Q&A: What Overturning Prop 22 Could Mean for the Future of the Gig Economy

Labor advocates got a major win last month when a California Superior Court judge ruled Proposition 22—the controversial ballot initiative that allowed ride share companies to keep classifying drivers as independent contractors rather than employees—was in fact unconstitutional.
Prop 22 was passed in November of 2020 in response to California Assembly Bill 5, which gave gig workers wage and benefit protections. Ride-share companies like Uber, Lyft, and DoorDash built their business model on gig workers. And they spent hundreds of millions of dollars to defend it, lobbying in support of Prop 22 and making it the most expensive ballot measure in California's history.
The Service Employees International Union sued the state in January to overturn the proposition, and on Aug. 20, an Alameda County Superior Court Judge Frank Roesche found Prop 22 violated the state's constitution, rendering it unenforceable. Uber and other ride-share companies have already announced their intent to appeal the ruling, and the case is expected to make its way up to the California Supreme Court.
dot.LA spoke with Catherine Fisk, Berkeley Law professor who wrote an amicus brief in favor of the drivers, about what the ruling means for the future of Prop 22, ride-share companies, drivers and the gig economy at large.
This interview has been condensed for brevity and clarity.
The Superior Court found that two sections of Prop 22 were unconstitutional, both of which you outlined in the amicus brief you and others wrote in favor of the drivers. Which parts of the proposition violated the state constitution?
One argument was that Prop 22 unconstitutionally limits the power of the legislature to provide for a complete and adequate system of workers' compensation. Workers' comp is a program that now every state has that provides a system of no-fault compensation for workers who are injured or become ill in the course of their employment. So legislatures everywhere created systems of workers compensation. Business groups, at that time, didn't want to pay the cost of compensating workers for their injuries and challenged these workers' comp systems often in court, and in many cases found judges to invalidate the workers' comp programs in whole or in part. So in California, the people amended the constitution to require that the legislature have plenary—that is complete power—to provide for a system of workers' compensation. This all happened over a century ago. So in the case of Prop 22, the court found that by carving out app-based drivers from the protections of workers' comp, it unconstitutionally limited the power of the legislature to provide for a complete and adequate system of workers' comp. Essentially, the transportation companies were trying to redo what businesses had done a century ago to eliminate workers' comp for some or all employees. And the court said no, because the California Constitution had been amended in 1918, specifically to prevent that kind of move by business.
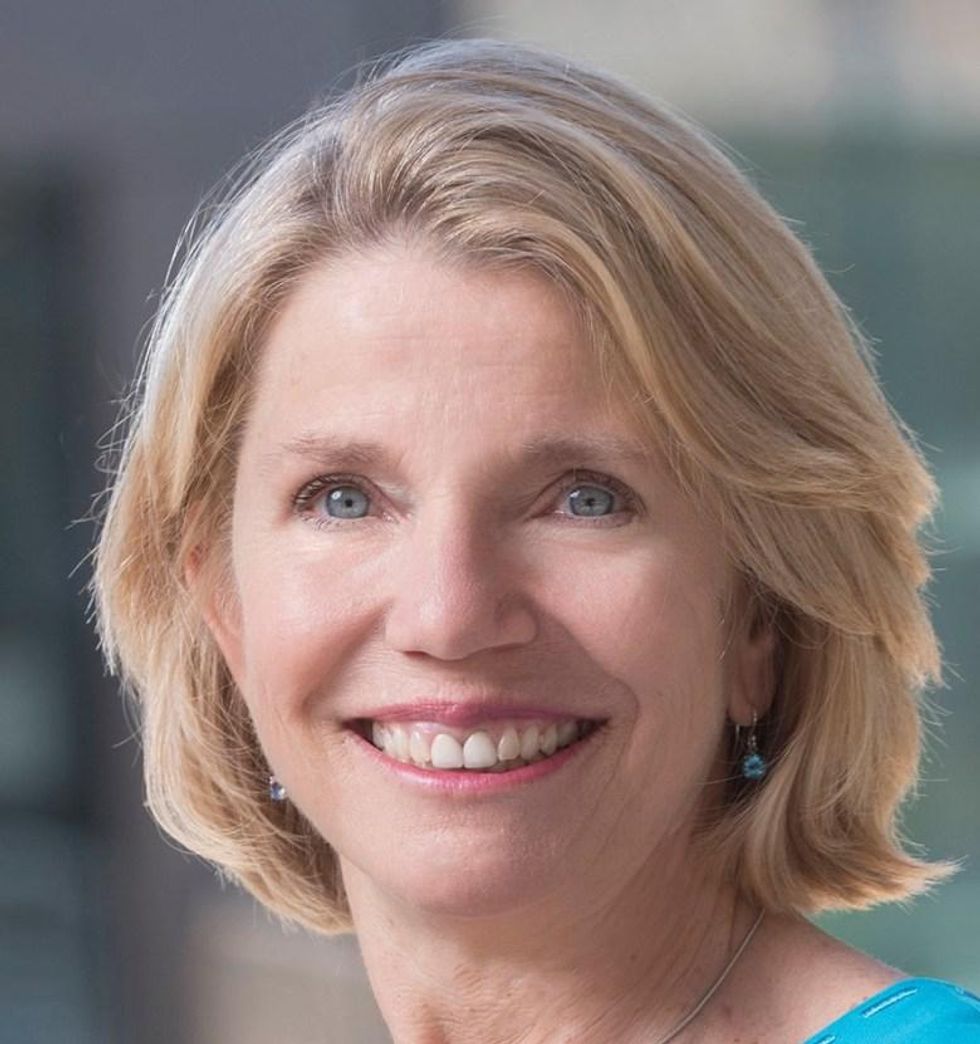

Berkeley Law professor Catherine Fisk
A second argument was that Prop 22 violates another provision of the California Constitution, which requires that any ballot initiative, like any other piece of legislation, must address only a single subject. The purpose of the single subject rule is to prevent voters from being confused or misled about what a ballot initiative would do. In the case of Prop 22, the particular confusion that the court focused on was that Prop 22 prohibits the legislature from enacting a law that would authorize drivers to negotiate collectively through a representative. This provision of Prop 22, which was buried in the fine print, was not described in the advertising in favor of the proposition. It wasn't even described in the voter information pamphlet, or the summary that appeared on the ballot.
Right, I don't remember hearing about that part of Prop 22 at all in 2020.
You had to read every single word of Prop 22. But even if you had read every single word, you wouldn't have understood what this provision would do. Because in order to understand it, you have to understand federal labor law, federal antitrust law, and their relationship to each other. Here's why. The real significance of that provision was that if the workers unionized it would enable the companies to sue the worker union for being in violation of federal antitrust law. There are 50 lawyers in the country who know enough about antitrust law, and enough about labor law to understand that that's what was going on.
So because this was hidden in the fine print and not described anywhere and had nothing to do with what the what Prop 22 said it was about—which was eliminating minimum standards for drivers—this, the court said violated the single subject rule, because it would confuse voters, you could read all the materials and still not understand what you were voting on. So that was another argument that the court found for why Prop 22 was unconstitutional.
Assuming this goes all the way to the state Supreme Court, the Superior Court decision is upheld, what might that mean for the ride-share companies and drivers?
It means Prop 22 will not be in effect, which means that the legislation that Prop 22 was designed to overrule [AB5] will go into effect, which means that drivers of transportation network companies will be entitled to be paid the minimum wage; they will be entitled to be paid overtime if they work more than 40 hours a week; they'll be entitled to protection against discrimination on the basis of race, religion, gender, etc; they'll be entitled to workers compensation benefits if they're injured. It will improve minimum standards for drivers.
And if the decision is ultimately overturned by the state supreme court, what legal options remain, if any, to get those protections for gig workers?
None. Well, to be clear, Prop 22 did say that the legislature could amend it by a seven-eighths vote. In other words, seven-eighths of the entire legislature would have to vote to change any provision of Prop 22. Why seven-eights? Because the proponents of the Prop 22 know that Democrats have a two-thirds majority of the legislature, and so they wanted to make the majority so great that the legislature could not amend it. Federal law can preempt state law or it can supersede state law. So Congress could provide that drivers are entitled to the minimum wage. Congress could provide that they're entitled to unemployment benefits, if they are laid off. Congress could create a compensation system for injured drivers. But it would have to go through Congress. And it's very hard to get anything through Congress.
Right, so high stakes.
Very high stakes.
What are the implications of this ruling then for the gig economy at large?
The gig economy, so called, especially for low-skill work like driving has been based on a low-wage model. Drivers get paid very little. Many are making way less than the minimum wage. They have no protection if they're injured in the scope of employment. And there's no reason that driving for a living has to be a low-wage job. In the 1950s, when truck driving was unionized, driving was a middle-class job.
So really what this fight is about is how to divide the profits of the app-based driving model. Should more of the money that's being made in this work, go to the workers? Or should more go to the investors? I've received a dozen phone calls or emails since the decision came down by people saying they represent investors in this industry who want to talk to me about what it means—I decline all those calls, by the way—because investors are making a bunch of money in this sector, and they want to know whether they're going to keep making a bunch of money, or whether it's going to be less profitable for investors, and more profitable for workers. That's what's at stake here.
Is there a model that could work?
When taxi cabs came into existence, everybody thought, "Oh, that's genius. Imagine being able to stand on the sidewalk and wave my arm at a yellow car, and have it stop for me and take me where I want to go." The real question is, are we going to regulate this innovative business to ensure that drivers are paid decently and have protection in the case of injury. We figured out how to have taxis and regulate them to protect both drivers and the public; cities all had taxi cab commissions that did exactly that, and they regulated fares. We could have the same model for app-based driving. The real question is, are we going to regulate this innovative business to ensure that drivers are paid decently and have protection in the case of injury. It will probably be more expensive. But when everybody said, "Wow, Uber is half the cost of a taxi," nobody thought, "and why is that?"
The thing about an Uber is that companies figured out that you could have a giant fleet of drivers on the road at all times, with zero fixed cost to the company. The drivers pay for the car; the driver pays their own time; the driver pays gas; the driver pays insurance; the drivers pay if they become injured; and the city picks up the cost of the road maintenance. So the company shifted all the risk and all the fixed costs of the business to the labor force, which was genius from the investing standpoint, but terrible for drivers.
- As Uber and Lyft Battle California Law, Texas Ride-Hailing Startups ... ›
- 8 Alternatives to Uber and Lyft in California - dot.LA ›
- Prop 22 , a Victory for Uber, Lyft - dot.LA ›




 Image Source: Skyryse
Image Source: Skyryse