This LA-Based Startup Aims to Permanently Treat Devastating Diseases Like Parkinson’s
Keerthi Vedantam is a bioscience reporter at dot.LA. She cut her teeth covering everything from cloud computing to 5G in San Francisco and Seattle. Before she covered tech, Keerthi reported on tribal lands and congressional policy in Washington, D.C. Connect with her on Twitter, Clubhouse (@keerthivedantam) or Signal at 408-470-0776.
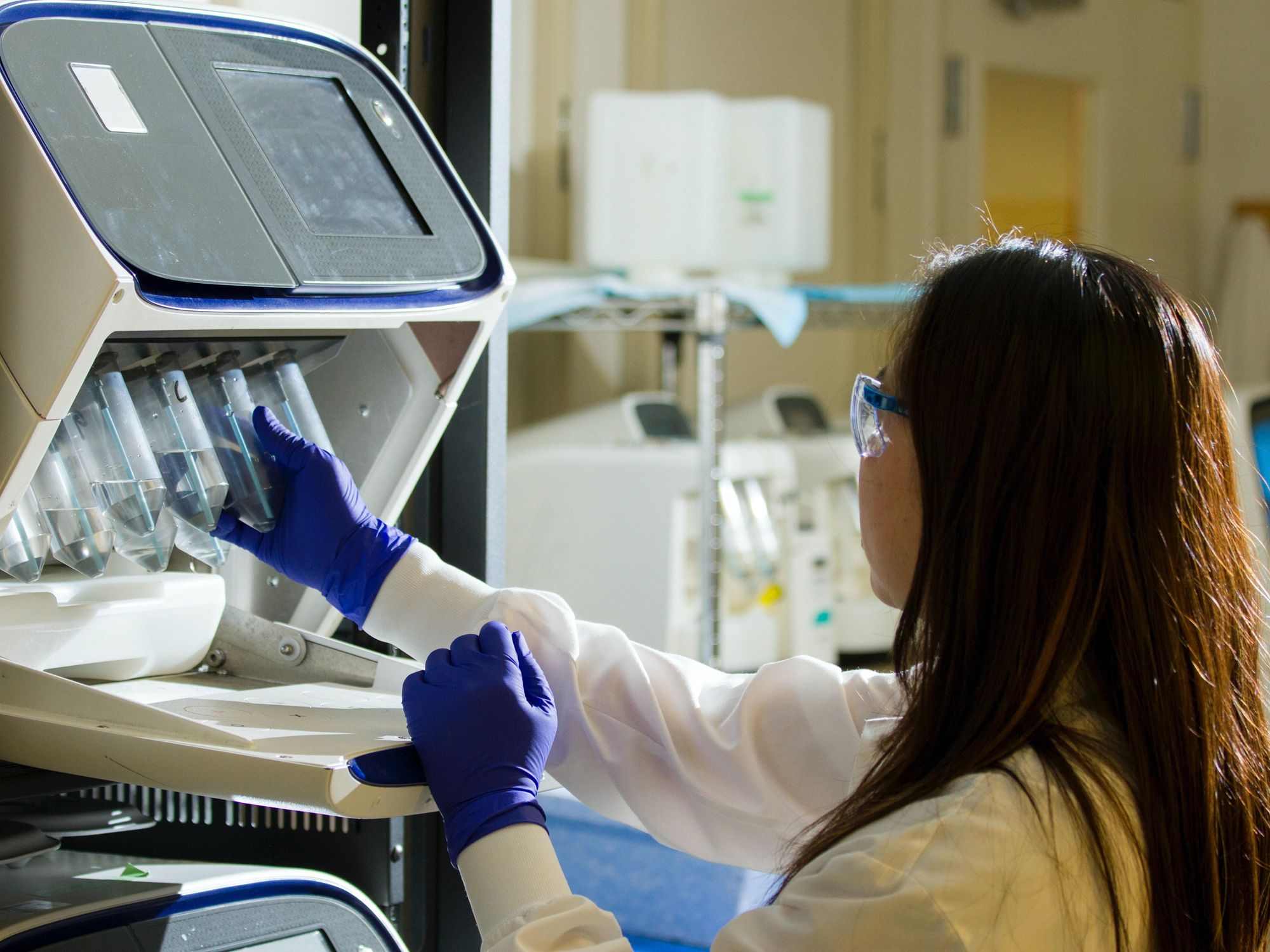

A Thousand Oaks startup that is creating gene therapies aimed at permanently treating devastating diseases like Alzheimer's announced Thursday it received $140 million in capital.
Capsida Biotherapeutics is joining the gene therapy craze with small encapsulated viruses known as adeno-associated viruses, which can target specific cells in the body to treat diseases. The method is similar to the one used by pharma companies that create coronavirus vaccines.
Westlake Village BioPartners and Versant Ventures backed the Series A round with $50 million. Another $90 million came from pharma company AbbVie through a partnership.
Gene therapies aren't new — as a matter of fact, gene therapies have been heralded as a safer, more long-term solution to many diseases. Their approach is often try to replace or get rid of mutated genes that are causing harm to the body, or add genes to help the body fight diseases like Parkinson's or Huntington's.
"Unlike a pill that you take your once, twice a day, it's one treatment and you're done," said Robert Pacifici, chief scientific officer at a nonprofit Huntington's research organization called CHDI Foundation.
Several recent gene therapies have yet to break through. The FDA recently rejected the approval of BioMarin's gene therapy for hemophilia bleeding.
Others, like BlueBird Bio (which billed a promising sickle-cell gene therapy) and Ultragenyx (which was testing a gene therapy cure for Angelman syndrome) suspended clinical trials after patients had adverse effects.
There are often two problems to using gene therapy — targeted therapies don't always get to their destination, and, in large doses, often lead to negative effects, but in small doses, don't produce the desired results. It's a delicate balancing act for drug developers who need to be able to prove their therapy works without harming the body.
"There's a whole swath of areas that really haven't been amenable to any treatments," said Capsida CEO Robert Cuddihy. "I've always had an interest in the gene therapies and been following it for more than a decade, but it really wasn't ready for prime time."
Capsida uses — as its name would suggest — capsids, the outer coating of a viral particle that gets injected into the body. The capsid increases the particle's ability to hone in on a specific organ or cell, making targeting easier.
"The same amount of virus can actually do a whole lot more because it's much better getting into the cell," Cuddihy said. "It's much more effective. That then lets you decrease the dose," which lowers the risk profile of the virus.
The technology behind Capsida came from Caltech neuroscientists Viviana Gradinaru, who took existing capsids that could only transfer around 5% to 10% of the genetic material to the body and upped it to 70%, improving efficacy. She also engineered capsids to de-target the liver (which sucks in many gene therapies), making it easier for the body to send the capsid to the necessary cell.
Inside the capsid, where specific genes or therapies are located, the company will use AI and machine learning to help guide the development of gene therapies through the body and find its precise targets.
Capsida's partnership with AbbVie net the company $80 million in cash and $10 million in equity, with the potential of $530 million, as both companies make steps in targeting three specific diseases that deal with the central nervous system.
The technology could prove to be immensely useful for rare diseases like Huntington's, or prevalent, devastating diseases like Alzheimer's (though the company declined to mention which three diseases it would be targeting).
- Westlake Village BioPartners Raises $500M - dot.LA ›
- Scientists Making Brain Computers Worry about Ethics, Safety - dot.LA ›
- Moxie the Robot Helps Children With Autism Through AI - dot.LA ›
- Capsida Biotherapeutics Opens a New Manufacturing Facility ›
Keerthi Vedantam is a bioscience reporter at dot.LA. She cut her teeth covering everything from cloud computing to 5G in San Francisco and Seattle. Before she covered tech, Keerthi reported on tribal lands and congressional policy in Washington, D.C. Connect with her on Twitter, Clubhouse (@keerthivedantam) or Signal at 408-470-0776.





 Image Source: Skyryse
Image Source: Skyryse