A Day in LA With the Deepfake Artists Trying To Make the Digital World As Real as the Physical One

The Palisades Village is a 125,000-square feet outdoor shopping center designed to look like a luxurious resort town in a Bond movie. The pathways are cobblestone. The lights are outfitted to look like gas lamps. Every restaurant serves Italian food.
Rick Caruso, L.A. mayoral candidate and the architect behind the project and myriad other “faux-Italian” shopping centers, is well known for this sort of architectural theme: Cloning the riviera for the American imagination. But Tom Graham, the CEO of Metaphysic, an artificial intelligence company creating synthetically generated versions of real people, is unimpressed.
“This place is weird,” he says, pointing to a patch of grass with a sign that says “Don’t Walk on the Grass.” “Why can’t you walk on the grass?”
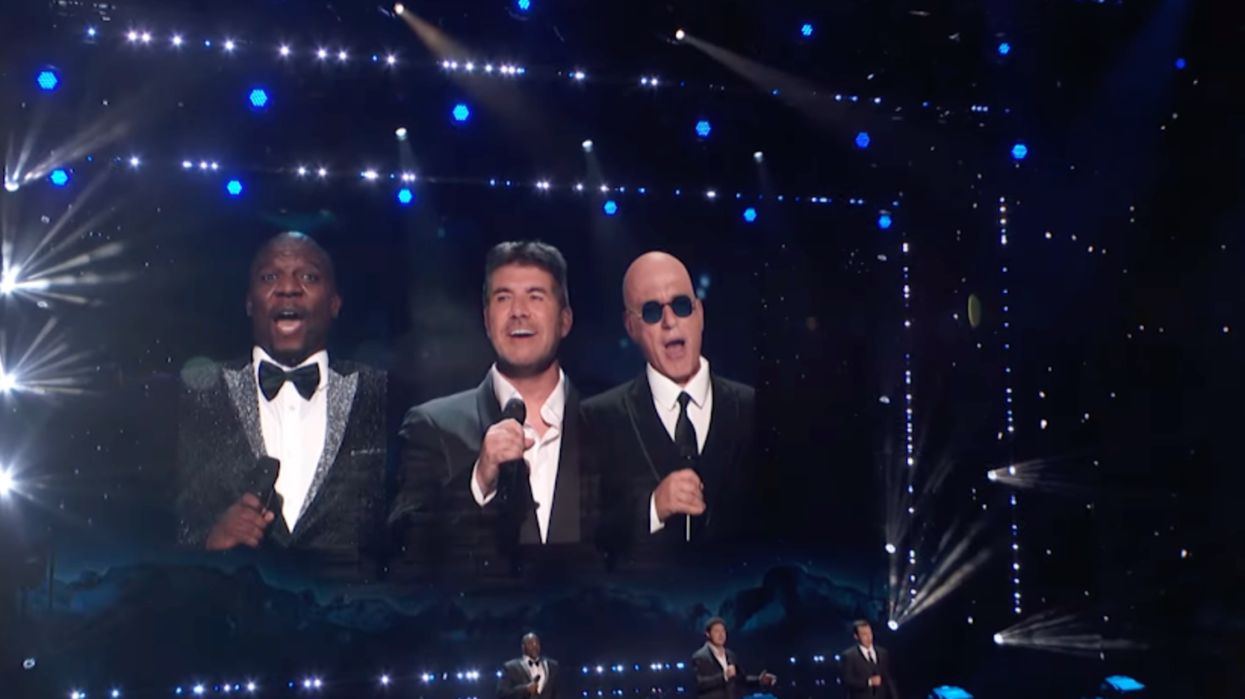
Graham is temporarily in Los Angeles along with Chris Umé — a VFX artist and the founder of Metaphysic. They’re getting ready for “America’s Got Talent” semifinals. Last month they wowed the judges with their hyperreal Simon Cowell avatar who sang Chicago’s “You’re the Inspiration” live on air.
Colloquially this type of content is better known as deepfakes. But, Graham says, what they’re developing at Metaphysic, “is sort of beyond.” Take, for example, their work with Miles Fisher — the most famous deepfake actor the world has ever known. Fisher is a Tom Cruise impersonator and the face behind @deeptomcruise. By now, you’ve probably seen Fisher as Cruise jumping over Keegan-Michael Key. Realizing there’s bubblegum inside a lollipop. And putting his arms around Paris Hilton.
To achieve this hyperreal effect, Metaphysic uses a neural network that’s patterned after the human brain. In the simplest terms, their technology processes data via an adaptive computing system that improves continuously. In the case of @deeptomcruise, this network inputs every image of Tom Cruise to output his every expression. His every wrinkle. The way Cruise’s eyebrows furl when he talks.
Again, the concept of deepfakes is hardly a new one. But Ume’s fakes aren’t typical. When I first saw one, it took more than a few Google searches to convince my brain that the real Tom Cruise has never wrapped his arms around Paris Hilton. And that he’s not actually on TikTok.
@deeptomcruise
@deeptomcruise When jokes fly over your head 😂✌️@Keegan-Michael Key
With millions of views, an appearance on 60 Minutes and featured in every publication from Vice to Today, the ersatz Tom Cruise is the face of Metaphysic’s technological capabilities. The computational magic trick, however, is also just the tip of the iceberg.
Metaphysic’s ultimate vision is to create a metaverse “so real that if after a month you tried to distinguish between the memories you made in the digital world you wouldn’t be able to distinguish them from the physical one,” says Graham. In short, he adds, “we want to make the content more important than the format.”
But here at the frontier of artificial intelligence, there’s a shadow following the deep-learning robot. Most notoriously, is the issue of deepfake porn. Reddit has already had to ban two different synthetic media subreddits (the most recent ban was instituted this past June) according to Unite.AI because so many “People kept requesting deepfake porn.”
“I think the most fundamental problem of the misuse of AI-generated synthetic media is the erosion of the public's trust in all online media,” says Siwei Lyu, director of University of Buffalo’s Media Forensic Lab and the founding co-director of the university’s Center for Information Integrity (CII). “By creating illusions of an individual's presence and activities that did not occur in reality, deepfakes can cause actual harm when they are weaponized.”
For instance, Lyu says, “a fake video showing a politician engaged in inappropriate activity” could sway an election. Or, he adds, “a falsified audio recording of a high-level executive commenting on her company’s financial situation could send the stock market awry.”
As such, says Wael Abd-Almageed, a research director at USC’s Information Sciences Institute, “if we want to continue to use artificial intelligence to create synthetic content, which is a fact of life, at least we need to create a signature or watermark to identify that the data is fake.”
Graham says Metaphysic has every intention of “bringing awareness to these issues.” But, he adds, “the technology is moving forward either way.”
Graham insists, that the issues around hyperreal, AI-generated content is a concern held primarily by people 60 or older who find themselves inside their social media feedback loop.
“We’ve looked at this,” he says. “And people who use words like ‘fear,’ ‘scared,’ ‘future,’ are all older people who share news clips about deepfakes on Facebook. Most people under the age of 40 have a very different understanding of this stuff. Millennials and Gen Z can really see its potential.”
To be clear, so does Lyu.
“For instance, used in the movie and advertisement industry, these technologies can lead to a significant reduction in cost and improved flexibility,” he says. Or, he adds, “to create multilingual versions of the same video.”
Metaphysic is not making any money from their deepfake Tom Cruise videos, but the technology they’re developing is key to the soon-to-be $824 billion industry they’re a part of. For now, Umé says his interest in hyperreal AI-generated content goes beyond the financial. His roadmap for Metaphysic is, more than anything, penned to Metaphysic’s larger philosophy:
“If you perceive something to be real,” says Graham. “Is it any less real?”
On a patch of grass on the outskirts of the Palisades Village, TikToker Larsen Thompson begins teaching Fisher the moves for the early summer viral dance “Jiggle Jiggle.” This is the first of four @deepTom videos that the crew will shoot today. Later, Fisher will sample some ice cream. Then he’ll flirt with a Russian influencer before singing with pop-music singer-songwriter Dudley Alexander.
Of course, the version of each performance you’ll see will not feature Fisher at all. You’ll only see Tom Cruise.
Fisher, a natural performer, picks up the TikTok dance quickly. Umé begins filming the action with his iPhone. Meanwhile Graham is busy managing the interests of one of Metaphysic’s AI-generated avatars that’s scheduled to appear in “America’s Got Talent.”
The team makes it all look easy. But Umé and Graham insist that developing their hyperreal content takes a lot of work.
Applying Tom Cruise’s face onto Fisher’s, Umé says, “is more than just pushing a button.” To that end, Umé describes the technology the way a 19th-century pictorialist might have: weaving his AI-generated content from a scientific to an expressive medium.
According to Graham, this approach distinguishes Umé from the growing number of people working in synthetic media.
“Chris is a perfectionist,” Graham says, adding that although “there are nine or 10 companies in the synthetic media space, no one possesses the same level of attention to detail as Chris.”
Ironically then, it’s Umé’s human touch that separates his model from face-swapping apps like Reface. And web-based platforms for creating videos with AI avatars and voices like Synthesia.
Ultimately, Umé says, his goal is to create such an immersive experience that he’s personally able to sit at his kitchen table and have breakfast with his grandmother who lives halfway across the world and to really feel like she’s right there with him, in the room.
Adding, “I want to be able to save that memory and share it with my grandkids.”
Simon, Terry, and Howie Sing "Nessun Dorma" on Stage?! Metaphysic Will Stun You | AGT 2022
- StoryFile Aims to Let Users Talk to the Dead, Digitally - dot.LA ›
- Flawless Launches to Use Deepfake Tech for Movie Dubbing - dot.LA ›
- Vocal Deepfakes Question Who You're Really Listening To - dot.LA ›
- Vocal Deepfakes Question Who You're Really Listening To - dot.LA ›



 Image Source: Revel
Image Source: Revel