Is a Commercial Space Station Possible? These Startups Are Racing To Be the First to Try It
Samson Amore is a reporter for dot.LA. He holds a degree in journalism from Emerson College. Send tips or pitches to samsonamore@dot.la and find him on Twitter @Samsonamore.
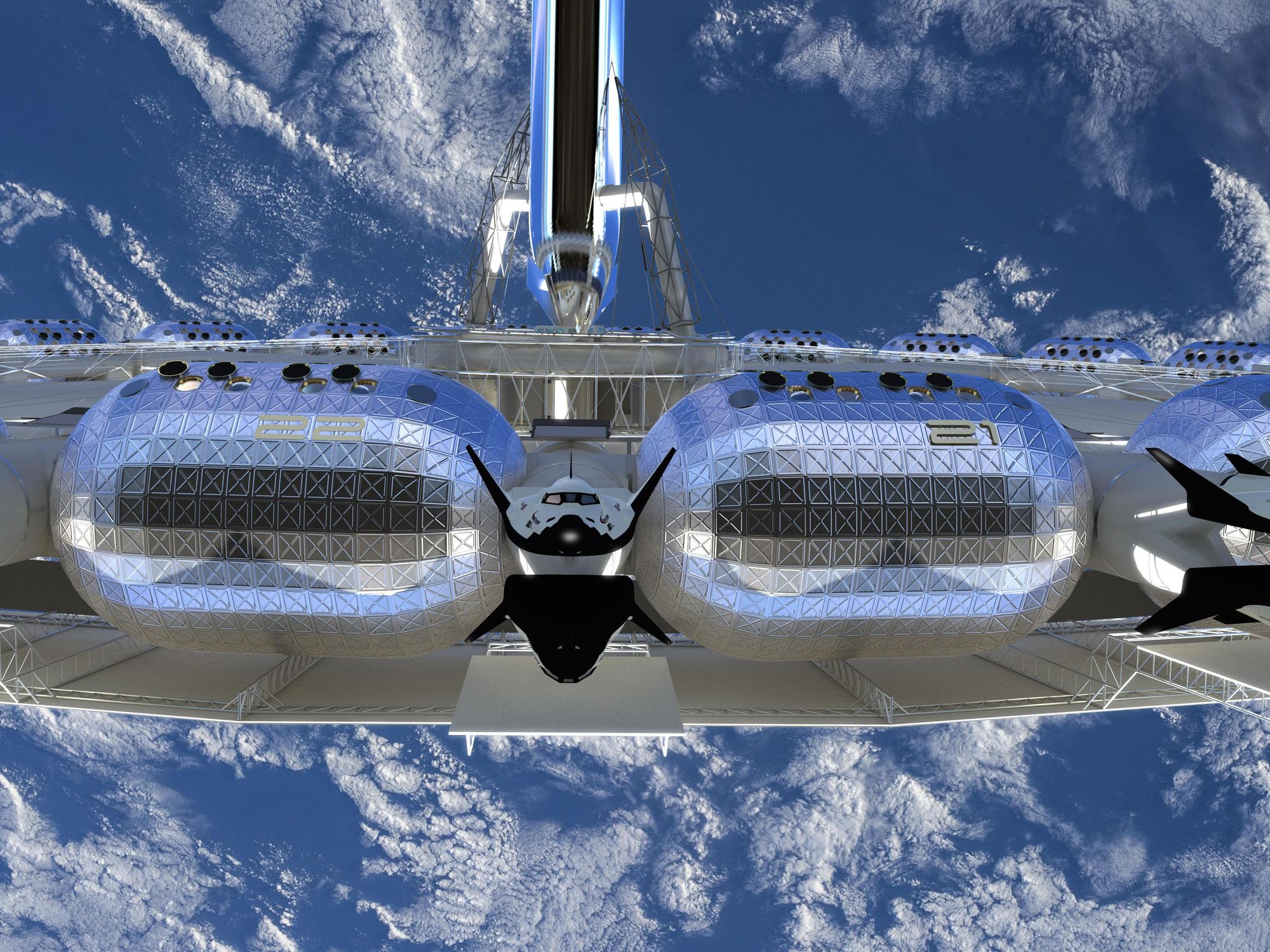

No longer content with terrestrial life, a new cohort of CEOs in Los Angeles have turned their focus to the stars, with the ambitious goal of launching space stations that could host tourists alongside astronauts and researchers.
“I've always thought it was really important that people move off the planet and out into the solar system,” Vast Space CEO and founder Jed McCaleb told dot.LA. “There's just way more resources and energy available up there. And also it provides a frontier, and I think that’s important for our collective psyche.”
McCaleb, a billionaire thanks to his prior ventures co-founding cryptocurrencies Ripple and Stellar Lumens, launched Vast Space last year, with the belief that it can be the first company to create a space station for commercial customers that simulates gravity in space.
Why artificial gravity? For starters, the negative health effects zero gravity can have on spacefarers are myriad, including muscle shrinkage, cardiovascular deconditioning and blood loss. Not to mention, simulated gravity in space could ease the transition to low Earth orbit for consumers; allowing them to experience the cool, floaty part of zero G while eliminating the need for full astronaut training.
But Vast is hardly the only company eyeing space tourism. Another is Fontana-based Orbital Assembly, which plans to create luxury hotels in space. According to Chief Operating Officer Tim Alatorre, Orbital Assembly is gearing up for its first launch, which will carry a small portion of Orbital’s first Pioneer space station for research use by 2025. Alatorre told dot.LA “once we've proved that the station is safe, then at that point, we will bring tourists on.”
Alatorre likened the quest to become a space hotelier to the expansion of the American railroads, when transport companies opened up hotels to encourage travel.
“That's why we're focusing on [tourism], because we see that as a step to that larger vision of having thousands of people really living in space, whether it's in [low Earth orbit] or the moon, or Mars,” he added.
Each company plans to rotate parts of the space station to replicate gravity. Basically, spinning the station’s mechanics in opposite directions (roughly one revolution every minute and a half) creates enough centrifugal force to allow the station to remain facing the sun and mimics gravity.
According to McCaleb, Vast plans to have artificial gravity in parts of the station where people eat, bathe, work and sleep, but a central area where passengers can indulge in the zero-gravity experience temporarily. The El Segundo-based company’s plan is to assemble everything on the ground, prior to launch, since in-space construction is still in its infancy. Once there’s more of a demand for in-space construction, McCaleb said other companies could contract Vast to build and launch facilities for them.
“What we're building is an orbital machine shop, essentially, where you can design your thing on the ground, ship it up to the station, like an IKEA-style thing where we can snap it together for you,” McCaleb explained.
McCaleb said he is his company’s sole funder. He wouldn’t tell dot.LA how much he’s invested into Vast, or how much he expects the endeavor to cost. That said, for comparison rival company Orbital Assembly’s CEO Rhonda Stevenson told dot.LA last June the company at the time estimated it would need $200 million to launch by 2023.
McCaleb said he was aware of Orbital Assembly and “a handful” of other competing firms but claimed, “there’s no one else that’s actually trying to do it seriously.” He told dot.LA that initially, Vast won’t target a high-end consumer, but will focus on selling space station access to governments or private companies. Vast wouldn’t provide further details about a target launch date.
“We’re definitely not building some sort of luxury space hotel,” McCaleb claimed. “I think some of the first customers will hopefully be NASA and other national astronaut programs,” he added, hinting at partnerships with other governments.
Tarek Waked, an aerospace investor and founding partner at Type One Ventures, said he’s skeptical.
“Vast claims to be the first gravity-enabled station. I think they won’t be the first to [do] it,” he said, pointing to older companies like Gravitics and its competitor Axiom Space, which is based in Houston and debuted in 2016.
As things currently stand, however, Vast appears better-funded than Orbital Assembly. Orbital has only raised $2.4 million to date. But Alatorre said his company is in the process of raising another round, though he wouldn’t disclose details.
Neither space station project will be possible without launch partners, though. SpaceX’s upcoming Starship rocket and Boeing’s Starliner are two developing projects that could help Vast and Orbital launch both people and cargo to space.
“Elon [Musk] is talking about getting payloads to space for about one to $200 a kilogram, which would be game changing,” Alatorre said. “If we can get people to space for even a million dollars a seat that really starts to open up that market, and that's going to be really transformative.”
According to David Barnhart, director of USC’s Space Engineering Research Center, the real question is twofold.
“Can any of this be done at a cost level that allows a commercial company to make any profit, even if it's only billionaires that can do it?” He asked. And furthermore, once the technology is up and running, how many civilians will take the risk?
- 'Best Day Ever!': Jeff Bezos' 11-Minute Ride to Space - dot.LA ›
- Orbital Assembly's Quest to Build Hotels in Space - dot.LA ›
- US Space Force Establishes Tech And Acquisition Arm in LA - dot.LA ›
- Space Tech Trends to Watch in 2022 - dot.LA ›
- Los Angeles Space Tech News - dot.LA ›
- Apex Space Raises $7.5M to Manufacture Small Satellites - dot.LA ›
- Solar Storms Could Cost North America Up To $2.6 trillion. The JPL Is Trying To Predict When They Might Occur - dot.LA ›
Samson Amore is a reporter for dot.LA. He holds a degree in journalism from Emerson College. Send tips or pitches to samsonamore@dot.la and find him on Twitter @Samsonamore.



 Image Source: Revel
Image Source: Revel