The Near Miss Apocalypse: Predictions for Post SVB Collapse
Spencer Rascoff serves as executive chairman of dot.LA. He is an entrepreneur and company leader who co-founded Zillow, Hotwire, dot.LA, Pacaso and Supernova, and who served as Zillow's CEO for a decade. During Spencer's time as CEO, Zillow won dozens of "best places to work" awards as it grew to over 4,500 employees, $3 billion in revenue, and $10 billion in market capitalization. Prior to Zillow, Spencer co-founded and was VP Corporate Development of Hotwire, which was sold to Expedia for $685 million in 2003. Through his startup studio and venture capital firm, 75 & Sunny, Spencer is an active angel investor in over 100 companies and is incubating several more.

The historic Silicon Valley Bank collapse dominated headlines recently, and the tech and financial communities have only just started processing the aftermath. The 48-hour breakdown was both historic and a few inches away from economically catastrophic, and thanks to the swift moves of the FDIC, complete disaster was avoided.
But it’s still been disruptive. SVB was the banking partner for nearly half of U.S. venture-backed technology and healthcare companies that listed on stock markets in 2022, making it one of the biggest lenders for early-stage startups. The aftershocks of SVB’s breakdown spread just as far and fast as the main event: the close of Signature Bank just two days later, major market volatility, other banking crises at Credit Suisse, tech industry troubles, and much more.
In the days since, things have settled slightly, and the world’s fingers are crossed that depositors are comforted enough and confident enough to avoid another bank run. It’s good news, but we aren’t out of the woods yet. Now that we know the second-largest bank failure in U.S. history could be looming around any corner, how does that change the ways startups do business?
Level, Set, Go
Before we get into what could happen, it’s smart to level-set about how we got here. (And for an introductory primer, this short podcast can help.)
- The government 100% did the right thing by assuring depositors that they will be made whole. The FDIC swooped in, steadied the ship, and made sure people had the money they needed when they needed it.
- Some have called this a ‘bailout', but it’s not for two reasons. 1) SVB shareholders and creditors will be wiped out and 2) taxpayer money is not being used to do any bailing.
- Remember: depositors are not creditors. When companies and people put money into their accounts at SVB, they had every reason to expect that it would be there when they needed to withdraw it. They weren’t loaning the money to SVB (as a creditor would), they were depositing money into their own account at SVB for safekeeping.
- People who say “depositors took a risk by having more than the FDIC insured $250K limit” are, ahem, a bit misguided. (I’m being polite). The truth is that $250K is not that much money for a company, especially of the size and scale of some of SVB's major customers.
Here’s where I think we should go from here.
The Short Term
While SVB’s failure didn’t launch us over the precipice, many people are rightfully feeling very nervous being this close to the edge.
Looking out to the next few weeks, I predict we’ll see venture funding slow way down. It’s been chilly out there recently, but it’s going to be ice cold, piggybacking on the already struggling tech landscape. Writing new checks will take a backseat to checking in on existing investments. VCs will need to assess where their cash is and where their portfolio companies stand, and likewise startups are going to have to start thinking hard about what it means to be lean and extend runway. Hopefully this only lasts a few weeks and the wheels of the machine start turning again before summer.
If there is a positive take on the SVB wreckage, it’s that the Fed will likely slow down the rate of increases. I’d predict a 25, maybe even 0, basis-point increase next week, and I wouldn’t be surprised if there was a rate cut later this year.
Whither venture debt?
Prior to SVB’s failure, it was very common for a startup to have enough cash at SVB for one year of runway, plus a venture debt line for an additional another year. SVB profited from this by charging interest plus warrants and requiring banking exclusivity. It was part and parcel of how they did business, and since they’ve transitioned from success story to cautionary tale, expect to see new regulations prohibiting banks from requiring customer exclusivity in exchange for additional services.
In the immediate term, companies who had venture debt lines with SVB are trying to decide whether to put their cash back in SVB in order to access that venture debt. The whole situation is surreal, since just a few days ago these same companies were scrambling to pull their money out of SVB, and now they are considering returning. There are conflicting reports, but it appears that SVB is allowing these companies to keep a second banking relationship with another bank (so no more exclusivity), but at least half of their cash must be with SVB.
For startups choosing not to access that venture debt line, now trying to figure out how to operate without venture debt (aka less hiring, less spending, less growth), they’re in for challenging times ahead. To fill that funding gap, maybe we’ll see more private lenders step in and provide venture debt as a product. If that is the case, I suspect terms will be tougher and many VCs will recommend against it for their companies.
Another prediction: audit committees of boards will come into play much earlier than they often do now. Given the ever larger seed and Series A/B rounds, it wasn’t uncommon to see startups that had raised $100M+ and had 200+ employees before an audit committee was formed. I suspect these will now be formed upfront and have a much bigger role to play in early stages.
Silver Lining
The good news: the world isn’t ending and won’t in the near future (at least, not because of this). Yes, things will be different and it will take some time to settle into a post-SVB startup environment, but with change comes adaptation. And with adaptation comes innovation, which is what startups are all about.
- SVB: What Startup Founders Could Expect From the Market in 2023 ›
- Who’s To Blame for the Silicon Valley Bank Mess? The Internet Investigates ›
- The SoCal Companies Affected By the Fall of Silicon Valley Bank ›
- Here’s How LA’s Tech Scene Is Reacting to the SVB Collapse ›
- Behind Her Empire: ComplYant's Shiloh Johnson On Taxes - dot.LA ›
Spencer Rascoff serves as executive chairman of dot.LA. He is an entrepreneur and company leader who co-founded Zillow, Hotwire, dot.LA, Pacaso and Supernova, and who served as Zillow's CEO for a decade. During Spencer's time as CEO, Zillow won dozens of "best places to work" awards as it grew to over 4,500 employees, $3 billion in revenue, and $10 billion in market capitalization. Prior to Zillow, Spencer co-founded and was VP Corporate Development of Hotwire, which was sold to Expedia for $685 million in 2003. Through his startup studio and venture capital firm, 75 & Sunny, Spencer is an active angel investor in over 100 companies and is incubating several more.



 Match Group and Tinder CEO Spencer Rascoff
Match Group and Tinder CEO Spencer Rascoff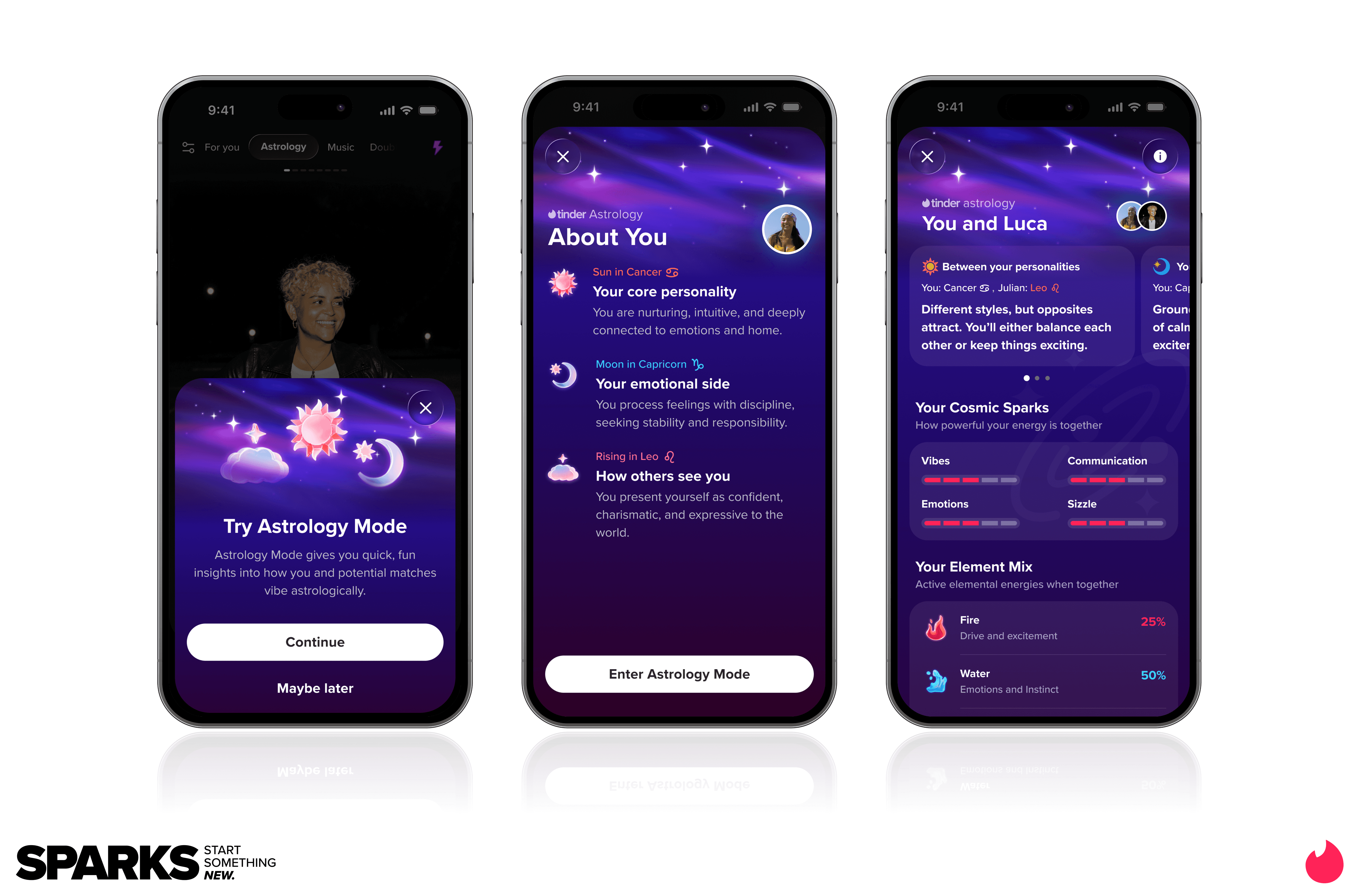 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder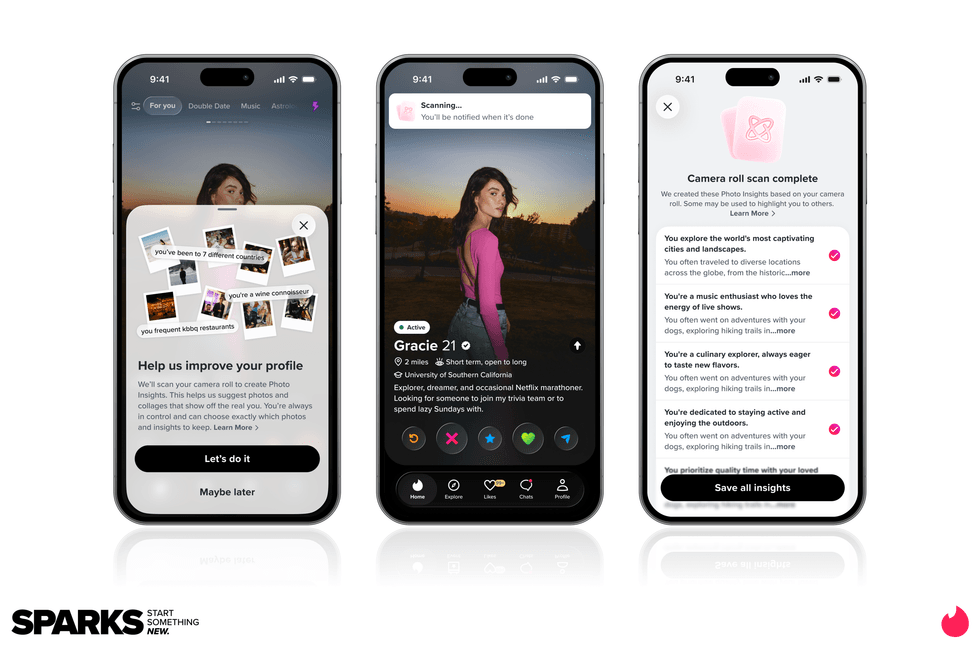 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder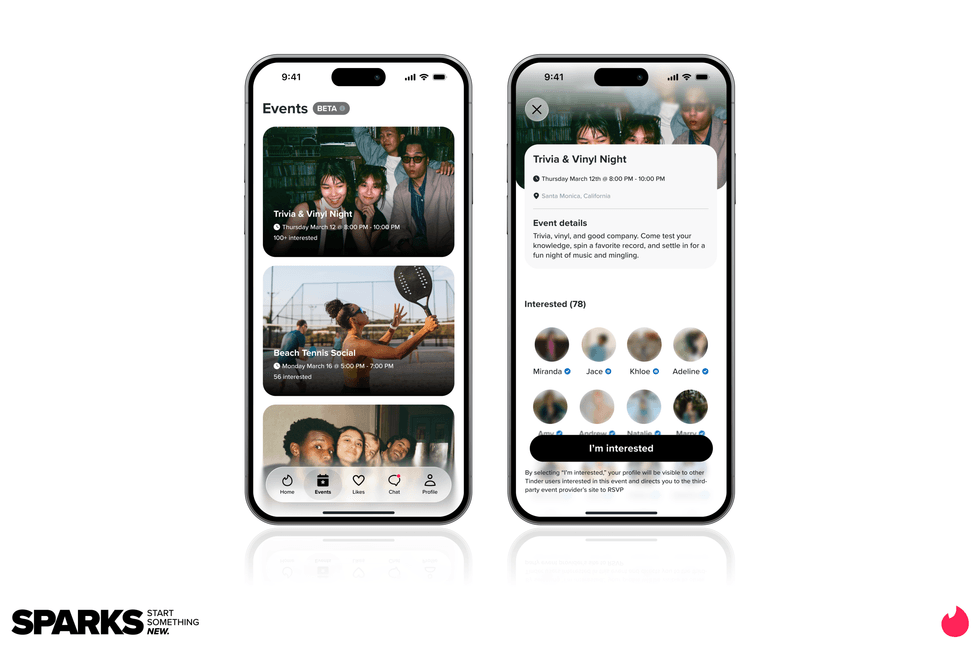 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder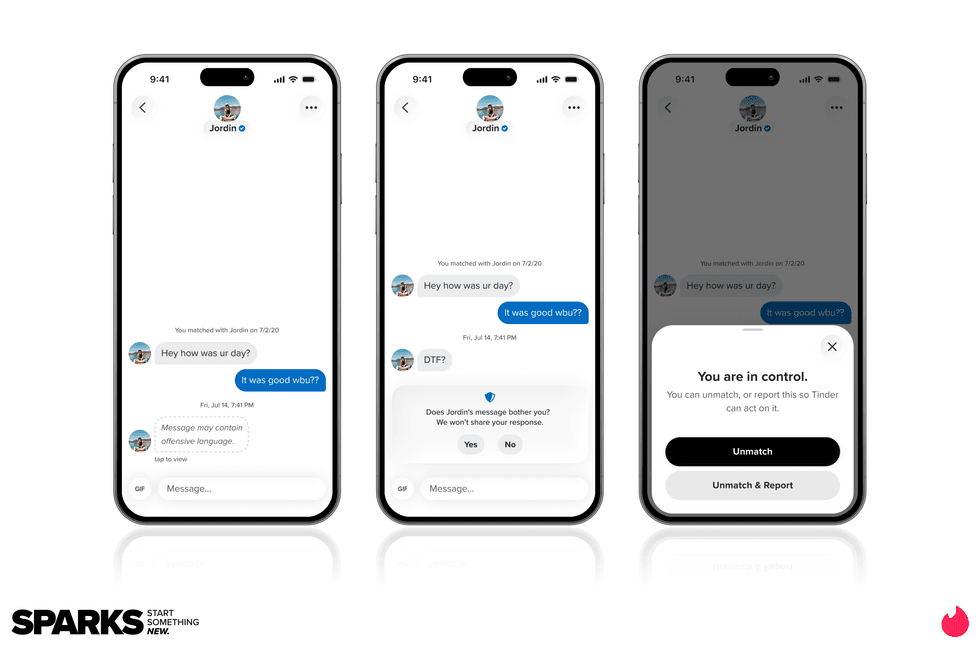 Image Source: Tinder
Image Source: Tinder

 Image Source: Revel
Image Source: Revel