'Sweetgreen is Not a Tech Company': The Company's CEO on How He's Adapting to the Pandemic
Ben Bergman is the newsroom's senior finance reporter. Previously he was a senior business reporter and host at KPCC, a senior producer at Gimlet Media, a producer at NPR's Morning Edition, and produced two investigative documentaries for KCET. He has been a frequent on-air contributor to business coverage on NPR and Marketplace and has written for The New York Times and Columbia Journalism Review. Ben was a 2017-2018 Knight-Bagehot Fellow in Economic and Business Journalism at Columbia Business School. In his free time, he enjoys skiing, playing poker, and cheering on The Seattle Seahawks.

Jonathan Neman, the 35-year-old co-founder and CEO of Sweetgreen, wants to make one thing clear.
"Sweetgreen is not a tech company," he says. "If you want to make that the headline, you can."
With a lofty $1.6 billion valuation, a sleek headquarters in Culver City down the street from Apple and Amazon, and talk with Kara Swisher about becoming a "food platform," one could be forgiven for thinking Neman has aspirations that go way beyond serving salads, bowls and now plates in 108 stores. These days everyone wants to be a tech company, even if they are just renting office space or selling stationary bikes. Neman certainly has lofty goals – wanting to expand to what he says is "well over" 1,000 locations. But he says he is trying to grow Sweetgreen in the mold of Starbucks, not Snapchat.
"We see ourselves as building the Starbucks of real food," Neman said. "We're actually not even valued like a tech company. If you look at the valuation it's much more like a high-growth food company. We leverage technology to build a better experience and make smarter decisions. And I think it is an accelerant to how we can grow and scale and build our model. However, at the core of what we do, we are a consumer brand."
Sweetgreen's origin story is decidedly techie. Neman hatched the concept with classmates Nicholas Jammet and Nathaniel Ru in a dorm room during their senior year at Georgetown University. Three months after graduation, they opened their first location in Washington D.C. in 2007. In 2016, they relocated to Los Angeles after opening their 39th location.
Last year, Sweetgreen reported $300 million in revenue and $3 million per store, well above Chipotle or Starbucks, which generated $2.2 and $945,270 per location, respectively.
The company would not disclose its numbers for this year but in an April blog post Neman and his co-founders described revenue being "dramatically affected" by the coronavirus. That month, Sweetgreen laid off about 10% of workers at its headquarters and furloughed nearly 2,000 store employees after deciding to return a $10 million PPP loan.
"As soon as we found out that they had run out of money, we decided to give it back, which we think was the right thing to do," Neman said.
Now 75% of the furloughed workers have been brought back and Sweetgreen has reopened all but 11 of locations. All dining rooms in California remain closed though some locations with outdoor seating can accommodate diners. Headquarters is officially open, though it is mostly empty as the company is not requiring anyone to come in for the foreseeable future. Despite some permitting delays because of COVID, Sweetgreen is planning to open 20 new locations this year and considerably more next year. And in late April, it introduced its first new major menu category since adding bowls four years ago – nine different plates, ranging from Hot Honey Chicken to Shroomy Asada, designed to increase dinnertime sales. On Wednesday, Sweetgreen will hold its first-ever $5 Greens Day where it will offer select bowls and salads for well under half the normal price.
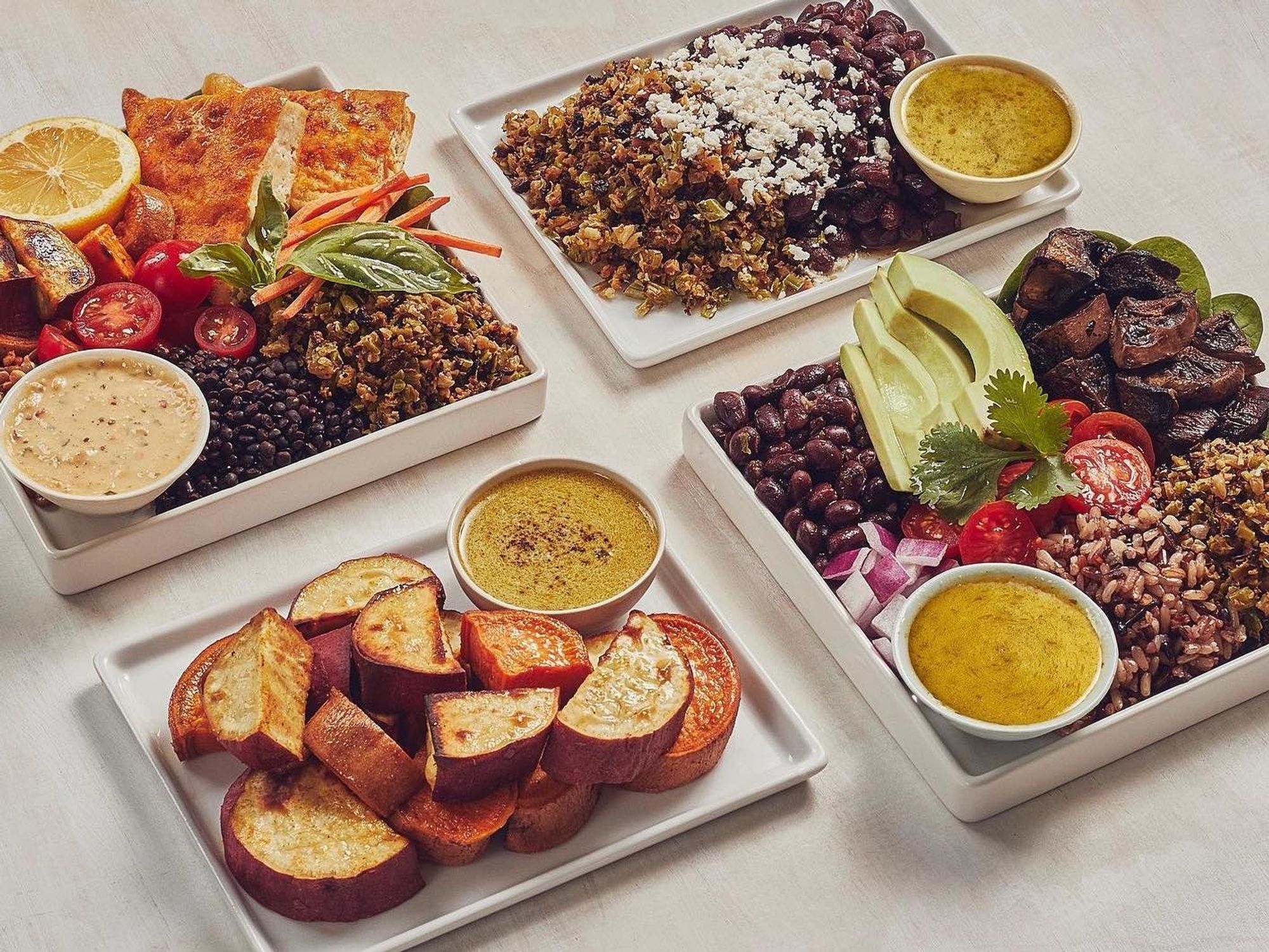

dot.LA spoke to Neman about how the company is adapting to the COVID era, why he ended an exclusive partnership with UberEats, and when Sweetgreen might IPO.
A lot of your business has been centered around offices. How are you adjusting since people aren't coming into offices?
To your point, we have a very high penetration in some urban areas and those are the ones that have been more severely impacted. Our restaurants that are more suburban-based are actually doing really well. Many of them have fully recovered to pre-COVID levels through just delivery and pickup. So really the impacts we're seeing are primarily only from the true demographic shifts rather than from changing consumer behaviors.

Jonathan Neman hatched the concept of with classmates Nicholas Jammet and Nathaniel Ru in a dorm room during their senior year at Georgetown University.
Does COVID change where you anticipate opening stores in the next few years?
Yeah, a little bit. We were already on a path of expanding beyond our current markets. This year, we have already opened in Denver and Miami and we're opening in Austin. And so we already penetrated a lot of the larger cities, and we're on our way to going into other markets that are more suburban. If you look at the makeup of the United States it's much more suburban than urban. So there was a lot more suburban growth coming, but I think this has accelerated a lot of that as our suburban model has done better. But we have not given up on the cities. We're going to continue to open in New York. We are very confident people will come back to work, although it may be different and we'll be well positioned for it.
Now that we're in a recession do you worry that people will see your menus and think of it as an indulgence to spend $14 on a salad?
Our prices are different by market. Definitely very top of mind for us is affordability. We like to balance all stakeholders when we think about price. So you have to think about how we pay our team members and our farmers.
This is why food is really complicated. I could charge less, and then pay my team members less and pay my farmers less and then I'd get heat for that as well. But having said that, I do think that Sweetgreen will do more over time to address different consumers and price sensitivity. Over time we will think about different menu items and formats and ways to make it more affordable. One way is when you think about our plates, $12 for lunch may be expensive but $12 for dinner is actually pretty affordable. Another way we do this is through things like Outpost [a central drop off shelf in buildings where Sweetgreen couriers drop off orders.] You're not paying the delivery service fee that you would for a lot of other places.
You had signed an exclusive deal with Uber Eats last year and then canceled it. What was the decision behind that?
We have a great relationship with Uber but I think we've realized over time that different consumers use different platforms and they're more incremental to each other than they are cannibalistic. Especially in a post-COVID world where delivery will be a bigger piece of the pie, we wanted to get in front of as many consumers as possible. We also are very focused on our native delivery which is which is by far our biggest delivery channel,
I'm curious how you think about delivery. Because for a lot of restaurants they're sacrificing huge margins...
Correct. Not only are they sacrificing huge margins, but they don't have a direct relationship with their consumers. We have a direct relationship where we can tell you when new menu items come out and we can personalize the experience to you.
So why not just have it all be native?
I think there's certain customers where the marketplace becomes a great place of discovery, it becomes, you know, almost like a customer acquisition marketing tool for us a way to amplify our message and reach more people.
Have you ever thought about doing brunch or breakfast?
We definitely have. Sweetgreen is an ethos, which is connecting people to real foods. Eventually we'd like to take that ethos and expand way beyond salad, bowls and plates, whether it be brunch or otherwise. The vision is to go much, much broader.
That's a perfect segue to my last question. What's your current thinking on a possible IPO?
There's no current thinking right now. We're just very focused on expanding the brand, delivering a great product to consumers and strengthening the business. Sure, one day, but not not anytime soon.
- sweetgreen - dot.LA ›
- Sweetgreen Reopens Stores and Brings Back Workers - dot.LA ›
- Sweetgreen Lays Off 10% of Staff at Its L.A. Headquarters - dot.LA ›
- Sweetgreen Files for an IPO - dot.LA ›
- Sweetgreen CEO Deletes Vaccine Hot Take After Backlash - dot.LA ›
- Sweetgreen's IPO Filing Reveals Recent Revenue Gains - dot.LA ›
- Sweetgreen Offers New Salad Discount Subscription - dot.LA ›
- Sweetgreen’s Jonathan Neman on How Tech Changed Restaurants - dot.LA ›
- Sweetgreen Launches New $10 Monthly Loyalty Program - dot.LA ›
Ben Bergman is the newsroom's senior finance reporter. Previously he was a senior business reporter and host at KPCC, a senior producer at Gimlet Media, a producer at NPR's Morning Edition, and produced two investigative documentaries for KCET. He has been a frequent on-air contributor to business coverage on NPR and Marketplace and has written for The New York Times and Columbia Journalism Review. Ben was a 2017-2018 Knight-Bagehot Fellow in Economic and Business Journalism at Columbia Business School. In his free time, he enjoys skiing, playing poker, and cheering on The Seattle Seahawks.



 Match Group and Tinder CEO Spencer Rascoff
Match Group and Tinder CEO Spencer Rascoff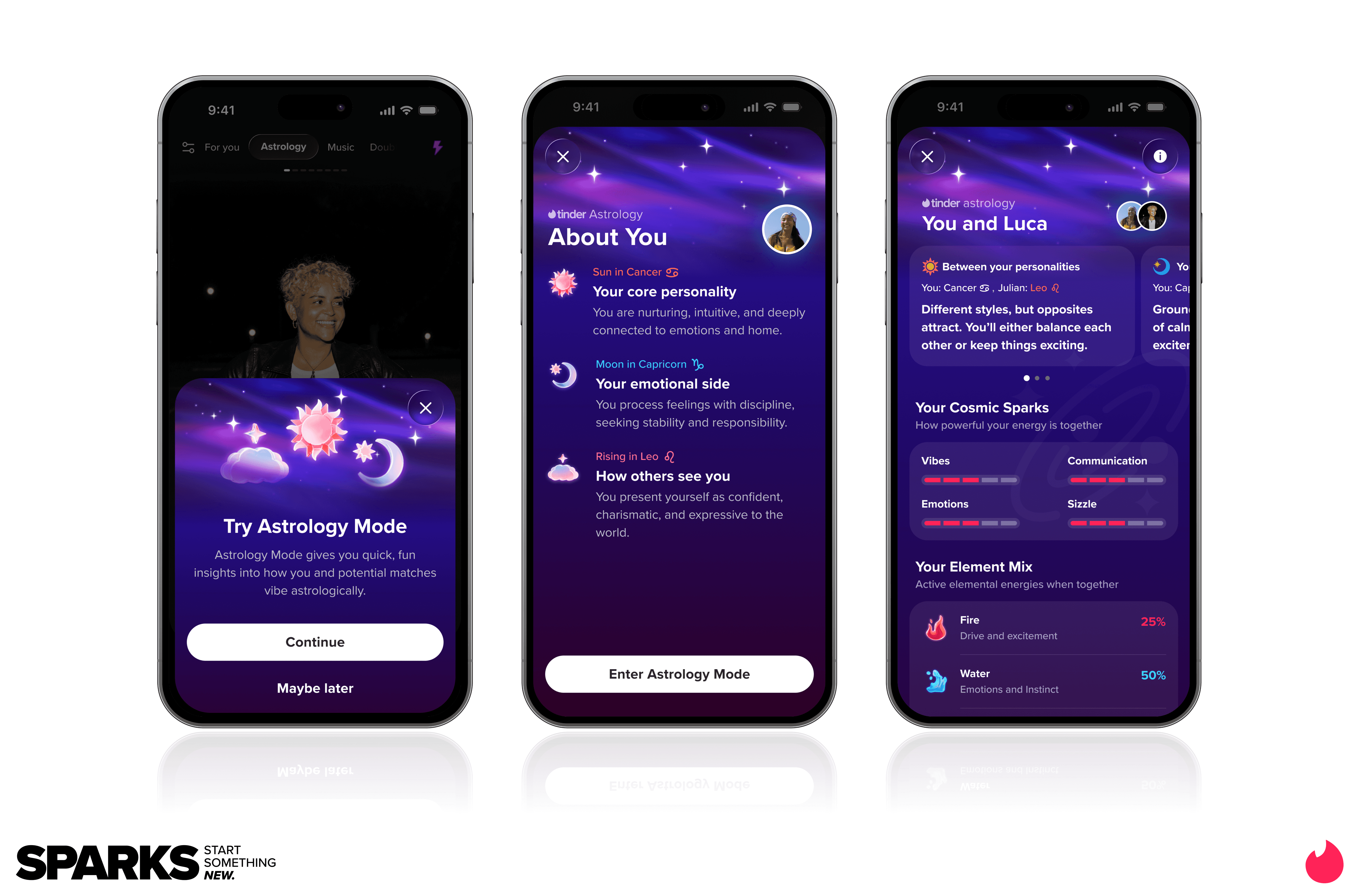 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder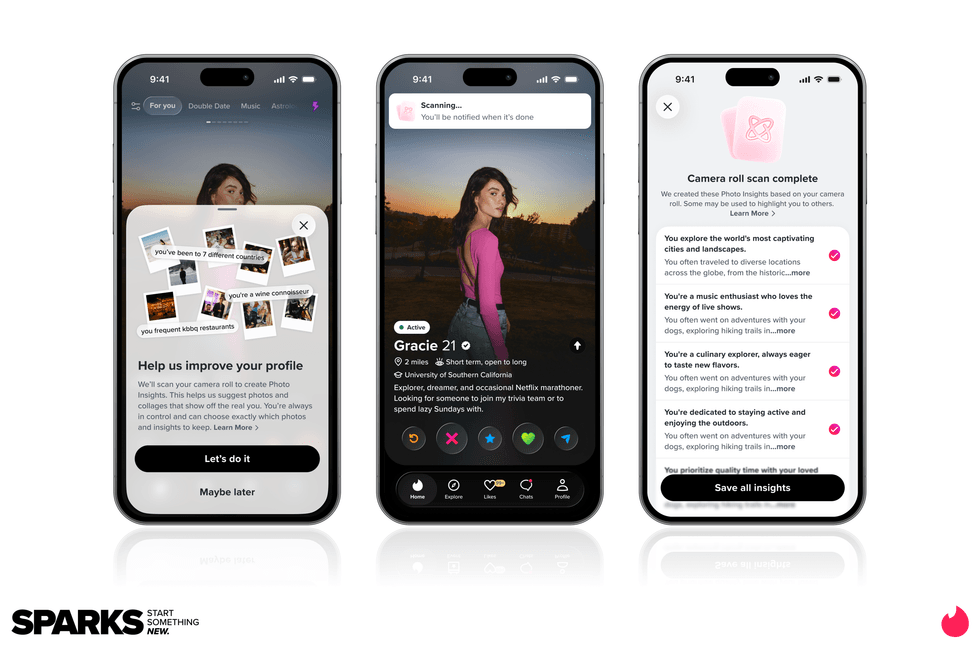 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder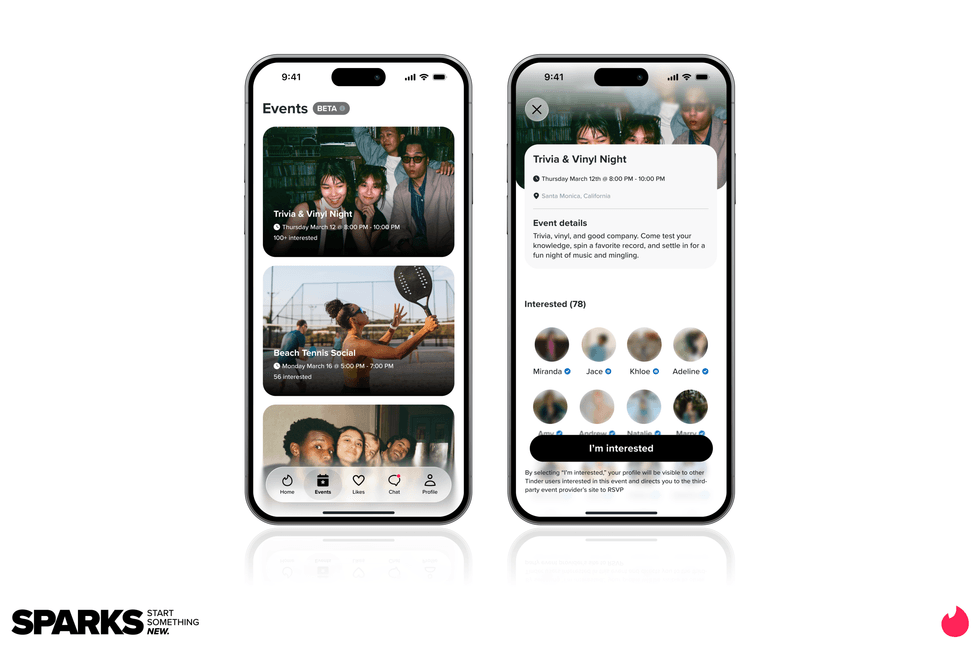 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder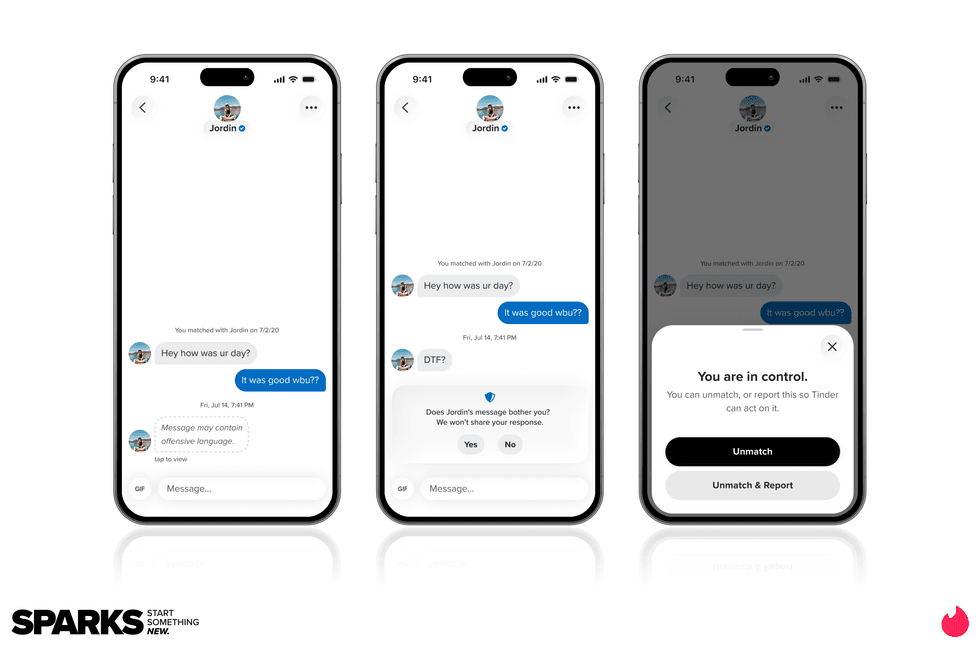 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder

 Image Source: Revel
Image Source: Revel