”
Scott Van Vliet, who headed up the team behind the Microsoft Teams collaboration platform as a corporate vice president, will oversee more than 150 of Relativity’s employees on its Integrative Software and Additive Manufacturing teams as senior vice president of software engineering. He’ll be based in the Los Angeles area.
Before his four-year stint at Microsoft, Van Vliet played a leading role in the development of Amazon’s Echo devices and Alexa voice-assistant platform. He told GeekWire that he’s looking forward to helping Relativity Space revolutionize industrial applications for 3-D metal printing, just as he helped Microsoft and Amazon blaze trails for collaborative software and AI assistants.

Scott Van Vliet has left Microsoft to become the senior vice president of software engineering at Relativity Space.
Image via Twitter
“Thinking about where we’re going with our Stargate family of printers, and the technologies that we’re building across the stack, we can apply similar models of machine learning to transform the way we do predictive modeling, predictive printing, and build the products that we’re going to build,” Van Vliet said.
Relativity Space’s first big product, its Terran 1 rocket, is due for its first launch this year, and the company is already working on a more powerful, fully reusable rocket called the Terran R.
Relativity CEO Tim Ellis, a veteran of Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin space venture who co-founded the company in a Seattle co-working space in 2015, said software will be key to the future of Relativity Space — and the future of the launch industry.
“Scott’s really the most senior hire the industry has made in software,” Ellis told GeekWire. “That’s exciting to me, because I very much do believe the quote from Andreessen-Horowitz that ‘software is eating the world.’ … Everything that Relativity is doing, transitioning manufacturing to more software- and data-driven approaches, is inevitable. We’re just the farthest along.”
Relativity is betting that automation and 3-D printing will dramatically reduce the cost of building rockets, resulting in far cheaper access to space.
The Factory Operating System is a key concept in Relativity’s approach: Van Vliet said he and his team will aim to boost the capabilities of a software platform that knits together all the processes involved in building rockets from piles of powdered metal. He compared the FOS to the platforms provided by Microsoft Windows, or Microsoft Teams, or Amazon’s Alexa voice assistant software.
“Frankly, it’s going to be the platform that enables things we haven’t even thought about yet — capabilities that the engineers and designers on our team will start to unlock as we think about an end-to-end integrated experience that can apply to any purpose,” Van Vliet said. “That’s the most exciting thing for me: building this platform that will accelerate the vision of Terran 1 and Terran R as well as other industries.”
Ellis acknowledged that the operating system he and Van Vliet have in mind could be applied more widely to other manufacturing markets — for example, planes, trains and automobiles. But at least for the time being, he insists that everything Relativity Space does will be focused on building the infrastructure needed to get to Mars, and eventually get industry going on the Red Planet.
Like SpaceX founder Elon Musk, Ellis is fond of saying that Relativity Space’s long-term goal is to make humanity a multiplanetary species. “We’re still only the second company in the world that has this core mission of wanting to make humanity multiplanetary,” he said. “And I do hope that there’s more. I hope we inspire dozens to hundreds of companies to be ambitious and go after these big plans.”
But unlike Musk, Ellis isn’t planning to build satellites.
“We see the opportunity for doubling down on our own platform and making our own better end products,” Ellis said. Focusing on software-optimized additive manufacturing is “an investment in that approach,” he said.
Ellis said Relativity Space’s fourth-generation Starbase 3-D printers are already theoretically capable of turning out a Terran 1 rocket in six days, and turning out a Terran R rocket in 30 days.
“There are other parts of the factory process — downstream processing, machining, inspections — and really, Scott and his team are going to be accountable for achieving that rate,” Ellis said.
Relativity seems likely to have the required wherewithal: Last June’s $650 million Series E funding round for Terran R sent total investment past the $1.3 billion mark, and total valuation is said to be in excess of $4 billion.
The company now has more than 600 employees, roughly double the workforce it had a year ago. Those workers aren’t just at the headquarters in Long Beach, Calif.: There are teams working in Washington, D.C.; at NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi; at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California; at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida — and even in Kent, Wash., not far from Blue Origin’s HQ. (Relativity says its Seattle-area office has four employees.)
“We were at a little over 100 at the beginning of the pandemic,” Ellis said. “I believe we’re the fastest-growing launch company in history, in terms of headcount growth and rate of growth over that period.”
And Relativity is still growing: Its career website lists more than 100 job openings. “This is an investment in hiring far more software engineers, data scientists, computer vision, machine learning,” Ellis said. “It’s really a kind of doubling down on a very different type of team that hasn’t existed in aerospace before to this level.”
Van Vliet said he’s long dreamed of working in the space industry, and he can hardly wait to jump in.
“I definitely have a lot to learn, getting involved with the company and starting, but I think there’s just such an incredible footprint already,” he said. “That’s what’s most exciting for me — there’s the experience that I have scaling up and leading large teams, and there’s an incredible set of assets that exist already.”
This story originally appeared on GeekWire.
- Relativity Space Is Planning a Reusable Rocket - dot.LA ›
- Relativity Space Raises $650M for Its Recyclable Rocket - dot.LA ›
- Relativity Space Soars, Lands $500M Investment - dot.LA ›
- Relativity Space Scores Department of Defense Contract - dot.LA ›
- Relativity Space Expands in Long Beach - dot.LA ›
- Microsoft in Talks to Invest $10 Billion in OpenAI - dot.LA ›
GeekWire contributing editor Alan Boyle is an award-winning science writer and veteran space reporter. Formerly of NBCNews.com, he is the author of "The Case for Pluto: How a Little Planet Made a Big Difference." Follow him via CosmicLog.com, on Twitter @b0yle, and on Facebook and MeWe.



 Image Source: Revel
Image Source: Revel