Inside the 'Aggressive' Goal to Make LA Port Ships 100% Zero Emission
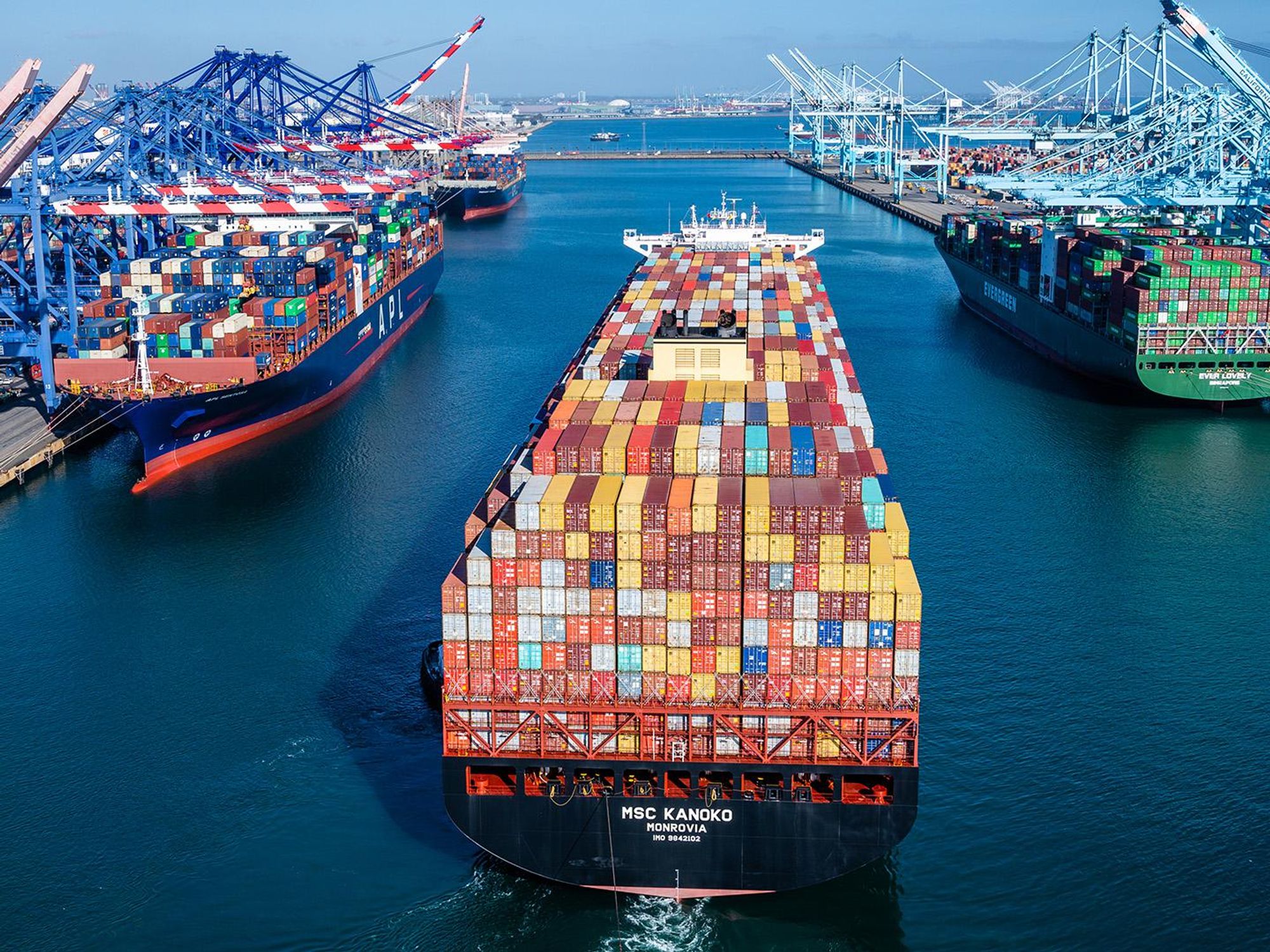

Los Angeles' City Council adopted an ambitious maritime resolution last week that calls on top importers like Walmart, Dole, Nike, Amazon and Home Depot on 100% zero-emissions ships by 2030, even though the technology doesn't yet exist.
Idling ships sitting off the San Pedro Bay Coast have captured national attention as a symbol of broken supply chains, but those ships are also big polluters.
Research suggests ship pollution contributes to more than 250,000 premature deaths each year around the world, and at least 1,300 premature deaths each year in Los Angeles and Long Beach. Low-income communities of color who live near the ports are especially affected.
While the city doesn't have any regulatory power over maritime rules, the move places pressure on some of the world's biggest retailers and their supply chains. The resolution asks shippers ferrying everything from televisions and cars to sofas and microwaves to "immediately adopt" existing emissions-reducing technologies, such as wind-assisted propulsion and slow-steaming.
It also calls for a broader effort to create zero-emission shipping corridors along the California coast and across the trans-Pacific trade route.
dot.LA spoke with Christopher Cannon, chief sustainability officer of the Port of Los Angeles, to discuss the resolution, and why he thinks all parties will do what they can to achieve such a drastic industry overhaul.

Port of Los Angeles Chief Sustainability Officer Christopher Cannon
dot.LA: In layman's terms what does this new resolution do?
Christopher Cannon: It really encourages the industry to move toward low carbon and zero carbon fuels as soon as possible and this is important.
We think that the move to low carbon fuels can happen pretty quickly, like in the next few years.
We see, for instance, that some of the shipping lines are talking about using methane feedstock that arrived from renewable sources starting in 2024.
The goal to get to 100% zero emission ships by 2030 is very aggressive.
Technology does not exist today to do that, but it does not mean that it isn't a good goal and an important goal, and we want to push ourselves and the maritime industry to get there.
Rapidly decarbonize the maritime shipping industry to create zero emissions corridors—we like that, and we want to create green shipping corridors. You start doing this stuff now, not waiting until zero emissions is possible. You start doing low carbon and even zero carbon elements in a shipping corridor.
Maybe not everything is fully zero [emissions], but you can have parts of it be zero. A lot of different activities can occur from the movement of cargo from one port to another: the loading and unloading, the sorting.
All the activity associated with moving that ship can be green and we can reduce the carbon footprint, we can decarbonize all of it with best management practices.

Does the city have any enforcement power, say if they adopt legislation, in this domain?
No, we don't run the ships and we don't control the ships. We don't regulate the ships. They are regulated by international bodies, but we certainly have the ability to exert influence on the shipping industry and on international regulators like the International Maritime Organization.
We're engaged in discussions with them on these goals. While we can't enforce, we certainly can influence what the industry does, and we will do our best to work with the industry and help to help them transition to these cleaner fuels.
What is the shipping industry saying about the push to zero emissions?
They tell us that their customers want the same thing, that their customers want low carbon and zero carbon and zero emission ships, too.
They are as interested in doing it as we are because that's what the Home Depots and Amazons are pushing for, too, and the reason those customers are pushing for it is because people like you and I, who are ultimately buying products, we're pushing for it. Everyone wants to do it.
It's just a matter of getting the technology to the point where it can be deployed. The industry is testing this equipment now. There are different pieces of the journey. There is the cargo handling equipment, there's the tugboats. There are other parts of the journey where we can improve efficiency and reduce carbon and get to zero carbon emissions, and we want to get every part of that journey.
We want zero emissions ultimately but you want to start out with low carbon right away, then get to zero carbon as quickly as you can, then get to zero emissions as quickly as you can after that.

Is there any concern that this could impact shipping in any way?
No, we hope not. I mean the industry, as I said, their customers are pushing for the same thing so their customers certainly don't want the delivery of their cargo to be adversely affected, so the shipping lines don't want to do that either.
It's pretty exciting because it's a case where everyone seems to now realize that we have to reduce our carbon footprint as soon as we possibly can in order to fight climate change.
So we're starting to see consumers are demanding it. Manufacturers of goods are seeking it. Goods and movement, the industry is hearing a strong message from their customers that they want it, so the goods and movement industry, the shipping lines, the trucks, even the trains, everybody is being pushed to do this and so we, too, want to push as hard as we can.
These resolutions, like the one from the City Council, are important because they send a message too that this is something that everybody wants.
Are there enough resources to make the technology a reality?
It's expensive. Private industry has to invest mostly, to be honest with you, but I think there's a role for government to help incentivize this activity through grants and other kinds of inducements; certainly ports can help to incentivize those by offering favorable rates and other things for people who are moving cargo in a manner that is convenient and ultimately with a zero carbon footprint.
The technology is expensive but I think everyone believes that once the technology becomes commercialized and ready for widespread deployment, that you'll have a reduction in cost.
This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
- Electrify America Invests $200M in Southern California - dot.LA ›
- Xos Trucks Launches Mobile Charging Stations for Fleets - dot.LA ›
- Braid Theory's Plan to Build the Next Cohort of Ocean Tech Startups - dot.LA ›
- Solid state batteries lower EV carbon emissions - dot.LA ›
- The Lull in Shipping Could Harm L.A.'s Clean Tech Startups - dot.LA ›



 Image Source: Revel
Image Source: Revel