Ambercycle’s CEO on Why Traditional Recycling Won’t Work, and What His Technology Does Instead
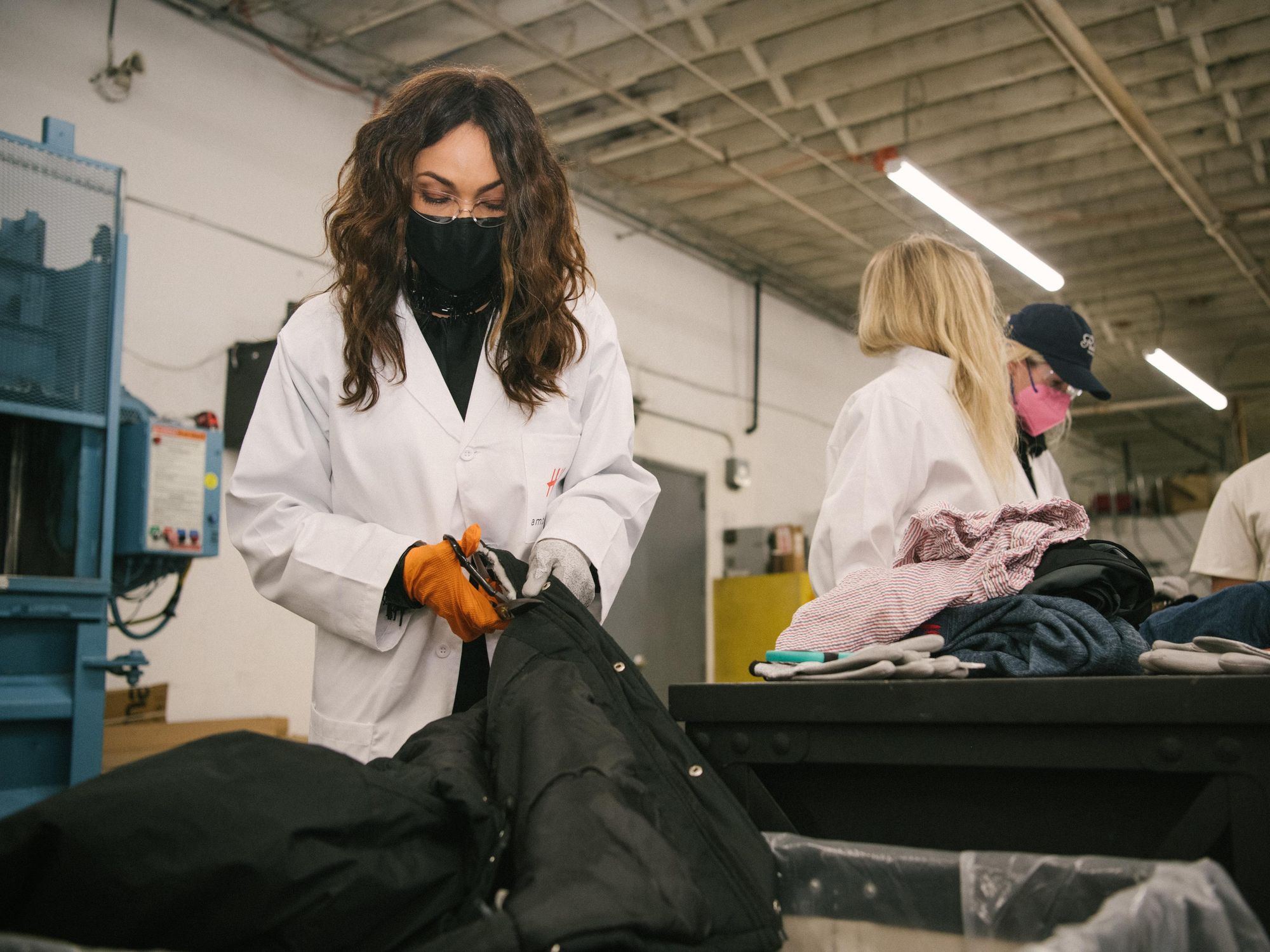

Few industries are as tangled with buzzwords as the fashion industry. Clothing brands, rightly concerned about their tremendous effects on the environment, are eager to call their collections “green” or “sustainable.” But making tangible changes in how clothing is produced and distributed has been a struggle.
On Tuesday, L.A.-based startup Ambercycle announced it raised a $21.6 million Series A round to try to tackle the problem. The funding comes from fashion heavyweights including H&M (which has used its technology in recent collections) and online fashion and shoe retailer Zalando, among others. It will go to ramping up production of the company’s fiber regenerative technology, which it created and piloted in a manufacturing plant downtown.
Ambercycle co-founders Shay Sethi and Moby Ahmed are scientists and former UC Davis college roommates. The two see themselves as different from traditional fashion or manufacturing founders – and other research-based innovators.
“Traditionally, people have always thought, ‘here's an interesting technology, how do we craft a story around it?’” Instead, Sethi says, Ambercycle “start[s] with the products that we would really like to see and then work backwards into the technology. We develop, do research and engineering that way instead of starting in the lab.”

Ambercycle CEO and co-founder Shay Sethi
Their technology is able to break down the components of clothing to its basic polyester materials, separating its natural fibers and dyes, and creating a new material in the process, which they call cycora.
“We imagined a technology that could take an old t-shirt and turn it back into the yarns required to make that green t-shirt again,” he adds. “Anything that's in your closet today – like yoga pants or dress shirts – that's traditionally made of polyester can be made with cycora.”
Sethi and Ahmed started their company in San Francisco in 2015, then moved it to Los Angeles’ garment district two years later, looking for a manufacturing hub close to a center of innovation.
“We felt like this is a really good nexus for innovation, fashion – as well as material sciences,” Sethi says. “There is a very strong industry and a very strong familiarity with manufacturing so we felt it was a perfect blend. Also we grew up in California and didn't want to leave.”
We chatted with Ambercycle co-founder Shay Sethi about his company’s journey, its new funding and how it plans to get beyond buzzwords in planning a sustainable future for fashion.
What are the biggest challenges to the fashion industry?
When we consider the future of humanity, there's a couple key things that need to change. The big one is – given that consumption will not decrease – the reliance on natural resources will put a strain on the way in which we can live on this planet. So in order to change that, we need to take advantage of these traditionally viewed as waste streams and turn them back into new resources. So the future upstream will be all of these textile materials that are in our closet. But it's not really easy today to throw away or recycle our old garments.
We need to be able to have a low-friction way to throw away our garments and have them go back into a circular system. If we can tell a transparent and traceable story to a person, then brands and retailers will start to care.
Why is it so hard to recycle clothing currently?
So let's talk about our clothing. They are mixtures of different fibers – polyester and cotton, as well as dyes, additives, zippers, tags and stains – when they're at their end of life. We can't really recycle those materials, because they're these complex, intimate blends. Recycling has really struggled as a business, and also as a solution to waste, because you can't create a high quality product from those materials once they are at their end of life.
How is Ambercycle different from other recycling processes?
Most recycling processes are shredding or very simple mechanical processes. You can turn a t-shirt into pillow stuffing in a similar way that you can turn paper into a sort of grey newspaper and then downcycle it; The same thing happens with textiles.
The Holy Grail is really being able to turn an old t-shirt into a new t-shirt. So over the past five years, we’ve developed technology that takes these mixtures of materials that have dyes and additives, put them through a process, and make the base raw materials needed to make those same yarns. This goes in line with what's traditionally known today as circular economy where you can reuse materials, again and again.
Will Ambercycle always be focused on apparel?
Right now our focus is on apparel.
We have a couple of luxury clients that are really interested in transitioning to circular systems. Over the next couple of years, we're going to be able to talk about those, but the major message we want to help shed light on is that every year, over 120 billion garments go to landfill. We need to, as a fashion industry, transition to a circular system. It's [not] just one or two companies that can do things; Everyone as a whole needs to adopt a new ecosystem, where things are being reused in supply chains over and over again. It's very important for this transition to involve all verticals in the power supply chain. The demand for these materials is already so high. So people already care. I think we're just trying to figure out the logistics of the society right now.
There's a lot of possibilities when you think about it. You can imagine this being transformed into a system that can take other materials as well. I think we're excited about the possibilities in the future but I’m really focused on the textile-to-textile stories today.
What do you plan to do with your recent funding?
We’re trying to scale up the number of projects we're doing with different companies across the apparel industry that will require a lot of manpower or womanpower. That's a key gap we need to fill. A technology like ours that uses sort of molecular separation technologies, that advanced material science requires a sort of scale before you can really start to see the fulfillment of these contracts.
It's very easy to make a couple of t-shirts, but it's very hard to make millions and millions and millions of kilograms of stuff. We're going to be scaling up production of one of our main materials today, cycora. Demands are already way through the roof. I felt like right now was the right time to raise external capital to accelerate that plan.
This interview was edited for clarity and brevity.
- Ambercycle Uses QR Codes to Tells Clothes' Stories - dot.LA ›
- Ambercycle Recycles Polyester Clothes - dot.LA ›
- MarqVision Raises $20M to Stop Online Counterfeiters - dot.LA ›



 Image Source: Revel
Image Source: Revel