Farm-to-Phone Apps Have Surged During the Pandemic. Will They Stay Once It's Safe to Return to the Grocery Store?
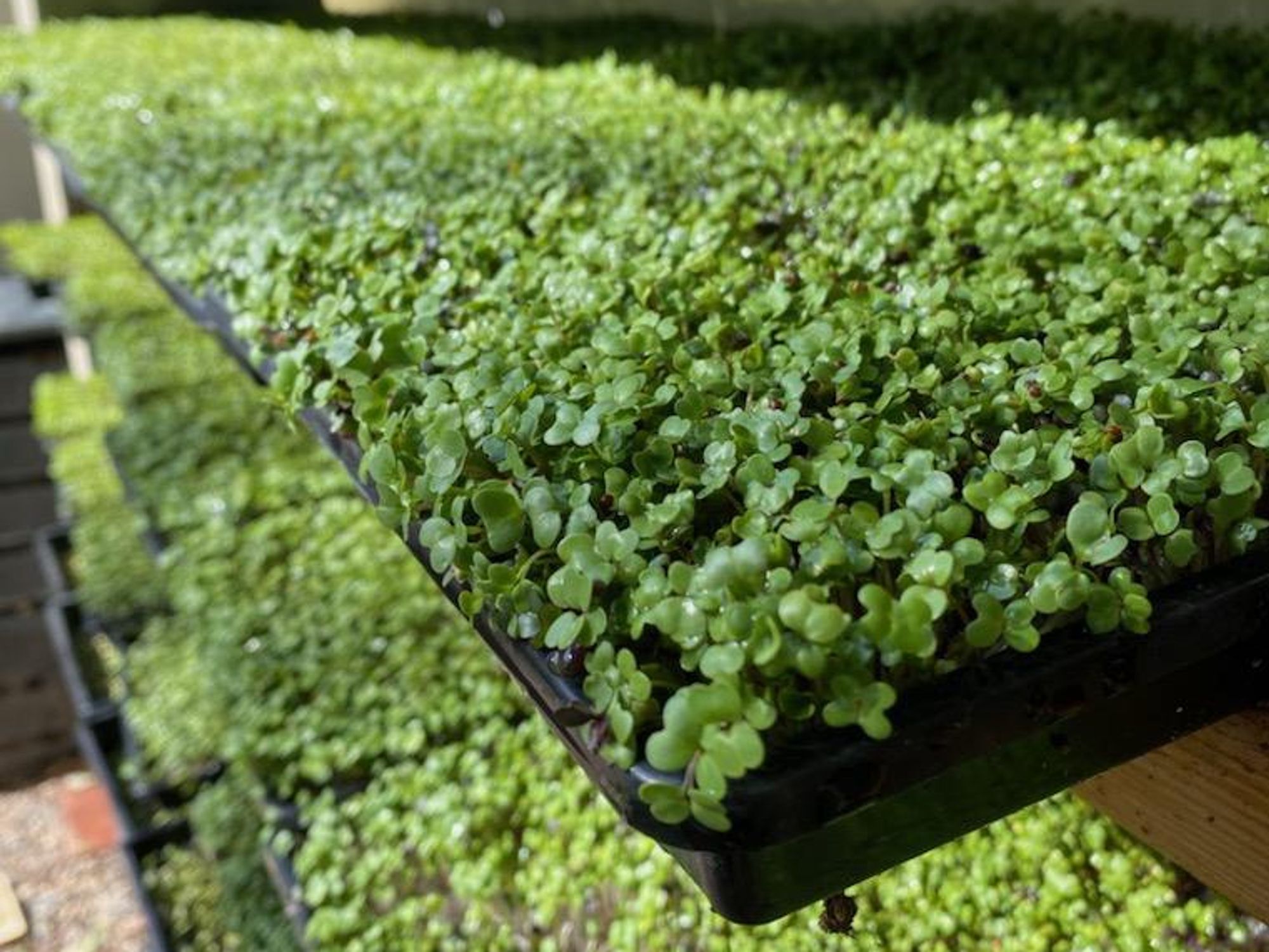

Sarah Hernandez is a full-time farmer, though she doesn't own a huge farm.
She grows microgreens, among other vegetables and herbs, in her yard in La Mirada. Microgreens, bite-sized version of larger veggies, don't require much space; Hernandez grows them vertically on 10x20 flats stacked on wooden shelves. She visits four farmers markets each week, then delivers microgreen boxes straight to customers who find her on CropSwap.
The app offers a farm-to-phone marketplace, connecting consumers directly to farmers. It's one of several services that have taken hold during the pandemic, allowing consumers who would otherwise go to farmers markets or grocery stores to get fresh produce or other goods delivered. CropSwap is also making it easier for some home-based growers to tap into the gig economy and sell within their communities.
CEO Rob Reiner co-founded the app with Daniel McCollister. The way Reiner tells it, they seem like an unlikely pair. Reiner grew up in Houston, studied computer science, and moved to NYC with the dream of being a Wall Street broker. There, he worked in software startups, but didn't find himself attached to a project that felt like a challenge.
Then he met McCollister in 2017, who invited him to see his gardens in Woodland Hills filled with an array of produce — kale, Brussels sprouts, onions, garlic, beans, tomatoes and more.
"I had believed you needed 100 acres to grow food, and here was Dan, showing me one acre that was growing more food than an entire neighborhood could consume," Reiner said.
McCollister wanted an easy way to sell or donate his food to his community — like a Craigslist or Offer Up for produce — so that's what the pair built. Their first version of CropSwap launched in 2017 and saw some 7,500 people selling or bartering various produce in the L.A. area alone. Got an orange tree? Put the fruit on CropSwap.
But Reiner found early on that users would often buy a bunch of oranges one week, but the next week, they'd go back to Whole Foods.
"There wasn't an understanding that the farmer was there to stay and could continually give you that produce," he said.
To attract both consistent consumers and — also key — investors, Reiner pivoted the app. Its goal became to teach people used to visiting chain grocery stores about local food systems and how to tap into them. He scaled back the bartering component of the app, though users can still trade messages with farmers.
"I could have a million users on CropSwap, but if I'm not attacking the WalMart consumer and the WalMart consumer is still buying [Walmart's] produce, then I haven't done my job," he said.
In 2019, CropSwap started offering curated boxes of seasonal, local produce that customers could receive right after it was harvested. Reiner described it as a hybrid consumer-supported agriculture ( CSA) box. Customers can subscribe to them or get a one-off. All farmers have to do is curate the boxes, put them on the app, and fulfill sales.
"We give farmers the tool to create their own delivery options," Reiner said. "They can do it all themselves and sell direct to consumers."
Customers who download the app can browse what's available in their area for either pickup or delivery. Farmers drop pins to indicate five-mile radiuses where they deliver, usually on specific days of the week.
One might be inclined to think that farmers markets would be CropSwap's biggest competitor, but Reiner said it's actually other apps such as Barn2Door and subscription services like San Francisco-based Imperfect Produce or Sacramento-based Farm Fresh to You.
Unlike those services, which use third-parties to box and handle deliveries, CropSwap farmers box their own food and the same farmhands who picked the produce are often the ones who deliver it.
In Los Angeles, the largest farm on the app is Sow a Heart, which also owns Sage Plant-Based Bistro with locations throughout the county. On CropSwap, they offer a Family Harvest box jammed with produce for $55, including delivery fees. By comparison, a Whole Foods cart on Amazon Prime that contains roughly the same items comes out to about $85, not including tip.
CropSwap does not charge sellers to be on the platform as others, including Seattle-based Barn2Door, do. Instead, it takes 8% of sales — in line with what a farmers market might charge — once a seller reaches 50 subscribers. Reiner said they're able to keep consumer costs low because they're not spending money on storage facilities, branding, marketing or transit.
From Consumer to Micro-Farmer
Hernandez had been following CropSwap on social media because she was interested in potentially trading her seeds for other produce. About six months ago, CropSwap reached out to ask her if she'd like to sell on the app. So far, she said "a good amount" of people have tried her variety microgreens box and she's gotten a lot of useful feedback. She currently has about 10 regular subscribers, a number that fluctuates with customer needs. Some are weekly buyers, while some purchase every other week. Hernandez said CropSwap is the most direct farmer-to-consumer experience she's had apart from the actual farmers market.
"I make the deliveries myself every week. My boyfriend helps me out, but it's just us two," she said "I'm growing it, we're cutting it, packaging it, and we're delivering it."
Through the app, she can tell her customers if she needs to change delivery dates to accommodate her market schedule or travel plans. Customers can also ask her questions, just like they would at the farmers market. If she gets more subscribers, she has space to add another set of shelves and she'd be able to hire an employee to help package and deliver produce.
There are other small vendors, too, like a beekeeper in West L.A. who sells honey flights, a jam maker in East Hollywood, and more home microgreen growers like Hernandez. Reiner said there are about 250 subscribers in L.A. Some get just one box, but some larger vegetarian or vegan families may purchase up to five.
The direct-to-consumer approach has served as a boon for some farmers during the pandemic. In Richmond, Virginia, Three Fox Farms' founder Alex King told RVA Magazine he didn't know what to do with his crops after restaurants and farmers markets closed at the onset of the pandemic. King ultimately partnered with Leafy Lanes Urban Farms to offer a box of assorted fresh vegetables, which they sold on CropSwap. They were so successful, the farmers said, they had one of their strongest seasons and King was able to invest in new hoop houses and a walk-in cooler.
Hernandez also had a good year saleswise. She said she found her customers wanted to eat healthier and appreciated the contact-free delivery experience CropSwap could provide.
Beyond the Pandemic
Reiner doesn't think pandemic subscriptions are a fluke, though he has had investors who question that. Still, he's betting the quality of fresh, local produce delivered straight to consumers will "ruin" them for inferior fruits and vegetables that have to be stored in a warehouse. Plus, he said, some CropSwap growers offer products that are hard to get in stores. For example, a farmer who specializes in iron-rich kale for vegan bodybuilders.
In its next iteration, Reiner plans to partner with chefs to make the boxes more of an experience by offering recipes and cook-alongs. CropSwap is also working on a partnership with Nourish LA to offer customers the ability to donate boxes to other families. Reiner also envisions a tracking system that lets customers know how their purchases will impact their health, environment, and communities and a future where CropSwap could make suggestions to make its customers healthier.
"Imagine if we knew your intake because of the product you were consuming," he said. "If I knew, for example, that you were low on iron, I could start suggesting boxes that might increase your iron."
CropSwap has also partnered with Jamiah Hargins' Crop Swap LA, founded in 2018 to allow Angelenos to share produce. Crop Swap LA is building new neighborhood gardens in West Adams. The produce they yield will be available on the CropSwap app, and neighbors will receive a code to become the urban farms' first subscribers.
"People are going to start seeing how much food can come from local gardens. And that's going to start deteriorating the mindset that you need so much land to grow food," Reiner said. "I would love it if kids could get involved in this and tell their parents I'm going to turn my whole backyard into selling food for my neighbors."
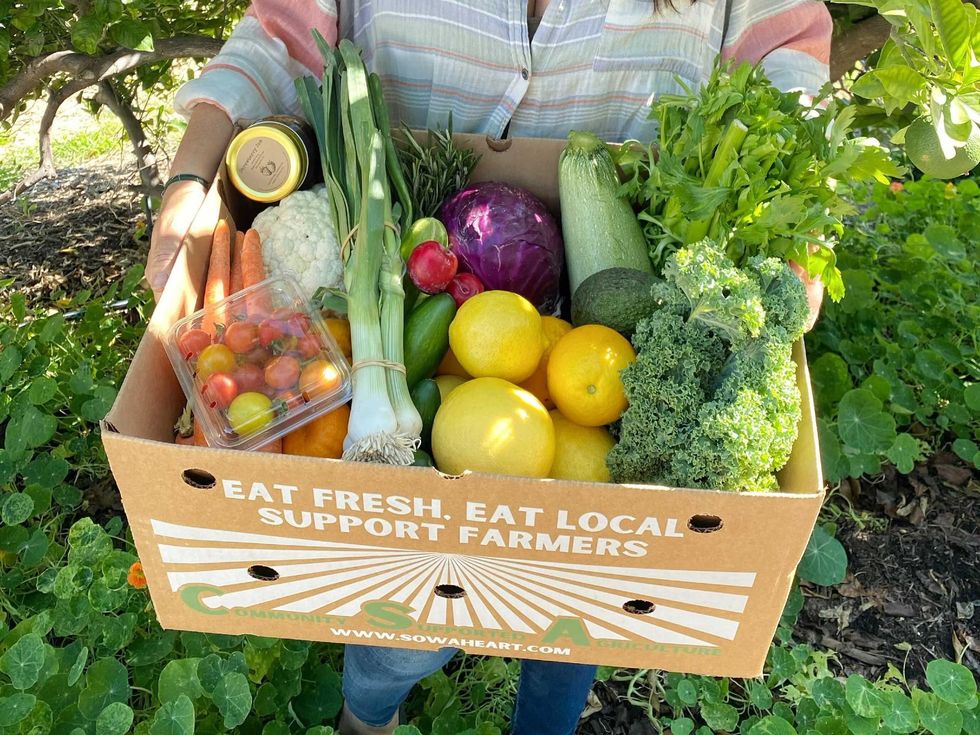




 Image Source: Northwood Space
Image Source: Northwood Space

 Image Source: JetZero
Image Source: JetZero