Santa Monica's Quantgene Uses Big Data to Solve the Cancer Riddle
Rachel Uranga is dot.LA's Managing Editor, News. She is a former Mexico-based market correspondent at Reuters and has worked for several Southern California news outlets, including the Los Angeles Business Journal and the Los Angeles Daily News. She has covered everything from IPOs to immigration. Uranga is a graduate of the Columbia School of Journalism and California State University Northridge. A Los Angeles native, she lives with her husband, son and their felines.

Jo Bhakdi thinks he can extend life with data.
Over the past years, the trained economist and co-founder of Quantgene has helped create a blood test that screens for early signs of some of the deadliest cancers, using millions of culled data points.
"We have a bigger vision behind this," Bhakdi said. "It's what I call decades in a decade — to extend the average human lifespan by ten years in the next ten years."
Quantgene has been developing so-called "liquid test" that can pinpoint the origin of multiple types of cancer by identifying their cellular mutations using artificial intelligence analytics and big data.
The project began five years ago at a U.C. Berkeley lab. Bhakdi partnered with co-founder Monika Hagen to create a system that would screen cancer using algorithms.
Late this year, Bhakdi and Hagen expect to roll out an early cancer screening subscription plan to consumers for an annual cost of around $2,200, pending regulatory approval. And they specifically came to Los Angeles, an image-conscious city that's embraced the idea of wellness, to launch it.
Blood tests are not a new technology for cancer screening, but Quantgene and others are trying to create a more precise tool to identify cancer in its earliest stages by finding mutation patterns that point to the disease. And in the process lower cancer death rates in the U.S.. This year, an estimated 600,000 people will die of the disease. Another 1.6 million will get the grim diagnosis. It's the second biggest killer of Americans year in and year out.
Most blood tests are currently used when doctors already know where the cancer exists, mostly in order to track its progression.
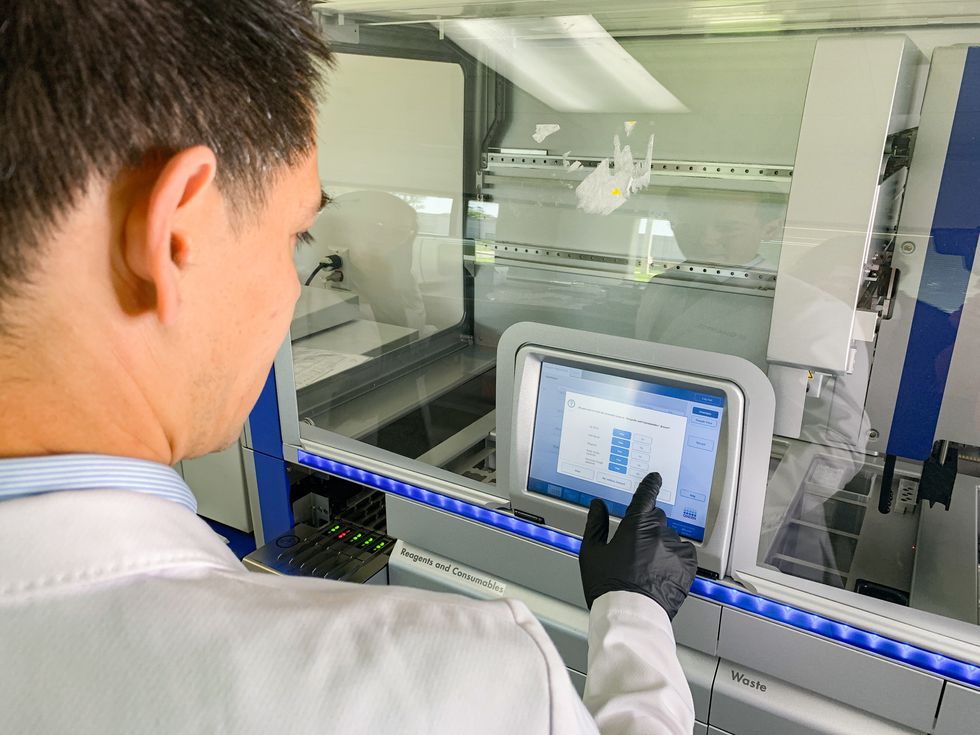
 Quantgene founders Jo Bhakdi and Monika Hagen
Quantgene founders Jo Bhakdi and Monika HagenThe new tests examine fragments of DNA that break loose in the bloodstream. Quantgene looks at the different mutations of these cells to identify patterns that signal early forms of cancer or other diseases. The company plans to sell the system as part of a line of tiered-price testing called "Serenity" that includes genetic counseling and profiles.
Quantgene is branding the complex sequencing and AI process that analyzes these mutations the "Griffin Deep Genomics Platform." The company has raised more than $13 million, and expects to raise a Series B round this fall. Bhakdi believes it could upend how people test for cancer. But it has competition.
Amazon-backed, Menlo Park-based Grail Inc. has raised nearly $2 billion. In March, the Silicon Valley company released a report that said it could detect 50 types of cancer across all stages, with a false-positive rate below 1%. The company said it can find its location with 93% accuracy. But finding early-stage cancer — the type that actually save lives — has proven elusive.
Of the 12 deadly cancer types that make up 63% of deaths in the U.S., Grail reported a detection rate of 67% for stages one to three. The company's test is expected to be available within 12 months. A spokeswoman said in an email, it's "too early to comment on cost, however, our principal goal is to ensure broad access to our test, and we hope to make this ground breaking technology available to as many people as possible." Investors include Bill Gates, Bristol-Myers Squibb and Merck.
"The problem with a lot of these liquid biopsy technologies right now — Grail and others — is that they are not really good at detecting cancers at the earliest stages. Because there just isn't that much tumor material in the blood," said Timothy Rebbeck, director of the Zhu Family Center for Global Cancer Prevention at Harvard. "So, it's not to say that it couldn't be done. It's just the right now the technology is not refined enough to do it that really well."
Getting to Cancer Screening at Earlier Stages
For the last few decades, physicians have screened individual organs for signs of cancer, trying to suss out whether a patient has a cancerous growth on the pancreas or breast or lung. These early screenings, coupled with advances in cancer treatments, have been credited with a decline in U.S. deaths related to cancer.
"The median point of diagnosis in these 1.6 million is between stage three and stage four.
If you can shift that point of stage two and one, you would be saving 400,000 people a year," Bhakdi said. "That's crazy if you think about that."
Bhakdi, who comes from a family of scientists and doctors, began the search less than a month before his own mother was diagnosed with stage four colon cancer.
At the time, a family member asked his help in solving a genomic question about whether one could determine if a random, isolated cell was cancer. The answer is very difficult to get. It lays in sequencing the cell's DNA and then comparing it to thousands of others. That ability to compare cells with a massive data trove is now at the heart of their company.

Bhakdi believes it would have saved his mother.
"If you are diagnosed with colon cancer at stage one, you have a 94% survival rate," he said. "In stage four, you have an 11% survival rate."
Sidestepping Insurers in Santa Monica
One of the best ways to bring down deaths is to diagnose cancer early, said Rebbeck. But even when these technologies are developed for widespread use they could exacerbate disparities for the poor, underserved and uninsured. That's because there remains systemic hurdles of access and cost.
Bhakdi said he understands those concerns. He had hoped originally to work with insurers to get the product out, but they required long-term economic studies to prove they would lower costs. Unable to produce that quickly, Quantgene moved to Santa Monica last year.
"We asked the question, 'What region has the most innovation-driven and future-oriented consumers and physicians and health care experts that are most likely to adopt new technologies?'," he said. "And what we found was very clear, very clear: Los Angeles."
In short, people in Los Angeles pay well to be healthy and beautiful. He pointed to companies that thrive in the metropolis like Next Health, a self-described longevity center that offers cryotherapy, or Remedy Place, a social wellness club.
"There's a big population here, a lot of whom are focused on health and wellness and are willing to spend the money," said David Whelan, chief executive of BioScienceLA, "The Goop effect sort of worked here. This is the place to be able to get a lot of customers very quickly when you're charging a high price point for customized service."
Beyond that, Bhakdi said there's also an extreme level of excellence in clinical infrastructure from medical institutions at UCLA, USC, City of Hope and Cedars-Sinai.
The move, he said, will hopefully allow Quantgene to demonstrate the product's value and convince insurers to offer it, eventually getting it into more people's hands. At the same time, the cost should draw down.
By 2024, the marketplace for personalized medicine and testing is expected to hit $85 billion, according to Pitchbook.
How does it work?
The company uses what's called cell-free DNA in the bloodstream to look for somatic mutations, those that are unrelated to hereditary factors and indicate a cancer growth.
"It's not a black and white thing," Bhakdi said.
It's more like matching different cancer profiles via machine learning. Using algorithms, the company traces the mutation patterns and compares those patterns to others who have the disease. By comparing the patient's mutation pattern along with their profile, Quantgene determines whether a specific cancer is maturing and tries to spot it.
"What the report does is not tell you whether you have cancer or not. That would be irresponsible," Bhakdi said. "It looks into the mutation pattern of the DNA that is in your gut — which means all the DNA that comes from, say, the diet in your body — and it takes these patterns and gives you a very high-resolution insight into how this compares with people with... all other kinds of medical conditions, including the ten leading cancers."
In 2016, Quantgene launched a clinical trial that will help them determine the sensitivity and specificity of the tests. Their goal is to have 10,000 patient blood samples. So far the company has about 5,000.

But those working with the company think once it comes to market, it could be a game changer, helping physicians figure out how to deal with early signs of cancer.
"A lot of the companies working in molecular diagnostics don't have a good approach to telling physicians what to do and helping out with decision making. Quantgene has come to understand that that aspect of integrating clinical information and then providing guidance on what to do based on probabilities is helpful and necessary," said Jorge Nieva, an advisor to the company and an oncologist and associate professor at the University of Southern California Keck School of Medicine. "It has the real potential to revolutionize the field of cancer screening because our approach to cancer screening up to this point has really been organ-based."
What distinguishes the company, he said, is they are largely driven by math instead of biology.
"With the large database that Quantgene has built of some 40,000 tumors across 15 different cancers types, you can begin to build those patterns so that you can map those genetic abnormalities back to the anatomy," Nieva said.
- The COVID-19 Crisis is Creating a New Biotech Culture in L.A. - dot.LA ›
- Wavemaker 360 Health Announces $100 Million Fund Aimed at ... ›
- Can LA County's New Fund Get Local Biotech Startups to Stick ... ›
- The New Tech at Dodger Stadium - dot.LA ›
- A LinkedIn For Esports - dot.LA ›
- Quantgene Releases At-Home Saliva Test to Help Detect Cancer - dot.LA ›
- Preveta Aims to Change the Game for Early Cancer Detection ›
- Appia Bio Aims to Offer Safer Cancer-Fighting Cell Therapies - dot.LA ›
- ImaginAb Aims to Help Our Immune Systems Better Detect Late-Stage Cancer - dot.LA ›
- ImmixBio Files for an IPO to Expand Its Cancer Therapies - dot.LA ›
Rachel Uranga is dot.LA's Managing Editor, News. She is a former Mexico-based market correspondent at Reuters and has worked for several Southern California news outlets, including the Los Angeles Business Journal and the Los Angeles Daily News. She has covered everything from IPOs to immigration. Uranga is a graduate of the Columbia School of Journalism and California State University Northridge. A Los Angeles native, she lives with her husband, son and their felines.


 Image Source: Valar Atomics
Image Source: Valar Atomics Image Source: Waymo
Image Source: Waymo Image Source: Apple
Image Source: Apple
