We’re Talking About Self-Driving Cars the Wrong Way
David Shultz reports on clean technology and electric vehicles, among other industries, for dot.LA. His writing has appeared in The Atlantic, Outside, Nautilus and many other publications.

In 2013, one of my first assignments in graduate school was to read an article in The New Yorker about Google’s new autonomous car. Back then it sounded like autonomous vehicle (AV) technology was just around the corner—that we stood on the precipice of some new golden era in transportation where cars would form fuel-efficient caravans on highways and parents could send those cars to pick the kids up at school without having to leave the office early. People with disabilities would have access to new levels of personal freedom. Traffic accidents would be a thing of the past.
Now, a full decade later, exactly none of those things have come to pass, and in the process autonomous vehicles have become emblematic of the tech companies’ tendency to over-promise and under-deliver. “Self-driving cars have been one year away for ten years,” the joke goes.
And no company has felt this scorn more directly than Tesla. The electric vehicle giant has endured a series of high profile missteps related to its autonomous technology, and CEO Elon Musk has been extremely incorrect about the timeline for its implementation. Last week Tesla announced a recall of 363,000 vehicles due to issues with its full self-driving software, which, despite its name, does not even offer full self-driving.
This is all to say that it was not without some trepidation that I decided to accept an invitation earlier this month to a ride in Waymo’s autonomous vehicle. Waymo began as the “Google Self-Driving Car Project” in 2009–four years before I’d read the New Yorker Story. The company changed its name and became a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc (Google’s parent company) in December 2016. Waymo is headquartered in Mountain View, CA, which would ordinarily put it outside the watchful purview of dot.LA, but the self-driving start up is setting up shop in Santa Monica.
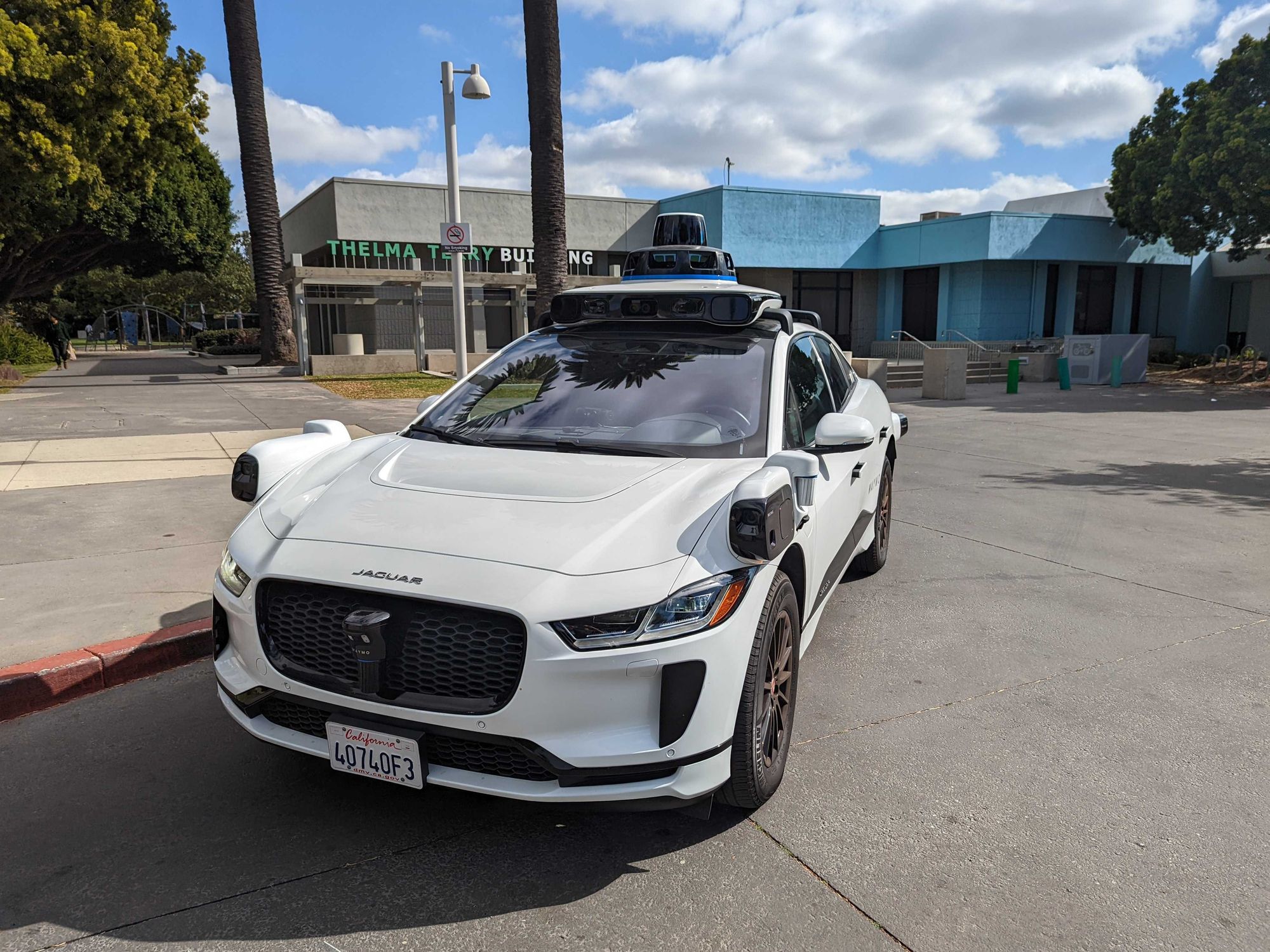
I meet Waymo Communications Manager Sandy Karp and product manager Vishay Nihalani a few miles from the Pacific Ocean at Virginia Avenue Park around 10am. They’re standing outside a white Jaguar E-PACE equipped with an ostentatious array of cameras, lidars, and radars. Our plan is to have the car drive us to a donut shop on Wilshire Blvd, get a donut, rendez-vous with the car again, and instruct it to chauffeur us back to the park.
The trip begins with the press of a button on a touch screen on the back of the center console. The elephant in the room (or in this case the car), is that there’s actually a person in the driver’s seat. Lindsay Alara, an Autonomous Specialist for Waymo, keeps her fingertips lightly in contact with the steering wheel and her feet waiting near the pedals just in case the vehicle does something it shouldn’t.
In Arizona, Waymo has been running its fully autonomous ride hailing operation with no human present in the car since as early as 2020. But California’s stricter regulatory environment means that her job is safe here, for now.. Waymo is applying for the necessary permits to move the system to fully autonomous, but the process is likely to take months, says Nihalani. The company is spending that time training and validating its AI in new neighborhoods.
“We've expanded in the cities that we're operating in,” says Nihalani. “In San Francisco we’re driving 24/7; in downtown Phoenix we’re driving 24/7. We're driving an increasing set of road speeds, weather conditions, so on and so forth,” says Nihalani. With its primary education complete in Arizona, Nihalani says the AI is picking up the subtleties driving in Los Angeles and San Francisco quite quickly. “That’s something that we're really excited by, I think it’s what's enabling an acceleration of momentum, which may have been different than what we've seen in the past few years.”
Waymo’s city-by-city, street-by-street approach to autonomous driving illuminates a paradigm shift in the way we need to think about the technology, says, Alex Bayen, a transportation and systems engineer at Berkeley. Autonomous driving will probably never be something that’s “solved” all at once, but rather something that develops over time. “I think the right way to look at things is that every year there are more and more use cases where an increased level of automation has become a reality,” says Bayen. “Every company which is trying to grab some real estate in this new technological world, what they're doing is they're trying new use cases. Autonomous vehicles are not going to go everywhere initially, and they are not going to be there all the time. They are only going to operate in specific conditions.”
As that envelope of use cases pushes outward, Bayen and other researchers say now is the time to talk about how autonomous vehicles should be regulated. As easy as it is to imagine the benefits of driverless cars, it’s equally easy to imagine the potential for pitfalls.
Ride sharing services, in general, have been shown to increase traffic and congestion in cities. So the potential for fleets of unoccupied “ghost cars” to exacerbate Los Angeles’ already abhorrent traffic conditions should be a real concern for policy makers today. Likewise, for private owners, it may prove cheaper to send a vehicle back home during the work day rather than pay for parking at the office. Or the convenience of autonomous vehicles may make it tempting for parents to use one to chauffeur their kids to school rather than have them take the bus. All of these scenarios would worsen traffic and increase emissions–even if the cars are electric. In one study, researchers at the University of Washington found that AVs could either cut our greenhouse gas emissions roughly in half or double them, depending on how the technology is implemented.
“There's a potential for real net positive, if we get leaders in the public sector and the private sector to work together to ameliorate some of those known problems that we suspect will happen,” says Ben Clark, a professor of public administration planning, public policy and management at the University of Oregon. “We don't want to be in the same position as we were when Uber came to town and we were very reactive.”
According to Clark, state governments should be thinking about how to tax or charge for miles driven by unoccupied vehicles and how to incentivize sharing individual vehicles between multiple people, families, or groups. As the use case envelope for autonomous vehicles expands, the model for car ownership may have to change in order for us to actually reap the benefits. The never ending delays to autonomous vehicles may be frustrating or amusing to consumers, but they also should be giving policy makers ample time to see these issues coming. “It's actually an invitation to elected officials to look at this and figure out how to not have a jungle, but how to have a well organized garden where things work properly,” says Bayen.
On our donut run, the vehicle moves cautiously and smoothly; it navigates streets lined with parked cars and turns with poor visibility. It identifies and avoids construction cones. It deftly changes lanes and passes unloading trucks.
Riding in an autonomous vehicle invites you to see the streets with fresh eyes, and suddenly it becomes easy to see why the technology has taken so much longer to arrive than we might’ve expected. Our roads are littered with “edge-case” obstacles. Other drivers don’t always follow the exact rule of law; people go out of turn at 4-way stops; cyclists filter through traffic at red lights, pedestrians jaywalk; emergency vehicles trump all the rules. “The California Stop is a real thing,” jokes Nihalani.
Still, none of that explains one strange moment as we cross over the 10 freeway where the car begins to slow down as we approach a greenlight even though there’s no obvious sign of danger or obstacle in our path. I instinctively look over my shoulder to see if someone is going to rear end us, but the moment passes quickly and the car–for whatever reason–decides the way forward is safe once more. While Alara never has to intervene, it’s a small reminder that the technology is still on its way.
Are we there yet? We’ll get there when we get there.
- Motional Links With Uber to Make Robotaxis a Reality ›
- Autonomous Vehicle Companies Doubled Their Testing Miles In California Last Year ›
- Motional Will Double Its Staff As It Begins Testing Autonomous Vehicles in Santa Monica ›
- The Evolution of LA’s Robotaxi Industry: A Timeline ›
- 🚙 DotLA's Experience in Waymo's Self-Driving Car - dot.LA ›
David Shultz reports on clean technology and electric vehicles, among other industries, for dot.LA. His writing has appeared in The Atlantic, Outside, Nautilus and many other publications.



 Image Source: Revel
Image Source: Revel