How LA-Based Super Hi-Fi Hopes to Change Streaming Audio Using AI
Sam primarily covers entertainment and media for dot.LA. Previously he was Marjorie Deane Fellow at The Economist, where he wrote for the business and finance sections of the print edition. He has also worked at the XPRIZE Foundation, U.S. Government Accountability Office, KCRW, and MLB Advanced Media (now Disney Streaming Services). He holds an MBA from UCLA Anderson, an MPP from UCLA Luskin and a BA in History from University of Michigan. Email him at samblake@dot.LA and find him on Twitter @hisamblake

- Super Hi-Fi's AI transports the skills of a trained radio DJ to digital music playlists. Spotify's former head of research Tristan Jehan recently joined as an advisor
- Founded in 2018 by veterans of the digital music business, the company's customers include iHeartMedia, Sonos, Peloton and Octave Music Group
- Its leaders envision a new audio listening experience — where everyone has a personalized, curated playlist, with artful, AI-generated sequences and layers of music, voice clips (e.g. news and podcasts), and branded messaging that drives new revenues to the music industry
Before the beat from "Baby Got Back" that underpins Nicki Minaj's "Anaconda" fades to silence at the song's end, a sound clip pops up, right on rhythm and with a similar energy, telling the listener what streaming service they're listening to. A new track seamlessly takes the baton from the Minaj song before the brief branded message concludes, and continues the upbeat mood as a music bed for a rapid sequence of audio clips – first a voice imploring listeners to get hyped, then a word from Kanye about his interview with Beyoncé, a snippet from that interview, and another in-the-spirit advert – before blending into the intro of the next song, Kanye's "Stronger": all of it interwoven as if it were a single track produced in a recording studio.
It is the automation of this art, once the preserve of skilled radio DJs, that Super Hi-Fi is bringing to the digital music industry. In doing so, the L.A.-based company thinks it can help music services and artists make more money, and give listeners a new and improved way of experiencing audio.

Super Hi-Fi's customers include iHeartMedia,
Founded in 2018 by a group of digital music business veterans, with customers that include iHeartMedia and Sonos, SHF recently announced that Tristan Jehan – a pioneer of applying AI and machine learning to music, most recently as head of Spotify's research team – has joined the company as an advisor.
Streaming, which has been powered in part by Jehan's work on recommendation algorithms, may have saved the music industry from piracy-fueled devastation, but Super Hi-Fi's founders believe companies like Spotify, Apple and Amazon have missed the mark in some important ways.
"We think digital services forgot that the primary user interface is your eardrums, not your eyeballs," Zack Zalon, Super Hi-Fi's chief executive, told dot.LA.
As a result, a listener cannot readily distinguish one service from another, he said. Visual branding can help, but especially as smart speakers grow more popular, listeners will have an increasingly difficult time knowing whether they are tuned in to Spotify, Apple Music, Pandora or any other service.
Zalon and Brendon Cassidy, another co-founder and Super Hi-Fi's chief technology officer, both built digital radio services for CBS, AOL, Yahoo and Cricket Wireless. They contrast the uniformity of streaming services to broadcast radio stations. Two stations in the same city, focusing on the same type of music, still tend to have their own personality, they say.
"It's not just the music," Zalon said. "It's the space between the songs that the radio stations are filling and (thereby) connecting with listeners in an emotional way."
Beyond differentiating the source of the sound, SHF believes that using the space between songs — as radio stations do — can transform the listening experience. Leaving aside stitching in voice clips and layering in all other kinds of audio, they say that even sequencing songs together is fraught with issues.
The two most common types of transitions that digital services use between songs are crossfading and brief pauses.
Pauses create dead air, which iHeartMedia's chief product officer Chris Williams told dot.LA is the "enemy of radio," because it takes listeners out of their flow and puts them in a position to make a decision: namely, whether to keep listening or not. "I want to minimize that," Williams said.
As for crossfading – which Zalon said tends to be applied uniformly across tracks, such as a six-second blend of the end of one song with the start of the next, irrespective of the songs' particulars – it doesn't always work. Williams said crossfading can be done without jarring the user or disrespecting the songs about 50% of the time, and ever less so as longer song lead-ins give way to snappy intros aimed at grabbing listeners' attention from the first note.
"Crossfades create crashes," he said.
A radio DJ, by contrast, is trained to avoid these issues.
"The techniques of trained radio DJs are pretty complicated," Zalon said. "Super Hi-Fi is AI that has all the skills of a trained radio DJ."
This AI is designed to help customers like iHeart provide listeners with custom playlists that artfully blend one song with the next – no matter which song it is – and incorporate additional sonic elements like branded logos, interview clips, voice segments and more to eliminate dead air while respecting the artistry of the underlying songs, and to potentially drive streaming revenues back up to or beyond the levels that CDs generated in their peak.
How Does It Work?
As Super Hi-Fi's first customer, iHeartMedia helped the company fine tune its AI model and algorithms.
"Their pool of some of the world's best music programmers and on-air DJs became in a way like our QA partners," Zalon said.
By now Super Hi-Fi has "fingerprinted" iHeart's entire music catalog – tens of millions of tracks, Williams said – to identify the songs' underlying characteristics: features like volume, rhythm, mood, vocal texture, tempo and more. Lots more.
"The data we have on the music takes up more file space than the music itself," Zalon said.
Super Hi-Fi's AI has also fingerprinted each of iHeart's 700 styles of sonic logo; there's a country version of the "You are listening to iHeart…", a hip-hop version, a reggae version, and so on.
So, too, with any audio file that any customer may want to include in a playlist.
"The real power of the AI is to understand all the content with enough depth to make pretty much any output decision that any service might want," Zalon said.
Results have been good for iHeart. Williams reported that since they've rolled out Super Hi-Fi across their streaming services, the company has seen listening durations double.
"That increases ad impressions," he said. "There are clear business upside reasons beyond aesthetically creating a better experience...and [achieving] clear differentiation [from competitors]."
The Next Song
After having recently reeled in Sonos and its new streaming service as a customer, Super Hi-Fi has its sights set on bigger streaming fish. Jehan may help them get to Spotify, and they'll also look to Apple Music.
Chief business officer John Bolton told dot.LA that Spotify's expansion into podcasts makes them a prime candidate to benefit from Super Hi-Fi's service. He pointed to their "Your Daily Drive" product – a mix of music they know listeners like and relevant news – and said he could see that sort of playlist growing to include podcast snippets, the weather, and various other forms of audio, all tailored to the listener's preferences and location.
"If we see this happen at scale you'll start to see listening experiences become something very different," said Bolton, who helped found Super Hi-Fi after leaving ByteDance, which acquired his social media-meets-music startup Flipagram.
Streaming platforms may well be working on their own blended-audio AI solutions, but Williams says iHeart has benefited by getting in with Super Hi-Fi early.
"Two years from now everyone should have this solution or some version but we'll have already taken this to the next step, so it gives me the opportunity to get ahead," he said.
Music lawyer Ed Buggé, partner at L.A.-based entertainment law firm Hertz Lichtenstein & Young, thinks Super Hi-Fi "could be an attractive target for digital streaming platforms (DSPs) as they look to differentiate their platform offerings."
Spotify's former chief economist agreed. Will Page said a major audio streamer could look to Super Hi-Fi as a way to stand out in a market of look-alike services competing for the same customers.
"All these services offer the same 60 million tracks for the same $9.99 price point. With so much similarity, the value of distinctiveness goes up," he said. "The end game could see it being acquired by a DSP."
More than Music
Even if Super Hi-Fi doesn't lure the big catches in streaming, it can serve other verticals, including digital fitness. Peloton is already a customer.
"They wanted something different," Zalon said. "They want to make sure there's no loss of energy between songs; there's nothing worse than having music drop off in the middle of a workout. So we've been working with them on the roadmap to use the AI to help create an exercise experience that never loses its energy." In addition to blending songs, this will include voice-over instructions from Peloton's instructors.
Retail music is another area the company's targeting. Octave Music Groups, which operates Apple Music for Business and manages the music that customers hear at Starbucks, along with many other bars, restaurants and stores throughout North America and Europe, is another Super Hi-Fi customer.
Just as a radio station manager works with a DJ to set ground rules for branding the station through its sonic choices – running a branded message every 15 minutes, a news break every 30, and keeping segues tight but breezy, for example – each customer works with Super Hi-Fi to customize the AI to fit its desired style.
In exchange for this AI-plus-support service, Super Hi-Fi receives a licensing fee. The company would not disclose its prices or finances, though Bolton said Super Hi-Fi has not raised any outside funding.
He thinks using AI to bring a new level of real-time curation, presentation and personalization can attract more advertising and subscription revenues to the music industry. That's all the more important in an era when live performance has evaporated.
"We have a big, bold vision and tech that can transform playlists into listening experiences that we think will eventually make the industry much more money and provide a much better product for consumers," he said.
---
Sam Blake primarily writes about media and entertainment for dot.LA. Find him on Twitter at @hisamblake and email him at samblake@dot.LA
- Sonos backs LA Podcast Studio QCODE with $6.4M Investment - dot.LA ›
- Rock the Bells' James Cuthbert on Building Hip Hop's Legacy - dot.LA ›
- What Is ‘Embodied Audio?’ And Can It Help Pro Sports Teams? - dot.LA ›
- How Laylo Plans To Use AI To Reinvent the Music Industry - dot.LA ›
Sam primarily covers entertainment and media for dot.LA. Previously he was Marjorie Deane Fellow at The Economist, where he wrote for the business and finance sections of the print edition. He has also worked at the XPRIZE Foundation, U.S. Government Accountability Office, KCRW, and MLB Advanced Media (now Disney Streaming Services). He holds an MBA from UCLA Anderson, an MPP from UCLA Luskin and a BA in History from University of Michigan. Email him at samblake@dot.LA and find him on Twitter @hisamblake



 Match Group and Tinder CEO Spencer Rascoff
Match Group and Tinder CEO Spencer Rascoff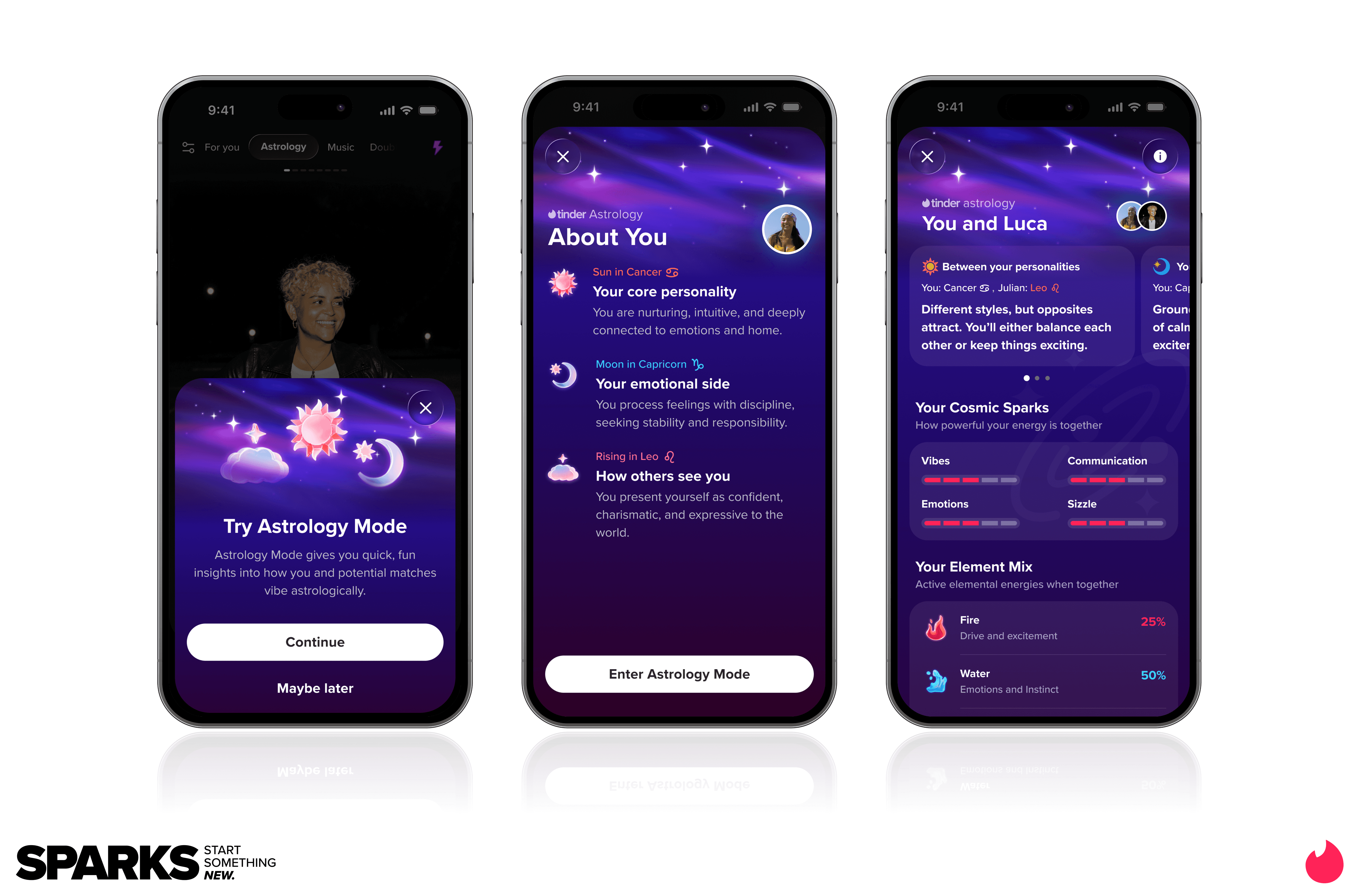 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder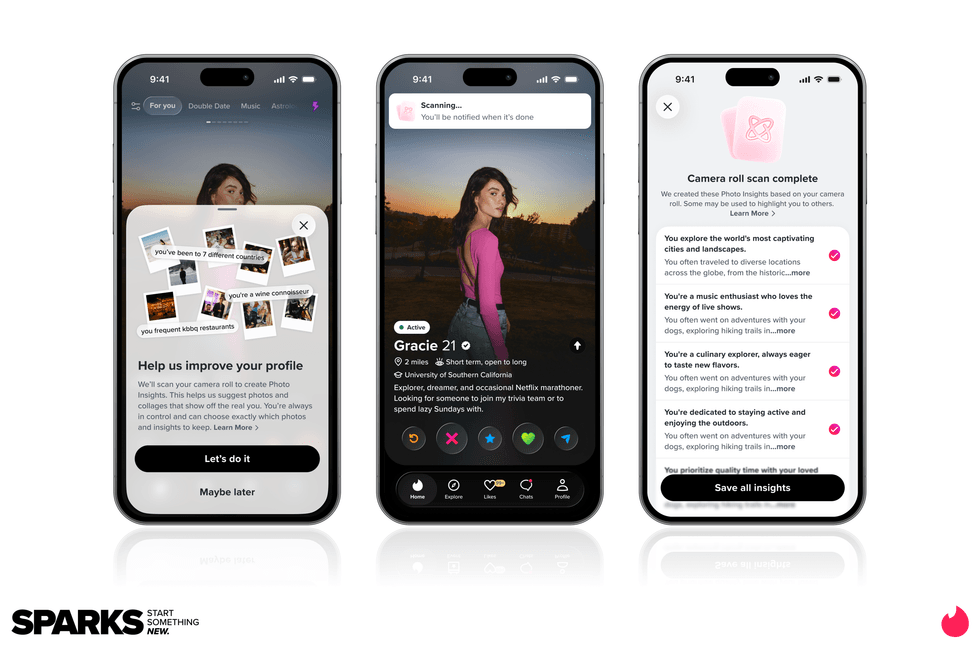 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder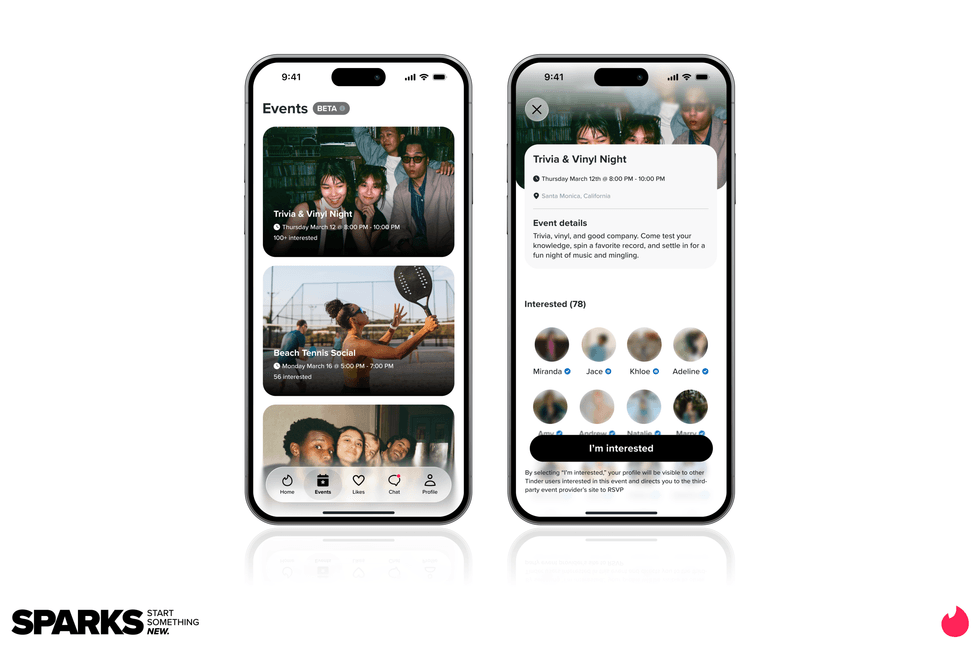 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder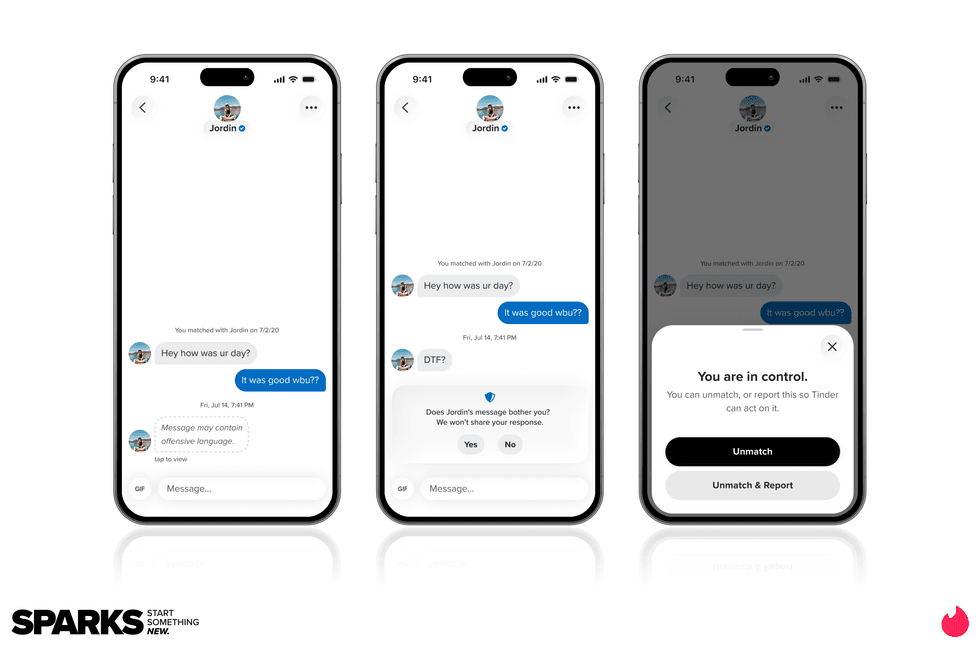 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder

 Image Source: Revel
Image Source: Revel