Parallel Systems Emerges From Stealth With $50 Million For Autonomous Electric Trains—But Will Its Plan Work?
David Shultz reports on clean technology and electric vehicles, among other industries, for dot.LA. His writing has appeared in The Atlantic, Outside, Nautilus and many other publications.

Parallel Systems has big dreams for the future of railway freight operations, and it seems that the venture capital world has taken notice.
The Los Angeles-based transportation startup announced a $49.55 million Series A funding round as it emerged from stealth mode on Wednesday. The round was led by Anthos Capital, with additional investments from the likes of Congruent Ventures, Riot Ventures and Embark Ventures.
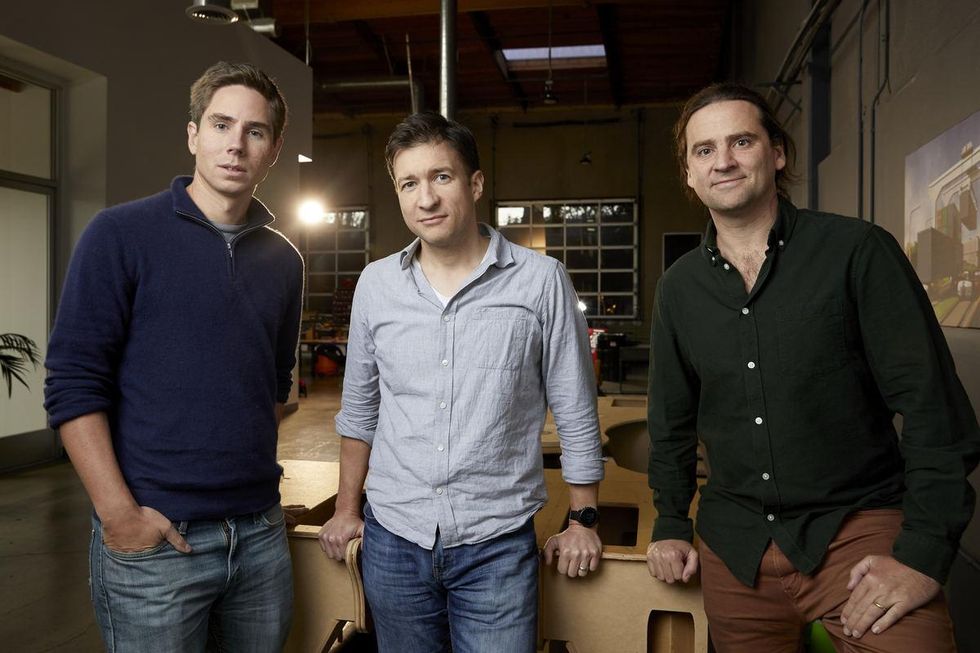
Comprised of former SpaceX, Google and Tesla engineers, Parallel Systems is aiming to develop autonomous and electric freight train cars that would make the American shipping industry greener and more efficient.
“We’ve been pretty quiet about what we’ve been doing,” Parallel Systems CEO Matt Soule, formerly the principal avionics engineer at SpaceX, told dot.LA. “Our website has been pretty barren.” Soule co-founded the company two years ago with fellow former SpaceX engineers John Howard and Ben Stabler. Including $3.6 million in seed funding, the startup has now raised more than $53 million to date.
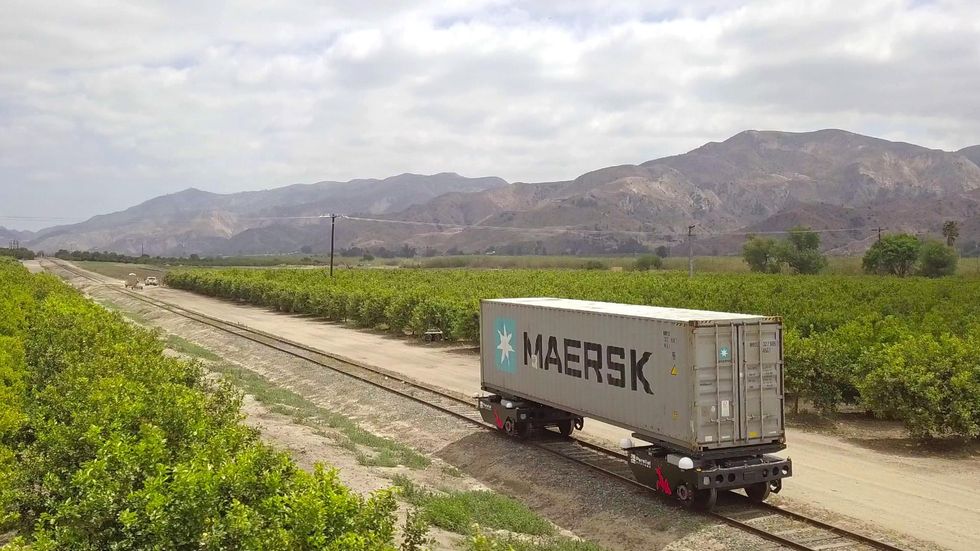
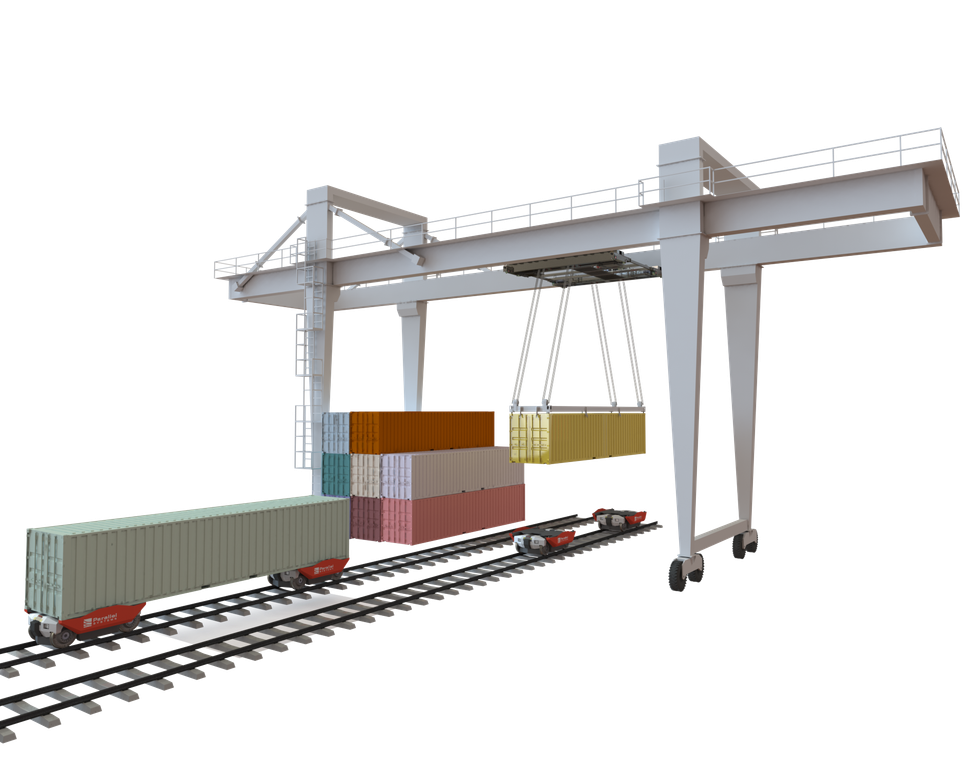
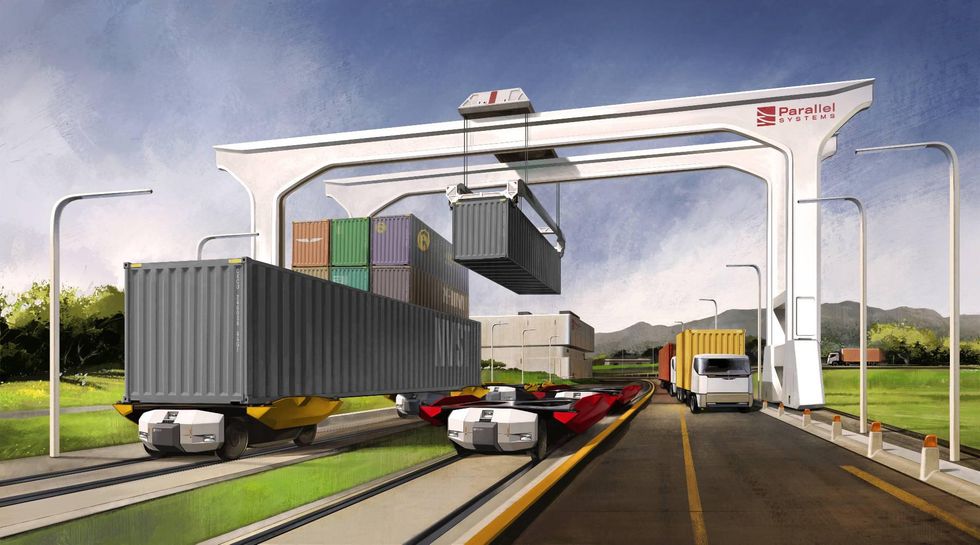
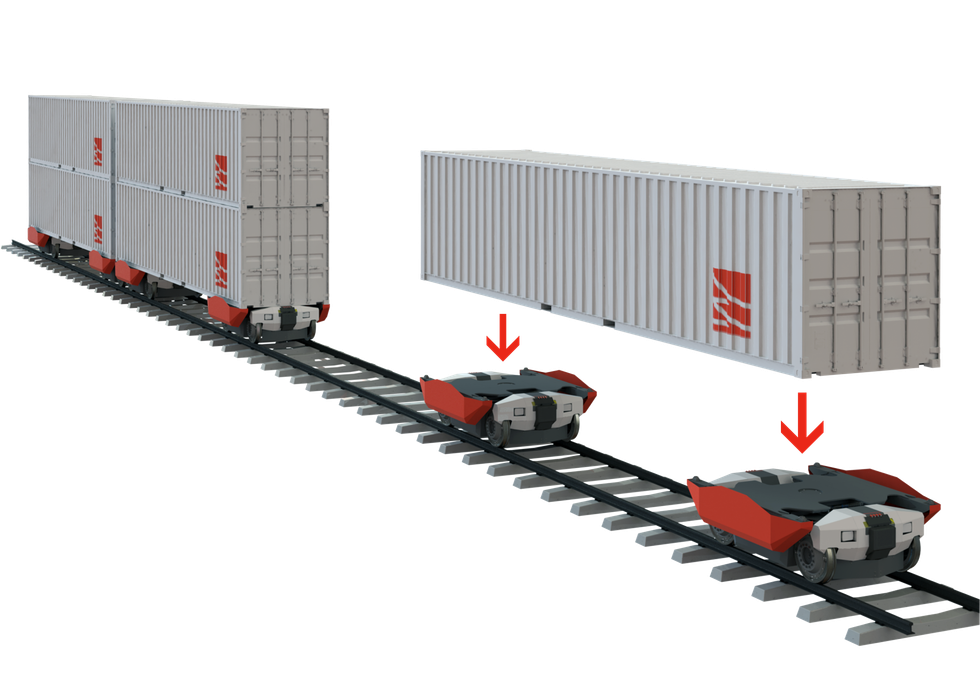
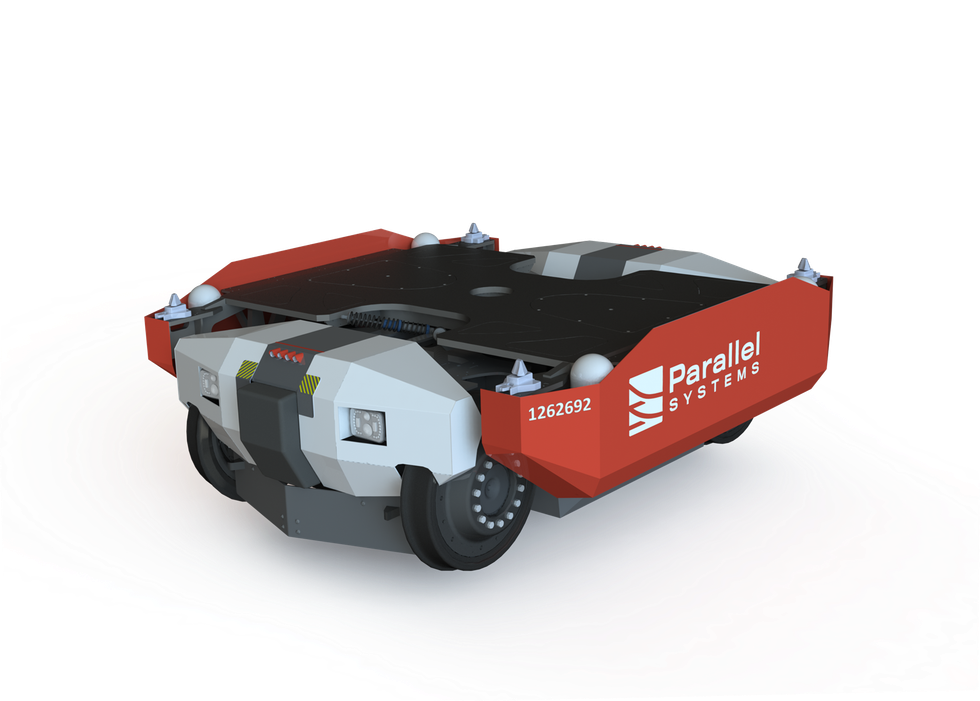
Parallel Systems’ technology relies on replacing traditional diesel-powered locomotives with battery-powered freight cars. In its model, each train car is self-powered, and can break apart from or join together with other cars as needed. In theory, this ability to autonomously break apart and reassemble as needed would reduce the need for switching stations, where trains are reorganized and rerouted manually.
It could also drastically reduce the significant physical footprint of trains, converting them from two-mile-long behemoths into “platoons” of 20-to-50 cars that wouldn’t require massive terminals for loading and unloading. Smaller trains would be able to travel closer to their final destinations before being unloaded—reducing trucking emissions, which account for roughly 7% of all greenhouse gas emissions in the U.S., in the process.
“The opportunity we’ve been after is kind of decarbonizing freight from a new angle,” Soule said.
All of these ideas would be beneficial toward alleviating America’s clogged supply chains and reaching its ambitious carbon emission goals—if they were able to be integrated into America’s existing rail infrastructure. On that front, some experts are skeptical.
“My first instinct was that this looks like SpaceX engineers getting bored and working on something that they know nothing about,” Chris Caplice, executive director of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s Center for Transportation & Logistics, told dot.LA. “They didn’t think about the larger system—whether it's regulatory, the network itself, the rail operations or the labor involved. I think they just found a technological solution to a problem they wanted to solve.”

Caplice worries that Parallel Systems’ technology fails to consider the realities of America’s existing rail network. Today, rail lines are divided into signal blocks, which can range from less than a mile to 15 miles long; these blocks are in fixed geographic positions, and only one train at a time is permitted into any signal block. For the new autonomous, single-car system to work, “you would have to put in thousands more control points in different places to get the network chopped down small enough to do this,” according to Dale Lewis, the former director of strategic analysis for CSX Transportation.
Even then, it likely still wouldn’t look like what Parallel Systems is imagining, with cars continuously breaking in and out of platoons. To realize what the company is pitching, Lewis says you’d need a complete revamp of the entire rail system.
“If [Parallel Systems] can bring in a couple people who have deep experience in operations planning…and sit with them for a day to go through how this would fit in the system, they’d probably come to some different conclusions about what they’ve got,” he said.
While the startup doesn’t employ any full-time railway operations specialists, Soule says Parallel Systems has brought in “veterans from the industry” who have helped them “understand the business.” He says safety is a top priority for the company; indeed, their vehicles would feature AI that would allow them to come to a stop quicker than traditional trains. No one is going to argue against safer trains—though most modern trains already come equipped with a system known as Positive Train Control, which autonomously prevents train-to-train collisions and other human errors.
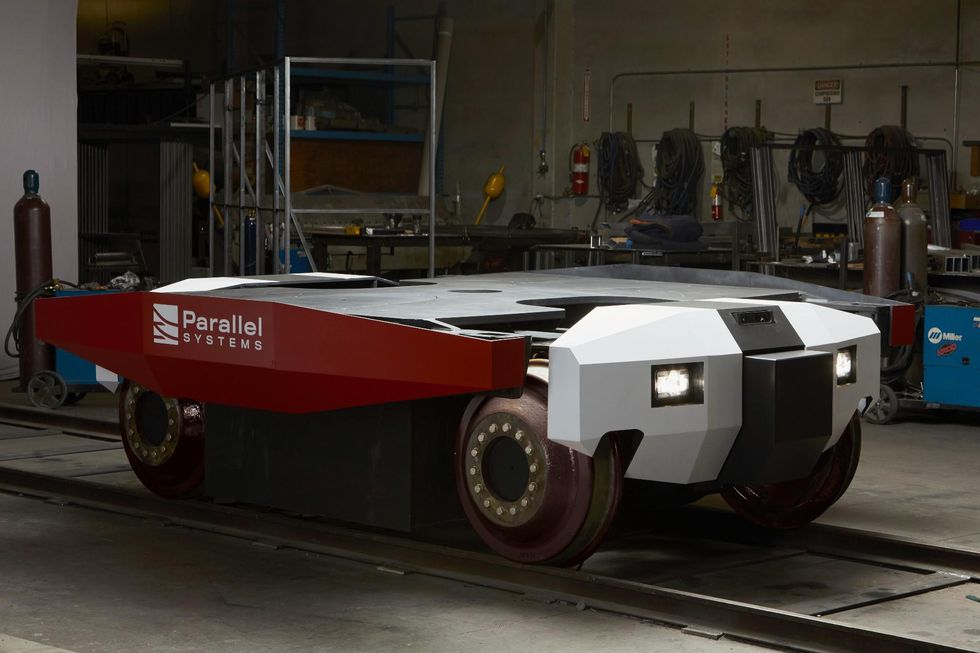
Still, the 24-person firm is planning to hire heavily on the software side as it tries to figure out how to integrate its ambitious designs into the existing infrastructure. On the hardware side, Parallel Systems is working toward the second iteration of its prototype battery-electric rail vehicle, and testing it on a closed track in California.
“We’re going as fast as we can in terms of building the tech,” Soule said.
Parallel Systems Explainer VideoVideo via www.youtube.com
- Pex Copyright Management System Gets $57M - dot.LA ›
- ABL Space Systems Rockets to $2.4 Billion Valuation ›
- Parallel Systems Lands Funds For Autonomous Electric Freight Cars - dot.LA ›
David Shultz reports on clean technology and electric vehicles, among other industries, for dot.LA. His writing has appeared in The Atlantic, Outside, Nautilus and many other publications.









 Match Group and Tinder CEO Spencer Rascoff
Match Group and Tinder CEO Spencer Rascoff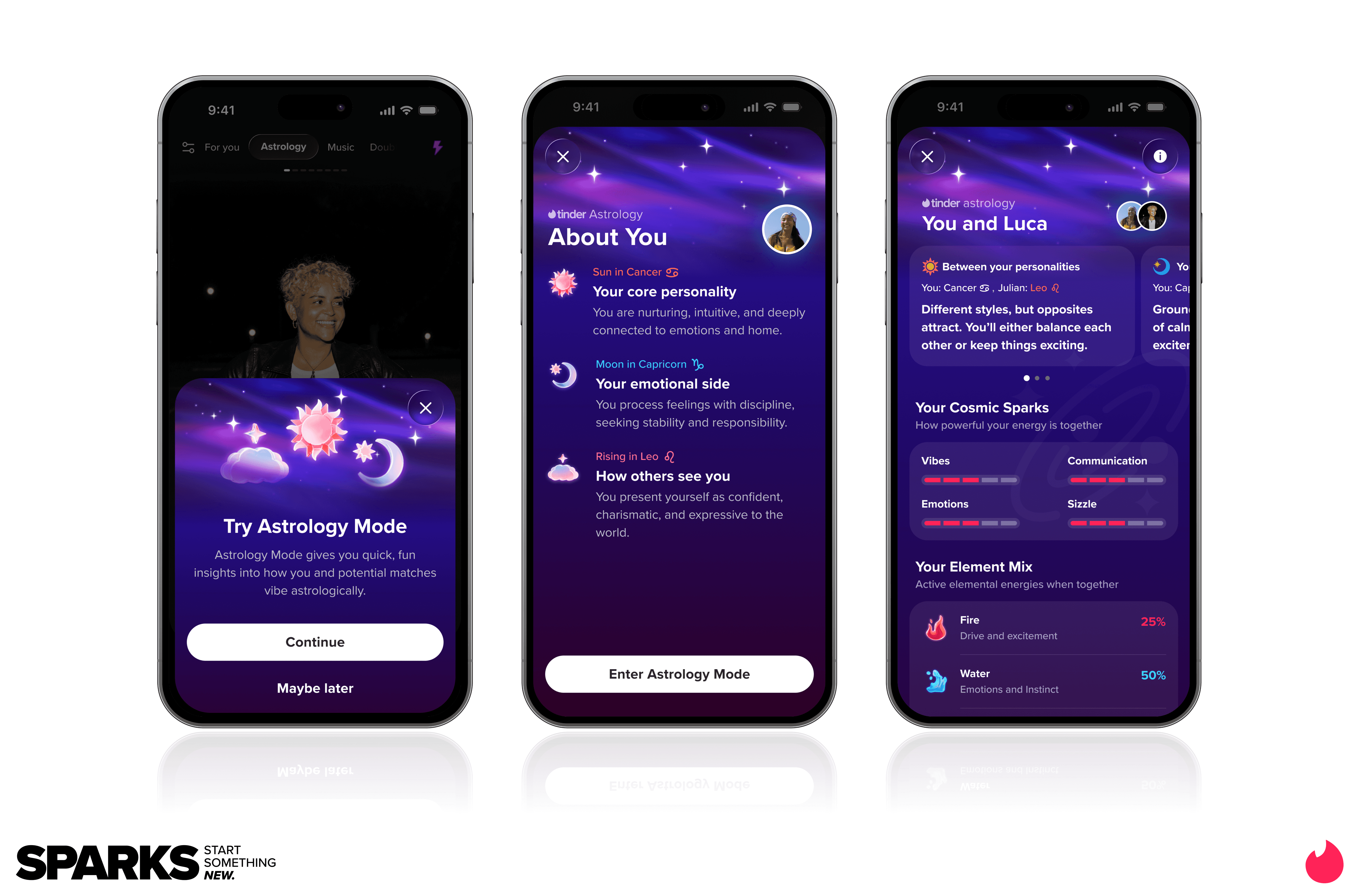 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder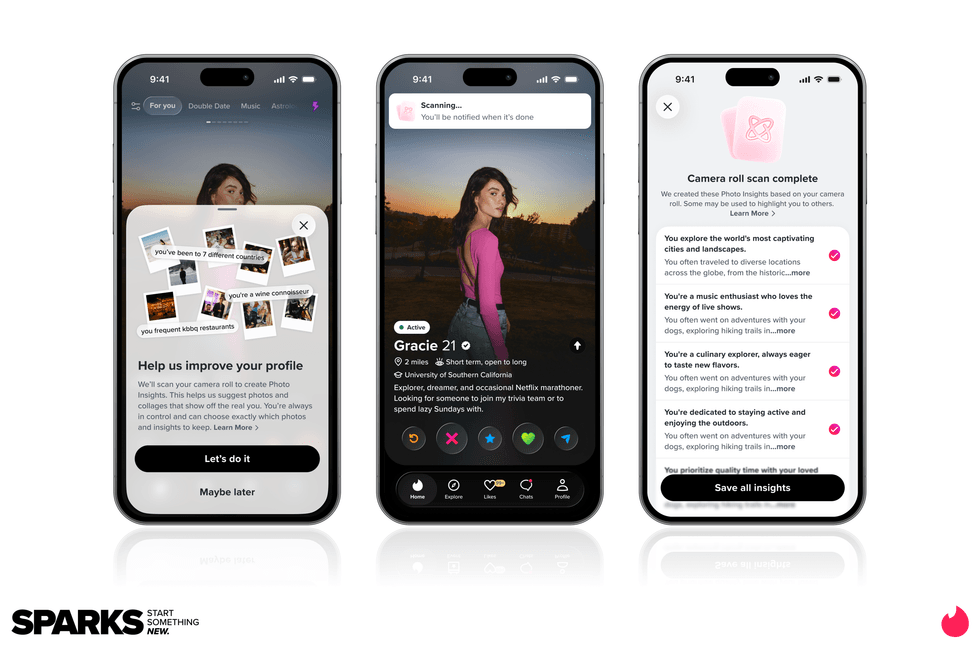 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder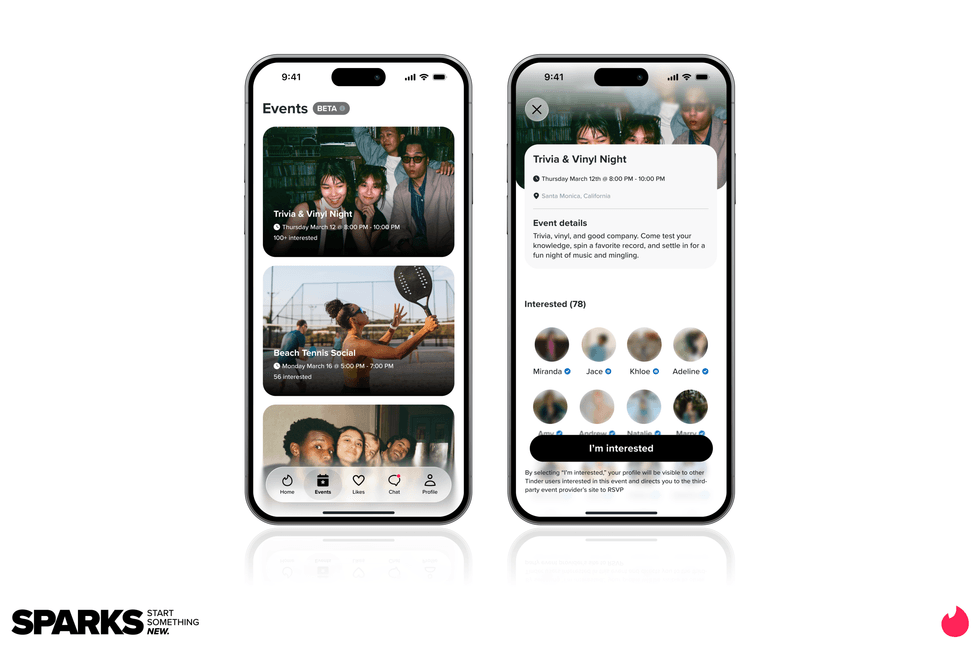 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder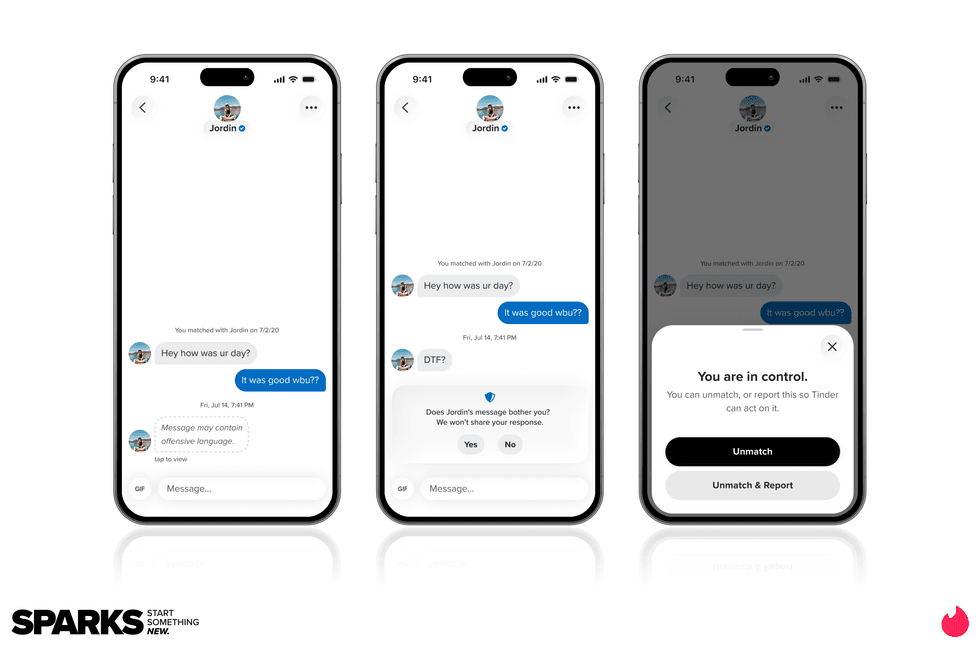 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder

 Image Source: Revel
Image Source: Revel